
A debit card, also known as a check card or bank card, is a payment card that can be used in place of cash to make purchases. The card usually consists of the bank's name, a card number, the cardholder's name, and an expiration date, on either the front or the back. Many new cards now have a chip on them, which allows people to use their card by touch (contactless), or by inserting the card and keying in a PIN as with swiping the magnetic stripe. Debit cards are similar to a credit card, but the money for the purchase must be in the cardholder's bank account at the time of the purchase and is immediately transferred directly from that account to the merchant's account to pay for the purchase.

Electronic Funds Transfer at Point Of Sale, abbreviated as EFTPOS, is the technical term referring to a type of payment transaction where electronic funds transfers (EFT) are processed at a point of sale (POS) system or payment terminal usually via payment methods such as payment cards. EFTPOS technology was developed during the 1980s.

A smart card (SC), chip card, or integrated circuit card, is a card used to control access to a resource. It is typically a plastic credit card-sized card with an embedded integrated circuit (IC) chip. Many smart cards include a pattern of metal contacts to electrically connect to the internal chip. Others are contactless, and some are both. Smart cards can provide personal identification, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Applications include identification, financial, public transit, computer security, schools, and healthcare. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within organizations. Numerous nations have deployed smart cards throughout their populations.

A stored-value card (SVC) or cash card is a payment card with a monetary value stored on the card itself, not in an external account maintained by a financial institution. This means no network access is required by the payment collection terminals as funds can be withdrawn and deposited straight from the card. Like cash, payment cards can be used anonymously as the person holding the card can use the funds. They are an electronic development of token coins and are typically used in low-value payment systems or where network access is difficult or expensive to implement, such as parking machines, public transport systems, and closed payment systems in locations such as ships.
Electronic cash was, until 2007, the debit card system of the German Banking Industry Committee, the association that represents the top German financial interest groups. Usually paired with a transaction account or current account, cards with an Electronic Cash logo were only handed out by proper credit institutions. An electronic card payment was generally made by the card owner entering their PIN at a so-called EFT-POS-terminal (Electronic-Funds-Transfer-Terminal). The name "EC" originally comes from the unified European checking system Eurocheque. Comparable debit card systems are Maestro and Visa Electron. Banks and credit institutions who issued these cards often paired EC debit cards with Maestro functionality. These combined cards, recognizable by an additional Maestro logo, were referred to as "EC/Maestro cards".
Suica is a prepaid rechargeable contactless smart card and electronic money system used as a fare card on train lines and other public transport systems in Japan, launched on November 18, 2001, by JR East. The card can be used across the nation as part of Japan's Nationwide Mutual Usage Service. The card is also widely used as electronic money for purchases at stores and kiosks, especially at convenience stores and within train stations. In 2018, JR East reported that Suica was used for 6.6 million daily transactions. As of October 2023, 95.64 million Suica have been issued, and 1.63 million stores accept payment via Suica's digital currency.
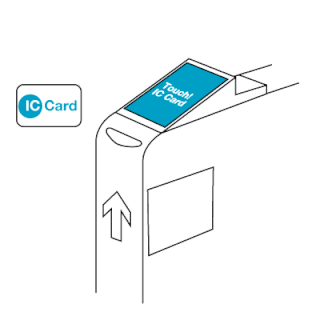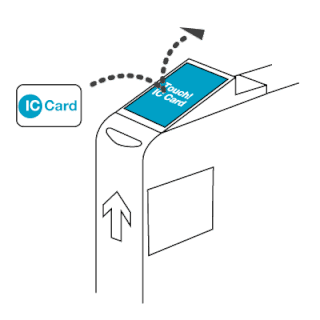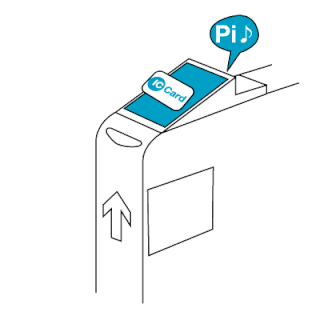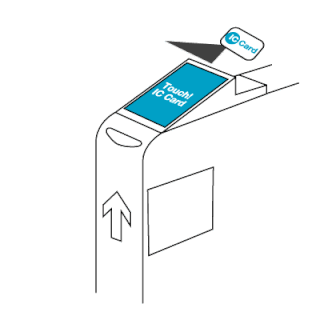
The EZ-Link card is a rechargeable contactless smart card and electronic money system that is primarily used as a payment method for public transport such as bus and rail lines in Singapore. A standard EZ-Link card is a credit-card-sized stored-value contact-less smart-card that comes in a variety of colours, as well as limited edition designs. It is sold by SimplyGo Pte Ltd, a merged entity of TransitLink and EZ-Link since 2024, a subsidiary of the Land Transport Authority (LTA), and can be used on travel modes across Singapore, including the Mass Rapid Transit (MRT), the Light Rail Transit (LRT), public buses which are operated by SBS Transit, SMRT Buses, Tower Transit Singapore and Go-Ahead Singapore, as well as the Sentosa Express.

Mastercard Maestro is a brand of debit cards and prepaid cards owned by Mastercard that was introduced in 1991. Maestro is accepted at around fifteen million point of sale outlets in 93 countries.

Payment cards are part of a payment system issued by financial institutions, such as a bank, to a customer that enables its owner to access the funds in the customer's designated bank accounts, or through a credit account and make payments by electronic transfer with a payment terminal and access automated teller machines (ATMs). Such cards are known by a variety of names, including bank cards, ATM cards, client cards, key cards or cash cards.

Chipknip was a stored-value payment card system used in the Netherlands. Based on the Belgian Proton system, it was started by Interpay on 26 October 1995, as a pilot project in the city of Arnhem and a year later rolled out countrywide. Chipknip was taken over by Currence due to a restructuring on 17 May 2005, who managed it with their licensees until its discontinuation on 1 January 2015. The Chipknip was primarily used for small retail transactions, as the card could contain a maximum value of 500 euros. The money needed to be transferred from a card holders main bank account using a loading station which were generally located next to ATMs.
A contactless smart card is a contactless credential whose dimensions are credit card size. Its embedded integrated circuits can store data and communicate with a terminal via NFC. Commonplace uses include transit tickets, bank cards and passports.

Network for Electronic Transfers, colloquially known as NETS, is a Singaporean electronic payment service provider. Founded in 1986 by a consortium of local banks, it aims to establish the debit network and drive the adoption of electronic payments in Singapore. It is owned by DBS Bank, OCBC Bank and United Overseas Bank (UOB).

The Breeze Card is a stored value smart card used on bus and rapid transit routes in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It is part of an automated fare collection system which Metropolitan Atlanta Rapid Transit Authority (MARTA) introduced to the general public in early October 2006. The card automatically debits the cost of the passenger’s ride when placed on or near the Breeze Target at the fare gate. Transit riders are able to add value or time-based passes to the card at Breeze Vending Machines (BVM) located at all MARTA stations. The major phases of MARTA's Breeze transformation took place before July 1, 2007 when customers were still able to purchase TransCards from ridestores or their employers. They were also able to obtain paper transfers from bus drivers to access the train. As of July 1, 2007 the TransCard and the paper transfers were discontinued and patrons now use a Breeze Card or ticket to access the system, and all transfers are loaded on the card. Breeze Vending Machines (BVM) distribute regional transit provider passes The Breeze Card employs passive RFID technology currently in use in many transit systems around the world.
CEPAS, the Specification for Contactless e-Purse Application, is a Singaporean specification for an electronic money smart card. The specification was prepared by the Cards and Personnel Identification Technical Committee (CPITC), under the purview of the IT Standard Committee of Singapore (ITSCS). It has been gazetted as Singapore Standard SS 518 by Enterprise Singapore. CEPAS has been deployed island-wide, replacing the previous original EZ-Link card effective 1 October 2009.

Contactless payment systems are credit cards and debit cards, key fobs, smart cards, or other devices, including smartphones and other mobile devices, that use radio-frequency identification (RFID) or near-field communication (NFC) for making secure payments. The embedded integrated circuit chip and antenna enable consumers to wave their card, fob, or handheld device over a reader at the point-of-sale terminal. Contactless payments are made in close physical proximity, unlike other types of mobile payments which use broad-area cellular or Wi-Fi networks and do not involve close physical proximity.
PaysafeCard is part of Paysafe Limited (“Paysafe”) (PSFE.WS), a global payments platform. PaysafeCard is a prepaid cash-based, online payment method based on vouchers with a 16-digit PIN code. The vouchers can be used to fund online transactions without a bank account, credit card, or other personal information.

girocard is an interbank network and debit card service in Germany connecting virtually all automated teller machines (ATMs) and banks. It is based on standards and agreements developed by the German Banking Industry Committee.

Debit Mastercard is a brand of debit cards provided by Mastercard. They use the same systems as standard Mastercard credit cards but they do not use a line of credit to the customer, instead relying on funds that the customer has in their bank account.

MetroCARD is a contactless smartcard ticketing system for public transport services in the Adelaide city and suburbs in South Australia. The system is managed by Adelaide Metro and is usable on their bus, train and tram services.
Apple Pay is a mobile payment service by Apple Inc. that allows users to make payments in person, in iOS apps, and on the web. Supported on iPhone, Apple Watch, iPad, Mac, and Vision Pro, Apple Pay digitizes and can replace a credit or debit card chip and PIN transaction at a contactless-capable point-of-sale terminal. It does not require Apple Pay–specific contactless payment terminals; it can work with any merchant that accepts contactless payments. It adds two-factor authentication via Touch ID, Face ID, Optic ID, PIN, or passcode. Devices wirelessly communicate with point of sale systems using near field communication (NFC), with an embedded secure element (eSE) to securely store payment data and perform cryptographic functions, and Apple's Touch ID and Face ID for biometric authentication.














