Related Research Articles

Microevolution is the change in allele frequencies that occurs over time within a population. This change is due to four different processes: mutation, selection, gene flow and genetic drift. This change happens over a relatively short amount of time compared to the changes termed macroevolution.

Comparative genomics is a field of biological research in which the genomic features of different organisms are compared. The genomic features may include the DNA sequence, genes, gene order, regulatory sequences, and other genomic structural landmarks. In this branch of genomics, whole or large parts of genomes resulting from genome projects are compared to study basic biological similarities and differences as well as evolutionary relationships between organisms. The major principle of comparative genomics is that common features of two organisms will often be encoded within the DNA that is evolutionarily conserved between them. Therefore, comparative genomic approaches start with making some form of alignment of genome sequences and looking for orthologous sequences in the aligned genomes and checking to what extent those sequences are conserved. Based on these, genome and molecular evolution are inferred and this may in turn be put in the context of, for example, phenotypic evolution or population genetics.

The Streptomycetaceae are a family of Actinomycetota, making up the monotypic order Streptomycetales. It includes the important genus Streptomyces. This was the original source of many antibiotics, namely streptomycin, the first antibiotic against tuberculosis.

Steven Dale Tanksley is the Chief Technology Officer of Nature Source Improved Plants. Prior to founding Nature Source Improved Plants, Tanksley served as the Liberty Hyde Bailey professor of plant breeding and biometry and chair of the Genomics Initiative Task Force at Cornell University College of Agriculture and Life Sciences. He is currently a Professor Emeritus at Cornell University.
Recombineering is a genetic and molecular biology technique based on homologous recombination systems, as opposed to the older/more common method of using restriction enzymes and ligases to combine DNA sequences in a specified order. Recombineering is widely used for bacterial genetics, in the generation of target vectors for making a conditional mouse knockout, and for modifying DNA of any source often contained on a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC), among other applications.
In genetics, a selective sweep is the process through which a new beneficial mutation that increases its frequency and becomes fixed in the population leads to the reduction or elimination of genetic variation among nucleotide sequences that are near the mutation. In selective sweep, positive selection causes the new mutation to reach fixation so quickly that linked alleles can "hitchhike" and also become fixed.
Spiegelman's Monster is the name given to an RNA chain of only 218 nucleotides that is able to be reproduced by the RNA replication enzyme RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, also called RNA replicase. It is named after its creator, Sol Spiegelman, of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign who first described it in 1965.
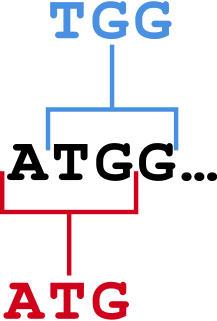
In bioinformatics, k-mers are substrings of length contained within a biological sequence. Primarily used within the context of computational genomics and sequence analysis, in which k-mers are composed of nucleotides, k-mers are capitalized upon to assemble DNA sequences, improve heterologous gene expression, identify species in metagenomic samples, and create attenuated vaccines. Usually, the term k-mer refers to all of a sequence's subsequences of length , such that the sequence AGAT would have four monomers, three 2-mers, two 3-mers and one 4-mer (AGAT). More generally, a sequence of length will have k-mers and total possible k-mers, where is number of possible monomers.
In genetics, an isochore is a large region of DNA with a high degree uniformity in guanine (G) and cytosine (C): G-C and C-G.
Anders Krogh is a bioinformatician at the University of Copenhagen, where he leads the university's bioinformatics center. He is known for his pioneering work on the use of hidden Markov models in bioinformatics, and is co-author of a widely used textbook in bioinformatics. In addition, he also co-authored one of the early textbooks on neural networks. His current research interests include promoter analysis, non-coding RNA, gene prediction and protein structure prediction.

A HEAT repeat is a protein tandem repeat structural motif composed of two alpha helices linked by a short loop. HEAT repeats can form alpha solenoids, a type of solenoid protein domain found in a number of cytoplasmic proteins. The name "HEAT" is an acronym for four proteins in which this repeat structure is found: Huntingtin, elongation factor 3 (EF3), protein phosphatase 2A (PP2A), and the yeast kinase TOR1. HEAT repeats form extended superhelical structures which are often involved in intracellular transport; they are structurally related to armadillo repeats. The nuclear transport protein importin beta contains 19 HEAT repeats.
Ziheng Yang FRS is a Chinese biologist. He holds the R.A. Fisher Chair of Statistical Genetics at University College London, and is the Director of R.A. Fisher Centre for Computational Biology at UCL. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 2006.
Methanothermus fervidus is a species of methanogen. It is notable for being extremely thermophilic. Its cells are rod-shaped; its complex cell envelope exhibits two layers, each about 12 nm thick; the inner represents the pseudomurein sacculus and the outer a protein envelope. The type strain is Methanothermus fervidus Stetter 1982. The cells are motile, strictly anaerobic and stain Gram positive. They can grow at temperatures as high as 97 °C. Strain V24ST can subsist on carbon dioxide and hydrogen alone. Its genome is 1,243,342 bp in length.
SNV calling from NGS data is any of a range of methods for identifying the existence of single nucleotide variants (SNVs) from the results of next generation sequencing (NGS) experiments. These are computational techniques, and are in contrast to special experimental methods based on known population-wide single nucleotide polymorphisms. Due to the increasing abundance of NGS data, these techniques are becoming increasingly popular for performing SNP genotyping, with a wide variety of algorithms designed for specific experimental designs and applications. In addition to the usual application domain of SNP genotyping, these techniques have been successfully adapted to identify rare SNPs within a population, as well as detecting somatic SNVs within an individual using multiple tissue samples.
Bat SARS-like coronavirus WIV1, also sometimes called SARS-like coronavirus WIV1, is a strain of severe acute respiratory syndrome–related coronavirus (SARSr-CoV) isolated from Chinese rufous horseshoe bats in 2013. Like all coronaviruses, virions consist of single-stranded positive-sense RNA enclosed within an envelope.
Mutation bias refers to a pattern in which some type of mutation occurs more often than expected under uniformity. The types are most often defined by the molecular nature of the mutational change, but sometimes they are based on downstream effects, e.g., Ostrow, et al. refer to the tendency for mutations to increase body size in nematodes as a mutation bias.
16BO133 is a SARS-like coronavirus (SL-COV) which was found in the greater horseshoe bat in South Korea. It was published in 2019 and its genome was completely sequenced. The sequenced Korean SARSr-CoV strain belongs to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 1, and its genome sequence similarity is 82.8%.
LYRa11 is a SARS-like coronavirus (SL-COV) which was identified in 2011 in samples of intermediate horseshoe bats in Baoshan, Yunnan, China. The genome of this virus strain is 29805nt long, and the similarity to the whole genome sequence of SARS-CoV that caused the SARS outbreak is 91%. It was published in 2014. Like SARS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, LYRa11 virus uses ACE2 as a receptor for infecting cells.
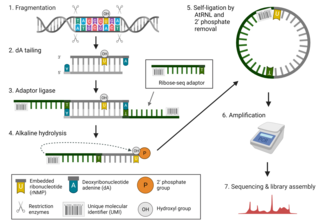
Ribose-seq is a mapping technique used in genetics research to determine the full profile of embedded ribonucleotides, specifically ribonucleoside monophosphates (rNMPs), in genomic DNA. Embedded ribonucleotides are thought to be the most common alteration to DNA in cells, and their presence in genomic DNA can affect genome stability. As recent studies have suggested that ribonucleotides in mouse DNA may affect disease pathology, ribonucleotide incorporation in genomic DNA has become an important target of medical genetics research. Ribose-seq allows scientists to determine the precise location and type of ribonucleotides that have been incorporated into eukaryotic or prokaryotic DNA.
References
- ↑ Kariin, S and Burge, C. (1995). "Dinucleotide relative abundance extremes: A genomic signature". Trends in Genetics. 11 (7): 283–290. doi:10.1016/S0168-9525(00)89076-9. PMID 7482779.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Karlin, S and Ladunga, I. (1994). "Comparisons of eukaryotic genomic sequences". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 91 (26): 12832–12836. Bibcode:1994PNAS...9112832K. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.26.12832 . PMC 45534 . PMID 7809130.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)