Electronic music broadly is a group of music genres that employ electronic musical instruments, circuitry-based music technology and software, or general-purpose electronics in its creation. It includes both music made using electronic and electromechanical means. Pure electronic instruments depended entirely on circuitry-based sound generation, for instance using devices such as an electronic oscillator, theremin, or synthesizer. Electromechanical instruments can have mechanical parts such as strings, hammers, and electric elements including magnetic pickups, power amplifiers and loudspeakers. Such electromechanical devices include the telharmonium, Hammond organ, electric piano and electric guitar.

An electronic musical instrument or electrophone is a musical instrument that produces sound using electronic circuitry. Such an instrument sounds by outputting an electrical, electronic or digital audio signal that ultimately is plugged into a power amplifier which drives a loudspeaker, creating the sound heard by the performer and listener.

Ambient music is a genre of music that emphasizes tone and atmosphere over traditional musical structure or rhythm. It is often "peaceful" sounding and lacks composition, beat, and/or structured melody. It uses textural layers of sound that can reward both passive and active listening and encourage a sense of calm or contemplation. The genre is said to evoke an "atmospheric", "visual", or "unobtrusive" quality. Nature soundscapes may be included, and the sounds of acoustic instruments such as the piano, strings and flute may be emulated through a synthesizer.

Isao Tomita, often known simply as Tomita, was a Japanese composer, regarded as one of the pioneers of electronic music and space music, and as one of the most famous producers of analog synthesizer arrangements. In addition to creating note-by-note realizations, Tomita made extensive use of the sound-design capabilities of his instrument, using synthesizers to create new sounds to accompany and enhance his electronic realizations of acoustic instruments. He also made effective use of analog music sequencers and the Mellotron, and featured futuristic science-fiction themes, while laying the foundations for synth-pop music and trance-like rhythms. Many of his albums are electronic versions and adaptations of familiar classical music pieces. He received four Grammy Award nominations for his 1974 album based on music by Claude Debussy, Snowflakes Are Dancing.

Morton Subotnick is an American composer of electronic music, best known for his 1967 composition Silver Apples of the Moon, the first electronic work commissioned by a record company, Nonesuch. He was one of the founding members of California Institute of the Arts, where he taught for many years.
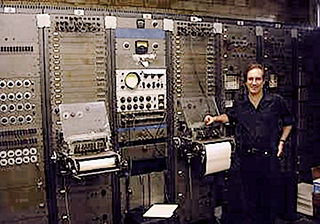
The RCA Mark II Sound Synthesizer was the first programmable electronic synthesizer and the flagship piece of equipment at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center. Designed by Herbert Belar and Harry Olson at RCA, with contributions by Vladimir Ussachevsky and Peter Mauzey, it was installed at Columbia University in 1957. Consisting of a room-sized array of interconnected sound synthesis components, the Mark II gave the user more flexibility and had twice the number of tone oscillators as its predecessor, the Mark I. The synthesizer was funded by a large grant from the Rockefeller Foundation.

The Freight Elevator Quartet (FEQ) were a music performance group specializing in improvised electronic music active in and around New York City. They performed and recorded continuously from 1996 to 2003, and collaborated extensively with experimental music artists such as DJ Spooky and Elliott Sharp, and avant-garde videographer Mark McNamara.

The Moog synthesizer is a modular synthesizer invented by the American engineer Robert Moog in 1964. Moog's company, R. A. Moog Co., produced numerous models from 1965 to 1981, and again from 2014. It was the first commercial synthesizer and established the analog synthesizer concept.

Benn Lee Jordan is an American musician operating under many pseudonyms. Since 1999, his most widely distributed electronic music has been released under the name of The Flashbulb. Other names Jordan has released as are Acidwolf, Human Action Network, and FlexE.

Halim Abdul Messieh El-Dabh was an Egyptian-American composer, musician, ethnomusicologist, and educator, who had a career spanning six decades. He is particularly known as an early pioneer of electronic music. In 1944 he composed one of the earliest known works of tape music, or musique concrète. From the late 1950s to early 1960s he produced influential work at the Columbia-Princeton Electronic Music Center.

Space music, also called spacemusic or space ambient, is a subgenre of ambient music and is described as "tranquil, hypnotic and moving". It is derived from new-age music and is associated with lounge music, easy listening, and elevator music.

Murcof is the performing and recording name of Mexican electronic musician Fernando Corona. Corona was born in 1970 in Tijuana, Mexico and raised in Ensenada. He was for a time a member of the Tijuana-based Nortec Collective of electronic musicians under the Terrestre project name. In 2000, he returned to Tijuana. Since 2006, Corona has been living in Barcelona, Spain.

Constance Mary Demby was an American musician, composer, painter, sculptor, and multimedia producer. Her music included new age, ambient, and space music styles. She is best known for her 1986 album Novus Magnificat and her two experimental musical instruments, the sonic steel space bass and the whale sail.

Gyula Julius Dobos is a composer, synthesist and music producer, best known for his electronic and orchestral music releases worldwide, and for his film scores and music used in major motion pictures and television programs in Europe and in the United States.
Mark Petersen may refer to:
Space-themed music is any music, from any genre or style, with lyrics or titles relating to outer space or spaceflight.

Mark Jenkins is a Welsh musician and music writer. He has written interviews and instrument reviews for UK and international magazines including Melody Maker, New Musical Express, Music Week, International Musician, Keyboard (US), and Mac Format, and has also written a book, Analog Synthesizers, 2nd Edition 2019. He currently writes for the US magazine, Synth & Software.
Mark Gibbons, Better known as Mark Mercury is an American composer. He has arranged, produced, recorded, and composed music since the 1970s.
Where in the Universe Is Carmen Sandiego? is an educational planetarium program and live theatrical production and part of the Carmen Sandiego franchise. Licensed to planetariums across the US, Canada, and Japan, the show premiered in 1998 or 1999. The program featured the effects work of Adrian Ropp and was produced by Dr. William A. Gutsch, with music composed by Mark Mercury. Inspired by the successful television programs Where in the World Is Carmen Sandiego? and Where in Time Is Carmen Sandiego?, the series aimed to promote listening and math skills through interactive sessions rather than relying on memorized facts. The shows encouraged audience participation by incorporating question-and-answer segments.

In music production, the recording studio is often treated as a musical instrument when it plays a significant role in the composition of music. Sometimes called "playing the studio", the approach is typically embodied by artists or producers who favor the creative use of studio technology in record production, as opposed to simply documenting live performances in studio. Techniques include the incorporation of non-musical sounds, overdubbing, tape edits, sound synthesis, audio signal processing, and combining segmented performances (takes) into a unified whole.