Related Research Articles

Richard Dixon Oldham FRS was a British geologist who made the first clear identification of the separate arrivals of P-waves, S-waves and surface waves on seismograms and the first clear evidence that the Earth has a central core.

There is a strong scientific consensus that the Earth is warming and that this warming is mainly caused by human activities. This consensus is supported by various studies of scientists' opinions and by position statements of scientific organizations, many of which explicitly agree with the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) synthesis reports.
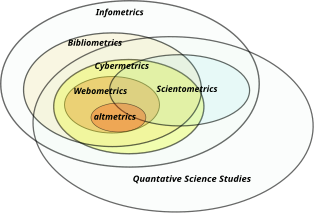
Informetrics is the study of quantitative aspects of information, it is an extension and evolution of traditional bibliometrics and scientometrics. Informetrics uses bibliometrics and scientometrics methods to study mainly the problems of literature information management and evaluation of science and technology. Informetrics is an independent discipline that uses quantitative methods from mathematics and statistics to study the process, phenomena, and law of informetrics. Informetrics has gained more attention as it is a common scientific method for academic evaluation, research hotspots in discipline, and trend analysis.

Darashaw Nosherwan Wadia FRS was a pioneering geologist in India and among the first Indian scientists to work in the Geological Survey of India. He is remembered for his work on the stratigraphy of the Himalayas. He helped establish geological studies and investigations in India, specifically at the Institute of Himalayan Geology, which was renamed in 1976 after him as the Wadia Institute of Himalayan Geology. His textbook on the Geology of India, first published in 1919, continues to be in use.
Citation impact is a measure of how many times an academic journal article or book or author is cited by other articles, books or authors. Citation counts are interpreted as measures of the impact or influence of academic work and have given rise to the field of bibliometrics or scientometrics, specializing in the study of patterns of academic impact through citation analysis. The journal impact factor, the two-year average ratio of citations to articles published, is a measure of the importance of journals. It is used by academic institutions in decisions about academic tenure, promotion and hiring, and hence also used by authors in deciding which journal to publish in. Citation-like measures are also used in other fields that do ranking, such as Google's PageRank algorithm, software metrics, college and university rankings, and business performance indicators.
The h-index is an author-level metric that measures both the productivity and citation impact of the publications, initially used for an individual scientist or scholar. The h-index correlates with obvious success indicators such as winning the Nobel Prize, being accepted for research fellowships and holding positions at top universities. The index is based on the set of the scientist's most cited papers and the number of citations that they have received in other publications. The index has more recently been applied to the productivity and impact of a scholarly journal as well as a group of scientists, such as a department or university or country. The index was suggested in 2005 by Jorge E. Hirsch, a physicist at UC San Diego, as a tool for determining theoretical physicists' relative quality and is sometimes called the Hirsch index or Hirsch number.
Women in geology concerns the history and contributions of women to the field of geology. There has been a long history of women in the field, but they have tended to be under-represented. In the era before the eighteenth century, science and geological science had not been as formalized as they would become later. Hence early geologists tended to be informal observers and collectors, whether they were male or female. Notable examples of this period include Hildegard of Bingen who wrote works concerning stones and Barbara Uthmann who supervised her husband's mining operations after his death. Mrs. Uthmann was also a relative of Georg Agricola. In addition to these names varied aristocratic women had scientific collections of rocks or minerals.
A lack of oversight and a lack of proper training for scientists have led to the rise of plagiarism and research misconduct in India. India does not have a statutory body to deal with scientific misconduct in academia, like the Office of Research Integrity in the US, and hence cases of plagiarism are often dealt in ad-hoc fashion with different routes being followed in different cases. In most cases, a public and media outcry leads to an investigation either by institutional authorities or by independent enquiry committees. Plagiarists have in some cases been suspended, removed or demoted. However, no fixed route has been prescribed to monitor such activities. This has led to calls for establishment of an independent ethics body.

Jayanta Kumar Ghosh was an Indian statistician, an emeritus professor at Indian Statistical Institute and a professor of statistics at Purdue University.
Bangalore Puttaiya Radhakrishna, was one of the leading geologists of India. He was often referred to as 'The Doyen of Indian geology'. He was a resident of Bangalore and regularly wrote the editorial in the Journal of the Geological Society of India published by the Geological Society of India.
Sudipta Sengupta is a professor in structural geology in Jadavpur University, Calcutta, India, and a trained mountaineer. She is one of the first Indian women to set foot on Antarctica. She is also popularly known in India for her book Antarctica in Bengali and numerous articles and television interviews on geosciences. She has published extensively in international peer-reviewed journals of structural geology. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded her the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for her contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 1991.
The Philatelic Society of India (PSI) was formed in 1897 by a group of, mainly, expatriate Englishmen resident in the country as the first all-India philatelic society. During its first fifty years the society included most of the important Anglo-Indian philatelists and had a particularly strong publications record with two award-winning books. The society meets every first and third Saturday at the Mumbai G.P.O., convened by Dhirubhai Mehta, President, and D.M. Pittie, Hon. Secretary.

Talat Ahmad is an Indian Earth scientist and professor at department of geology, University of Delhi. He commenced his second stint as vice chancellor of University of Kashmir on 6 August 2018 after serving as vice chancellor of Jamia Millia Islamia after he resigned from the post a few months short of his full term. He was shortlisted by a committee constituted by the governor to shortlist a panel for the post. He had earlier taken over as vice-chancellor of University of Kashmir from Professor Riyaz Punjabi on 1 June 2011. Prior to this, he was teaching geology at the University of Delhi.
Asis Datta is an Indian biochemist, molecular biologist and genetic engineer, known for his research on genetically modified foods and food nutritional security. He was the founding Director of the National Institute of Plant Genome Research and is credited with the discovery of genes that assist in extended preservation of fruits and vegetables. He is a recipient of the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Award, the highest Indian award and in the Science category, and was awarded the fourth highest civilian award of the Padma Shri, by the Government of India, in 1999. In 2008, he was included again in the Republic Day Honours list for the third highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan.
Kshitindramohan Naha (1932–1996) was an Indian geologist and a professor and CSIR Emeritus scientist at the Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur. He was known for his studies on structural geology of Precambrian era and was an elected fellow of the Indian National Science Academy, and the Indian Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 1972.
Bhamidipati Lakshmidhara Kanakadri Somayajulu (1937-2016) is an Indian geochemist and a CSIR Emeritus Scientist at Physical Research Laboratory, Ahmedabad. He is known for his studies on ancient and contemporary marine processes and is an elected fellow of several science societies such as the National Academy of Sciences, India, Geological Society of India, Indian Geophysical Union, American Geophysical Union, European Association for Geochemistry, Indian Academy of Sciences and the Indian National Science Academy. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 1978.
Kunchithapadam Gopalan is an Indian geochronologist and an emeritus scientist at National Geophysical Research Institute. He is known for his studies on the chronologies of critical rock suites of the Indian subcontinent and is an elected fellow of the Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy, Indian Geophysical Union and the National Academy of Sciences, India. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to earth, atmosphere, ocean and planetary sciences in 1982.

Sri Niwas (1946–2012) was an Indian geophysicist and a professor at the Department of Earth Sciences of the Indian Institute of Technology, Roorkee. He was known for his researches on the Inversion of Geophysical Data. He was an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies viz. Indian National Science Academy, Indian Academy of Sciences, National Academy of Sciences, India as well as Indian Geophysical Union and was an elected member of the Association of Exploration Geophysicists. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 1991.
Guntupalli Veera Raghavendra Prasad is an Indian paleontologist and the head of the department of geology at the University of Delhi. He is known for his studies on the Mesozoic vertebrate groups of India and is an elected fellow of all the three major Indian science academies viz. Indian Academy of Sciences, Indian National Science Academy and the National Academy of Sciences, India as well as The World Academy of Sciences. The Council of Scientific and Industrial Research, the apex agency of the Government of India for scientific research, awarded him the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology, one of the highest Indian science awards for his contributions to Earth, Atmosphere, Ocean and Planetary Sciences in 2003.

The Geological Society of Sri Lanka is the premier professional forum dedicated to promotion of Geology/Geological Sciences in Sri Lanka. The GSSL is the platform for Sri Lankan Geologists in both academia and industries to join together and share their knowledge, research findings and experience while disseminating knowledge in geological sciences to the general public in Sri Lanka.
References
- ↑ Preservation of India's culture and environment,
- ↑ Renjith, V.R.; Pradeepkumar (2021). "Top 100 Most Cited Papers of the Journal of Geological Society of India (JGSI) in Web of Science (WoS): A Scientometric Assessment". Library Philosophy and Practice. 4892.
- ↑ Jammu University: Departments: Geology