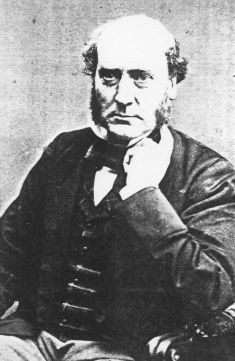William Butterfield was a British Gothic Revival architect and associated with the Oxford Movement. He is noted for his use of polychromy.
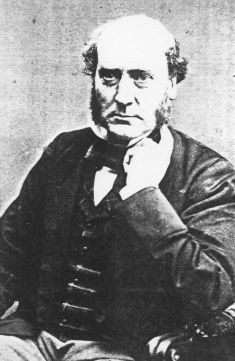
Sir George Gilbert Scott, largely known as Sir Gilbert Scott, was a prolific English Gothic Revival architect, chiefly associated with the design, building and renovation of churches and cathedrals, although he started his career as a leading designer of workhouses. Over 800 buildings were designed or altered by him.

George Frederick Bodley was an English Gothic Revival architect. He was a pupil of Sir George Gilbert Scott, and worked in partnership with Thomas Garner for much of his career. He was one of the founders of Watts & Co.
Samuel Sanders Teulon was an English Gothic Revival architect, noted for his use of polychrome brickwork and the complex planning of his buildings.

Ewan Christian (1814–1895) was a British architect. He is most frequently noted for the restorations of Southwell Minster and Carlisle Cathedral, and the design of the National Portrait Gallery. He was Architect to the Ecclesiastical Commissioners from 1851 to 1895. Christian was elected A RIBA in 1840, FRIBA in 1850, RIBA President 1884–1886 and was awarded the Royal Gold Medal in 1887.
Richard Charles Hussey, often referred to as R. C. Hussey, was a British architect. He was in partnership with Thomas Rickman from 1835, whose practice he assumed in 1838 with the latter's failing health; Rickman died on 4 January, 1841.
Benjamin Ferrey FSA FRIBA was an English architect who worked mostly in the Gothic Revival.
Charles Francis Hansom was a prominent Roman Catholic Victorian architect who primarily designed in the Gothic Revival style.

Henry Woodyer (1816–1896) was an English architect, a pupil of William Butterfield and a disciple of A. W. N. Pugin and the Ecclesiologists.

Sydenham is an eastern suburb of the town of Leamington Spa, Warwickshire, England.
Henry Isaac Stevens FRIBA was an architect based in Derby. He was born in London, in 1806, and died in 1873. In the late 1850s he changed his name to Isaac Henry Stevens.

Henry Clutton was an English architect and designer.
John West Hugall was an English Gothic Revival architect from Yorkshire.

St. Mary's Church, Leamington Spa is a Grade II listed parish church in Leamington Spa, England.

Edward Mansell FRIBA was an architect based in Birmingham.
St Matthew's Church, Duddeston and Nechells is a Grade II listed parish church in the Church of England in Birmingham.
Edward Banks JP was an English architect based in Wolverhampton.

St Luke's Church, Blakenhall is a Grade II* listed former parish church in the Church of England in Blakenhall, Wolverhampton.

George Woodhouse was an English architect who practised from offices in Bolton, and Oldham, then in the county of Lancashire. He collaborated with William Hill on the designs for Bolton Town Hall.
Reverend John Craig (1805-1877) was a Church of England priest, known for construction of All Saints Church, Leamington Spa and Holy Trinity Church, Leamington Spa, and funding of the Craig telescope.