
The Great Society was a set of domestic programs in the United States launched by President Lyndon B. Johnson in 1964 and 1965. The term was first referenced during a 1964 speech by Johnson at Ohio University, then later formally presented at the University of Michigan, and came to represent his domestic agenda. The main goal was the total elimination of poverty and racial injustice.
In the United States government, independent agencies are agencies that exist outside the federal executive departments and the Executive Office of the President. In a narrower sense, the term refers only to those independent agencies that, while considered part of the executive branch, have regulatory or rulemaking authority and are insulated from presidential control, usually because the president's power to dismiss the agency head or a member is limited.

The Overseas Private Investment Corporation (OPIC) was the United States Government's Development finance institution until it merged with the Development Credit Authority (DCA) of the United States Agency for International Development (USAID) to form the U.S. International Development Finance Corporation (DFC). OPIC mobilized private capital to help solve critical development challenges and in doing so, advanced the foreign policy of the United States and national security objectives.
The Fair Deal was a set of proposals put forward by U.S. President Harry S. Truman to Congress in 1945 and in his January 1949 State of the Union Address. More generally, the term characterizes the entire domestic agenda of the Truman administration, from 1945 to 1953. It offered new proposals to continue New Deal liberalism, but with a conservative coalition controlling Congress, only a few of its major initiatives became law and then only if they had considerable Republican Party support. As Richard Neustadt concludes, the most important proposals were aid to education, national health insurance, the Fair Employment Practices Commission, and repeal of the Taft–Hartley Act. They were all debated at length, then voted down. Nevertheless, enough smaller and less controversial items passed that liberals could claim some success.

The Commission on Security and Cooperation in Europe (CSCE), also known as the U.S. Helsinki Commission, is an independent U.S. government agency created by Congress in 1975 to monitor and encourage compliance with the Helsinki Final Act and other Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) commitments. It was initiated by House representative Millicent Fenwick and established in 1975 pursuant to Public Law No. 94-304 and is based at the Ford House Office Building.

The United States Senate Committee on Finance is a standing committee of the United States Senate. The Committee concerns itself with matters relating to taxation and other revenue measures generally, and those relating to the insular possessions; bonded debt of the United States; customs, collection districts, and ports of entry and delivery; deposit of public moneys; general revenue sharing; health programs under the Social Security Act and health programs financed by a specific tax or trust fund; national social security; reciprocal trade agreements; tariff and import quotas, and related matters thereto; and the transportation of dutiable goods. It is considered to be one of the most powerful committees in Congress.

The energy policy of the United States is determined by federal, state, and local entities. It addresses issues of energy production, distribution, consumption, and modes of use, such as building codes, mileage standards, and commuting policies. Energy policy may be addressed via legislation, regulation, court decisions, public participation, and other techniques.
The agricultural policy of the United States is composed primarily of the periodically renewed federal U.S. farm bills. The Farm Bills have a rich history which initially sought to provide income and price support to US farmers and prevent them from adverse global as well as local supply and demand shocks. This implied an elaborate subsidy program which supports domestic production by either direct payments or through price support measures. The former incentivizes farmers to grow certain crops which are eligible for such payments through environmentally conscientious practices of farming. The latter protects farmers from vagaries of price fluctuations by ensuring a minimum price and fulfilling their shortfalls in revenue upon a fall in price. Lately, there are other measures through which the government encourages crop insurance and pays part of the premium for such insurance against various unanticipated outcomes in agriculture.

The creation of a National Infrastructure Reinvestment Bank was first proposed by United States Senator Christopher J. Dodd and Senator Chuck Hagel in 2007. However, several other iterations of a National Infrastructure Bank have been proposed and considered and it is likely that implementing legislation for the Bank will look quite different from that which was proposed in the original legislation.

Public Law 110-343 is a US Act of Congress signed into law by U.S. President George W. Bush, which was designed to mitigate the growing financial crisis of the late-2000s by giving relief to so-called "Troubled Assets."
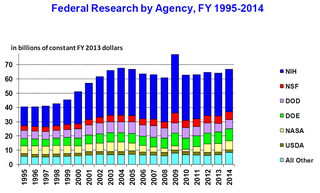
The science policy of the United States is the responsibility of many organizations throughout the federal government. Much of the large-scale policy is made through the legislative budget process of enacting the yearly federal budget, although there are other legislative issues that directly involve science, such as energy policy, climate change, and stem cell research. Further decisions are made by the various federal agencies which spend the funds allocated by Congress, either on in-house research or by granting funds to outside organizations and researchers.

André D. Carson is an American politician serving as the U.S. representative for Indiana's 7th congressional district since 2008. A member of the Democratic Party, his district includes the northern four-fifths of Indianapolis, including Downtown Indianapolis. He became the dean of Indiana's congressional delegation after Representative Pete Visclosky retired in 2021.
Smart grid policy in the United States refers to legislation and other governmental orders influencing the development of smart grids in the United States.

Nuclear Safety, Research, Demonstration, and Development Act of 1980, 42 U.S.C. § 9701, established nuclear safety policy for nuclear power plants supplying electric energy and electricity generation within the United States. The Act authorized a five-year demonstration program simulating conditions with light water nuclear reactors for the observation of control monitoring and phases of operation for nuclear reactor cores. The U.S. Department of Energy was authorized by the Act of Congress to conduct the nuclear reactor demonstration study while establishing a reactor engineering simulator facility at a United States national laboratory. The nuclear safety demonstration program was to provide research data regarding reactor design and simplification improvements given thermal power station simulations subjecting nuclear reactors to hypothesized calamity and customary operating conditions.

John Delaney is a Democrat who served as the U.S. Representative representing Maryland's 6th congressional district from 2013 to 2019. He announced his 2020 campaign for President of the United States on July 28, 2017. He suspended his campaign on January 31, 2020.

The Biomass Energy and Alcohol Fuels Act of 1980 is a statute that addresses general biomass energy development in its various forms, and the use of gasohol. It was one of six acts enacted by the U.S. Energy Security Act.

The Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion Act of 1980 (OTECA) is an act authorized by Congress to address ocean thermal conversion. It is one of six acts enacted by the Energy Security Act of 1980. Ocean thermal energy conversion is the extraction of energy from the thermal differentials of subsea and surface water in regions with tropical oceans.

The Renewable Energy Resources Act of 1980 or Renewable Energy Initiatives (REI) is legislation passed by the 96th U.S. Congress to incentivize the use of renewable energy resources. It was enacted with five other acts by the Energy Security Act of 1980.

For Solar Energy Research, Development and Demonstration Act of 1978, please see Solar Photovoltaic Energy Research, Development, and Demonstration Act of 1978 - Wikipedia.
For the Geothermal Energy Act of 1980, please see Geothermal Act.










