Africa is a continent comprising 63 political territories, representing the largest of the great southward projections from the main mass of Earth's surface. Within its regular outline, it comprises an area of 30,368,609 km2 (11,725,385 sq mi), excluding adjacent islands. Its highest mountain is Kilimanjaro; its largest lake is Lake Victoria.

The Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) is the largest country of sub-Saharan Africa, occupying some 2,344,858 square kilometres (905,355 sq mi). Most of the country lies within the vast hollow of the Congo River basin. The vast, low-lying central area is a plateau-shaped basin sloping toward the west, covered by tropical rainforest and criss-crossed by rivers. The forest center is surrounded by mountainous terraces in the west, plateaus merging into savannas in the south and southwest. Dense grasslands extend beyond the Congo River in the north. High mountains of the Ruwenzori Range are found on the eastern borders with Rwanda and Uganda.
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).

The geography of Mozambique consists mostly of coastal lowlands with uplands in its center and high plateaus in the northwest. There are also mountains in the western portion. The country is located on the east coast of southern Africa, directly west of the island of Madagascar. Mozambique has a tropical climate with two seasons, a wet season from October to March and a dry season from April to September.

Russia is the largest country in the world, covering over 17,125,191 km2 (6,612,073 sq mi), and encompassing more than one-eighth of Earth's inhabited land area. Russia extends across eleven time zones, and has the most borders of any country in the world, with sixteen sovereign nations.

Algeria comprises 2,381,740 square kilometres (919,590 sq mi) of land, more than 80% of which is desert, in North Africa, between Morocco and Tunisia. It is the largest country in Africa. Its Arabic name, Al Jazair, is believed to derive from the rocky islands along the coastline of the Mediterranean Sea. The northern portion, an area of mountains, valleys, and plateaus between the Mediterranean and the Sahara Desert, forms an integral part of the section of North Africa known as the Maghreb. This area includes Morocco, Tunisia, and the northwestern portion of Libya known historically as Tripolitania.

The Great Dividing Range, also known as the East Australian Cordillera or the Eastern Highlands, is a cordillera system in eastern Australia consisting of an expansive collection of mountain ranges, plateaus and rolling hills. It runs roughly parallel to the east coast of Australia and forms the fifth-longest land-based mountain chain in the world, and the longest entirely within a single country. It is mainland Australia's most substantial topographic feature and serves as the definitive watershed for the river systems in eastern Australia, hence the name.

South Africa occupies the southern tip of Africa, its coastline stretching more than 2,850 kilometres from the desert border with Namibia on the Atlantic (western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique on the Indian (eastern) coast. The low-lying coastal zone is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography. The total land area is 1,220,813 km2 (471,359 sq mi). It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of 1,535,538 km2 (592,875 sq mi).

The Western Ghats, also known as the Sahyadri, is a mountain range that stretches 1,600 km (990 mi) along the western coast of the Indian peninsula. Covering an area of 160,000 km2 (62,000 sq mi), it traverses the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu. The range forms an almost continuous chain of mountains along the western edge of the Deccan Plateau, from the Tapti River to Swamithoppe in Kanyakumari district at the southern tip of the Indian peninsula. The Western Ghats meet with the Eastern Ghats at Nilgiris before continuing south.

The geography of North Carolina falls naturally into three divisions — the Appalachian Mountains in the west, the central Piedmont Plateau, and the eastern Atlantic Coastal Plain. North Carolina covers 53,819 square miles (139,391 km2) and is 503 miles (810 km) wide by 150 miles (241 km) long. The physical characteristics of the state vary from the summits of the Smoky Mountains, an altitude of near seven thousand feet (2,130 m) in the west, sloping eastward to sea level along the coast and beaches of the Atlantic Ocean.
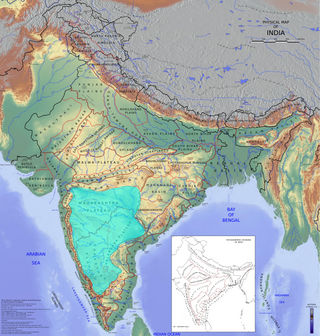
The Deccan is a large plateau and region of the Indian subcontinent located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada River. This definition is sometimes expanded to include the entire peninsular region. To the north, the plateau is bounded by the Satpura and Vindhya Ranges. It covers the modern-day Indian States of Maharashtra, Telangana, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh.

The Eastern Ghats are a discontinuous range of mountains along India's eastern coast. The Eastern Ghats pass through the states of Odisha and Andhra Pradesh to Tamil Nadu by, passing parts of Karnataka and Telangana on the way. They are eroded and cut through by four major rivers of peninsular India, namely, the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and. Zindagad Konda is the highest point in both Andhra Pradesh and the Eastern Ghats at 1,690 metres (5,540 ft). The Biligiriranga Hills in Karnataka are the tallest hill range in the Eastern Ghats, with many peaks above 1500 m in height.

The Chota Nagpur Plateau is a plateau in eastern India, which covers much of Jharkhand state as well as adjacent parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, West Bengal and Bihar. The Indo-Gangetic plain lies to the north and east of the plateau, and the basin of the Mahanadi river lies to the south. The total area of the Chota Nagpur Plateau is approximately 65,000 square kilometres (25,000 sq mi).

Periyar, is the longest river and the river with the largest discharge potential in the Indian state of Kerala. It is one of the few perennial rivers in the region and provides drinking water for several major towns. The Periyar is of utmost significance to the economy of Kerala. It generates a significant proportion of Kerala's electrical power via the Idukki Dam and flows along a region of industrial and commercial activity. The river also provides water for irrigation and domestic use throughout its course besides supporting a rich fishery. Due to these reasons, the river has been named the "Lifeline of Kerala". Kochi city, in the vicinity of the river mouth, draws its water supply from Aluva, an upstream site sufficiently free of seawater intrusion. Twenty five percent of Kerala's industries are along the banks of the Periyar. These are mostly crowded within a stretch of 5 kilometres (3 mi) in the Eloor-Edayar region (Udhyogamandal), about 10 kilometres (6 mi) north of Kochi harbor.

The North American Cordillera, sometimes also called the Western Cordillera of North America, the Western Cordillera, or the Pacific Cordillera, is the North American portion of the American Cordillera, the mountain chain system along the Pacific coast of the Americas. The North American Cordillera covers an extensive area of mountain ranges, intermontane basins, and plateaus in Western and Northwestern Canada, Western United States, and Mexico, including much of the territory west of the Great Plains.

The Annamite Range or the Annamese Mountains is a major mountain range of eastern Indochina, extending approximately 1,100 km (680 mi) through Laos, Vietnam, and a small area in northeast Cambodia.

The Indian State of Karnataka is located between 11°30' North and 18°30' North latitudes and between 74° East and 78°30' East longitude.It is situated on a tableland where the Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats converge into the complex, in the western part of the Deccan Peninsular region of India. The State is bounded by Maharashtra and Goa States in the north and northwest; by the Lakshadweep Sea in the west; by Kerala in the south-west and Tamil Nadu in the south and south-east, Andhra Pradesh in the south-east and east and Telangana in the north-east. Karnataka extends to about 850 km (530 mi) from north to south and about 450 km (280 mi) from east to west.

The Geography of South India comprises the diverse topological and climatic patterns of South India. South India is a peninsula in the shape of a vast inverted triangle, bounded on the west by the Arabian Sea, on the east by the Bay of Bengal and on the north by the Vindhya and Satpura ranges.

Odisha is one of the 28 states in the Republic of India. Odisha is located in the eastern part of the Indian peninsula and the Bay of Bengal lies to its East while Chhattisgarh shares its border in the west and north-west. The state also shares geographic boundaries with West Bengal in the north-east, Jharkhand in the north and Andhra Pradesh in the south. The state is spread over an area of 1,55,707 km2 and extends for 700 km from north to south and 500 kilometres from east to west. Its coastline is 450 km long. The state is divided into 30 districts which are further subdivided into 314 blocks called tahasil.

Kaimur Range is the eastern portion of the Vindhya Range, about 483 kilometres (300 mi) long, extending from around Katangi in Jabalpur district of Madhya Pradesh to around Sasaram in Rohtas district of Bihar. It passes through the Rewa and Mirzapur divisions. The range never rises more than a few hundred metres above the surrounding plains and has a maximum width of around 80 km.



















