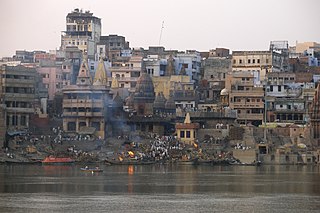The Ganges River is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The 2,525 km (1,569 mi) river rises in the western Himalayas in the Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna, the lower stream of the Brahmaputra, and eventually the Meghna, forming the major estuary of the Ganges Delta, and emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The Ganges–Brahmaputra–Meghna system is the second-largest river on earth by discharge.
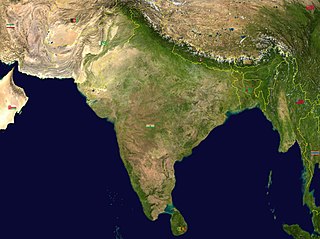
India is situated north of the equator between 8°4' north to 37°6' north latitude and 68°7' east to 97°25' east longitude. It is the seventh-largest country in the world, with a total area of 3,287,263 square kilometres (1,269,219 sq mi). India measures 3,214 km (1,997 mi) from north to south and 2,933 km (1,822 mi) from east to west. It has a land frontier of 15,200 km (9,445 mi) and a coastline of 7,516.6 km (4,671 mi).

The Indo-Gangetic Plain, also known as the North Indian River Plain, is a 700-thousand km2 (172-million-acre) fertile plain encompassing northern regions of the Indian subcontinent, including most of modern-day northern and eastern India, most of eastern-Pakistan, virtually all of Bangladesh and southern plains of Nepal. Also known as the Indus–Ganga Plain, the region is named after the Indus and the Ganges rivers and encompasses a number of large urban areas. The plain is bounded on the north by the Himalayas, which feed its numerous rivers and are the source of the fertile alluvium deposited across the region by the two river systems. The southern edge of the plain is marked by the Deccan Plateau. On the west rises the Iranian Plateau. Many developed cities like Delhi, Dhaka, Kolkata, Lahore, Islamabad and Karachi are located in the Indo-Gangetic Plain.

Dhoby Ghaut is a place in Singapore that often refers to the Dhoby Ghaut MRT station, a major interchange station on Singapore's Mass Rapid Transit network connecting the North-South Line, North East Line, and the Circle Line. As a place, Dhoby Ghaut lies along the eastern end of Orchard Road. There is a shopping mall above the MRT station called Plaza Singapura.
Indo-Mauritians are Mauritians who trace their ethnic ancestry to the Republic of India or other parts of the Indian subcontinent in South Asia.

Chitrakoot Dham is a city in the Chitrakoot district, in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. It is the headquarters of the Chitrakoot district. Situated in the Bundelkhand region, it holds great cultural, historical, religious and archaeological importance and it is said that Rama, a major deity in Hinduism, spent 11 years of exile in Chitrakoot. It is connected to the town of Chitrakoot, situated in the Satna district of Madhya Pradesh.

Mauritians are nationals or natives of the Republic of Mauritius and their descendants. Mauritius is a multi-ethnic society, with notable groups of people of South Asian, Sub-Saharan African, European, and Chinese descent, as well as those of a mixed background from any combination of the aforementioned ethnic groups.

The Immigration Depot is a building complex located in Port Louis on the Indian Ocean island of Mauritius, the first British colony to receive indentured, or contracted, labour workforce from many countries. From 1849 to 1923, half a million Indian indentured labourers passed through the Immigration Depot, to be transported to plantations throughout the British Empire. The large-scale migration of the labourers left an indelible mark on the societies of many former British colonies, with Indians constituting a substantial proportion of their national populations. In Mauritius alone, 68 percent of the current total population is of Indian ancestry. The Immigration Depot has thus become an important reference point in the history and cultural identity of Mauritius.

Temple tanks are wells or reservoirs built as part of the temple complex near Indian temples. They are called pushkarini, kalyani, kunda, sarovara, tirtha, talab, pukhuri, ambalakkuḷam, etc. in different languages and regions of India. Some tanks are said to cure various diseases and maladies when bathed in. It is possible that these are cultural remnants of structures such as the Great Bath of Mohenjo-daro or Dholavira, which was part of the Indus Valley civilization. Some are stepwells with many steps at the sides.

The ongoing pollution of the Ganges, the largest river in the Indian subcontinent, poses a significant threat to human health and the environment. The river, which is severely polluted with human waste and industrial contaminants, provides water to about 40% of India's population across 11 states, serving an estimated population of 500 million people, more than any other river in the world.

Maharaja Vibhuti Narayan Singh was the king of Benares, a city considered holy, located in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. He was the last Bhumihar Brahmin king of the Kingdom of Kashi.

Situated in the northern part of India, bordering with the capital of India New Delhi, Uttar Pradesh is one of the most popular and an established tourist destination for both Indians and non-Indians alike in India. The most populous state of India, Uttar Pradesh contains many historical monuments and places of religious significance. Geographically, Uttar Pradesh is very diverse, with Himalayan foothills in the extreme north and the Gangetic Plain in the centre. It is also home of India's most visited sites, Hinduism's holiest city, Varanasi. Kumbh city, Prayagraj. Kathak, one of the eight forms of Indian classical dances, originated from Uttar Pradesh. Uttar Pradesh is at the heart of India, hence it is also known as The Heartland of India. Cuisine of Uttar Pradesh like Awadhi cuisine, Mughlai cuisine and Bhojpuri cuisine are very famous not only in India but also many places abroad.

The Sapta Puri are a group of seven Hindu tirtha, or holy pilgrimage sites, located in India. Pilgrimage to these sites is said to bless the pilgrim with moksha.

Satti Chaura Ghat or Massacre Ghat is a famous ghat in Kanpur, the industrial hub of Uttar Pradesh state in north India. It is located on the bank of the River Ganges in Kanpur Cantonment near Jajmau.

The Kānvar Yātrā is an annual pilgrimage of devotees of Shiva, known as Kānvarias (कावड़िया) or "Bhole" (भोले), to Hindu pilgrimage places of Haridwar, Gaumukh and Gangotri in Uttarakhand and Ajgaibinath, Sultanganj in Bhagalpur, Bihar to fetch holy waters of Ganges River. Millions of pilgrims fetch sacred water from river Ganga and carry on their shoulders for hundreds of miles to offer it in their local Śiva shrines, or specific temples such as Pura Mahadeva temple in Baghpat district and Augharnath temple in Meerut, Kashi Vishwanath temple in Varanasi, Baidyanath temple in Deoghar etc. In 2023, the Kanwar Yatra was held from 04-15 July.

Ghats in Varanasi are riverfront steps leading to the banks of the Ganges river. The city has 84 ghats. Most of the ghats are bathing and puja ceremonial ghats, while two ghats, Manikarnika and Harishchandra, are used exclusively as cremation sites.

Manikarnika Ghat is one of the holiest cremation grounds among the sacred riverfronts (ghats), located on the banks of River Ganga, in the city of Varanasi in the Indian state of Uttar Pradesh. In Hinduism, death is considered a gateway to another life marked by the result of one's karma. It is believed that a human's soul attains moksha, and hence breaks the cycle of rebirth when cremated here.
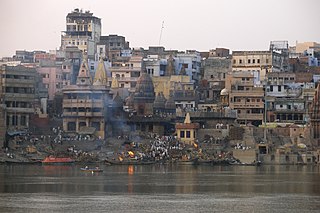
Varanasi is a city on the Ganges river in northern India that has a central place in the traditions of pilgrimage, death, and mourning in the Hindu world. The city has a syncretic tradition of Muslim artisanship that underpins its religious tourism. Located in the middle-Ganges valley in the southeastern part of the state of Uttar Pradesh, Varanasi lies on the left bank of the river. It is 692 kilometres (430 mi) to the southeast of India's capital New Delhi and 320 kilometres (200 mi) to the southeast of the state capital, Lucknow. It lies 121 kilometres (75 mi) downstream of Prayagraj, where the confluence with the Yamuna river is another major Hindu pilgrimage site.
Varanasi, also known as Kashi, is considered as the religious capital of Hinduism. In the Hindu faith, it is the holiest of all of its cities; the four dhams in the four cardinal directions of the country – Badrinath in the north, Puri in the east, Dwarka in the west and Rameshwaram in the south – are all represented in the city in "archetypal forms" as the presiding deities at Badrinath Ghat, Assi's Jagannath Temple area, Shankudhara Pokhra, and Mir Ghat respectively. Other Hindu holy places, such as the Kedarnath at Kedar Ghat, Mathura at Bakaruia Kund or Nakhi Ghat, Prayagraj (Allahadbad) at Dashahvamedha Ghat, Kamakhya (Assam) at Kamachha, Kurukshetra at Kurkukshetra Kund near Asi, and Lake Manasarovar at Mansarovar near Shyameshvara are a part of the city's religious and cultural heritage.

Ganga Dussehra, also known as Gangavataran, is a Hindu festival celebrating the avatarana (descent) of the Ganges. It is believed by Hindus that the holy river Ganges descended from heaven to earth on this day. Ganga Dussehra takes place on Dashami of the waxing moon of the Hindu calendar month Jyeshtha. The festival celebration lasts ten days, including the nine days preceding this holy day.