Related Research Articles

Sir Thomas Bouch was a British railway engineer. He was born in Thursby, near Carlisle, Cumberland, and lived in Edinburgh. As manager of the Edinburgh and Northern Railway he introduced the first roll-on/roll-off train ferry service in the world. Subsequently as a consulting engineer, he helped develop the caisson and popularised the use of lattice girders in railway bridges. He was knighted after the successful completion of the first Tay Railway Bridge, but his reputation was destroyed by the subsequent Tay Bridge disaster, in which 75 people are believed to have died as a result of defects in design, construction and maintenance, for all of which Bouch was held responsible. He died within 18 months of being knighted.

The Tay Bridge carries rail traffic across the Firth of Tay in Scotland between Dundee and the suburb of Wormit in Fife. Its span is 2.75 miles. It is the second bridge to occupy the site.
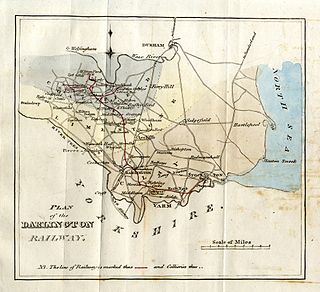
The Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was a railway company that operated in north-east England from 1825 to 1863. The world's first public railway to use steam locomotives, its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Darlington and Stockton in County Durham, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. The movement of coal to ships rapidly became a lucrative business, and the line was soon extended to a new port at Middlesbrough. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.

Teesside is a built-up area around the River Tees in northern England, split between County Durham and North Yorkshire. The area contains the towns of Middlesbrough, Stockton-on-Tees, Billingham, Redcar, Thornaby-on-Tees, and Ingleby Barwick. Teesside's economy was once dominated by heavy manufacturing until deindustrialisation in the latter half of the 20th century. Chemical production continues to contribute significantly to Teesside's economy.

Locomotion No. 1 is an early steam locomotive that was built in 1825 by the pioneering railway engineers George and Robert Stephenson at their manufacturing firm, Robert Stephenson and Company. It became the first steam locomotive to haul a passenger-carrying train on a public railway, the Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR).

Darlington Works was established in 1863 by the Stockton and Darlington Railway in the town of Darlington in the north east of England. The main part of the works, the North Road Shops was located on the northeast side of the Stockton and Darlington Railway

The Tay Bridge disaster occurred during a violent European windstorm on Sunday 28 December 1879, when the first Tay Rail Bridge collapsed as a North British Railway (NBR) passenger train on the Edinburgh to Aberdeen Line from Burntisland bound for its final destination of Dundee passed over it, killing all aboard. The bridge—designed by Sir Thomas Bouch—used lattice girders supported by iron piers, with cast iron columns and wrought iron cross-bracing. The piers were narrower and their cross-bracing was less extensive and robust than on previous similar designs by Bouch.

The South Durham and Lancashire Union Railway (SD&LUR) built a railway line linking the Stockton and Darlington Railway near Bishop Auckland with the Lancaster and Carlisle Railway at Tebay, via Barnard Castle, Stainmore Summit and Kirkby Stephen. The line opened in 1861 and became known as the Stainmore Line.
William Bouch was an English railway engineer, who is famous for the steam locomotives he designed for the Stockton and Darlington Railway.

John Fowler was an English agricultural engineer who was a pioneer in the use of steam engines for ploughing and digging drainage channels. His inventions significantly reduced the cost of ploughing farmland, and also enabled the drainage of previously uncultivated land in many parts of the world.

John Vaughan, known as Jacky, was born in Worcester on "St Thomas' Day" in 1799, the son of Welsh parents. He worked his way up the iron industry, becoming an ironmaster and co-founder of the largest of all the Victorian iron and steel companies, Bolckow Vaughan. Where Henry Bolckow provided the investment and business expertise, Vaughan contributed technical knowledge, in a long-lasting and successful partnership that transformed Middlesbrough from a small town to the centre of ironmaking in Britain.
The Cleveland Railway was a railway line in north-east England running from Normanby Jetty on the River Tees, near Middlesbrough, via Normanby and then via Guisborough through the Eston Hills, to Loftus in East Cleveland. It carried minerals from numerous iron ore mines along its route to the River Tees for shipment to Tyneside and elsewhere. The line was jointly proposed by the West Hartlepool Harbour and Railway (WHH&R), who provided half its capital, together with various landowners. The WHH&R lay on the north bank of the Tees, to which it had a cross-river connection via a jetty at Normanby.

Isaac Wilson was an English industrialist and Liberal politician.

The Tees railway viaduct was a railway bridge in the county of Durham, England, which carried the South Durham and Lancashire Union Railway over the River Tees west of Barnard Castle.

Tees Marshalling Yard is a railway marshalling yard, used to separate railway wagons, located near Middlesbrough in North Yorkshire, Northern England.

The North British, Arbroath and Montrose Railway was a company established by Act of Parliament in 1871 to construct and operate a railway line from north of Arbroath via Montrose to Kinnaber Junction, 38 miles (61 km) south of Aberdeen. The company was originally a subsidiary of the North British Railway but was absorbed into its parent in 1880.

The Belah Viaduct was a railway viaduct on the South Durham and Lancashire Union Railway, crossing the River Belah, in Cumbria, England, about 1 mile (1.6 km) south of the village of Barras and 4 miles (6.4 km) east north east of Kirkby Stephen. It was completed in 1860 and was demolished in 1963.

The 1825 to 1863 Stockton and Darlington Railway (S&DR) was the world's first public railway to use steam locomotives. Its first line connected collieries near Shildon with Stockton-on-Tees and Darlington, and was officially opened on 27 September 1825. While coal waggons were hauled by steam locomotives from the start, passengers were carried in coaches drawn by horses until carriages hauled by steam locomotives were introduced in 1833.

John Harris was a railway engineer who worked on the Stockton and Darlington Railway from 1836 to 1847.
References
- ↑ Kirby, Maurice W. (1993), The Origins of Railway Enterprise: The Stockton and Darlington Railway 1821-1863, p. 134
- ↑ "Middlesbrough Council Civic History & Events's post". Facebook. Retrieved 9 January 2025.
- ↑ "Edgar Gilkes". Graces Guide. Retrieved 9 January 2025.
- ↑ "The Stainmore Route Viaducts", www.stainmore150.co.uk, 2010
- ↑ Panel for Historical Engineering Works for Belah Viaduct, Institute of Civil Engineers, 1980, archived from the original on 12 August 2014
- ↑ Burn, Duncan Lyall, The Economic History of Steelmaking 1867-1939: A Study in Competition, pp. 28–29
Sources
- Lowe, J.W. (1989), British Steam Locomotive Builders, Guild Publishing
Further reading
- Harman, Fred W. (1999), The History and Locomotives of the Tees Engine Works. The Gilkes, Wilson & Hopkins Partnerships, ISBN 0953531341