
The atmospheric engine was invented by Thomas Newcomen in 1712, and is often referred to as the Newcomen fire engine or simply as a Newcomen engine. The engine was operated by condensing steam drawn into the cylinder, thereby creating a partial vacuum which allowed the atmospheric pressure to push the piston into the cylinder. It was historically significant as the first practical device to harness steam to produce mechanical work. Newcomen engines were used throughout Britain and Europe, principally to pump water out of mines. Hundreds were constructed throughout the 18th century.

The Watt steam engine design was an invention of James Watt that became synonymous with steam engines during the Industrial Revolution, and it was many years before significantly new designs began to replace the basic Watt design.

The Abbey Pumping Station is a museum of science and technology in Leicester, England, on Corporation Road, next to the National Space Centre. With four working steam-powered beam engines from its time as a sewage pumping station, it also houses exhibits for transport, public health, light and optics, toys and civil engineering.

Boulton & Watt was an early British engineering and manufacturing firm in the business of designing and making marine and stationary steam engines. Founded in the English West Midlands around Birmingham in 1775 as a partnership between the English manufacturer Matthew Boulton and the Scottish engineer James Watt, the firm had a major role in the Industrial Revolution and grew to be a major producer of steam engines in the 19th century.

Claymills Pumping Station is a restored Victorian sewage pumping station on the north side of Burton upon Trent, Staffordshire, England DE13 0DA. It was designed by James Mansergh and used to pump sewage to the sewage farm at Egginton.

William Foster & Co Ltd was an agricultural machinery company based in Lincoln, Lincolnshire, England often called "Fosters of Lincoln." The company can be traced back to 1846, when William Foster purchased a flour mill in Lincoln. William Foster then proceeded to start small scale manufacturing of mill machinery and threshing machinery. The mill was converted to an iron foundry by 1856, thus becoming the original Wellington Foundry. By 1899 the works had moved to the Wellington foundry in New Boultham and the original works were then occupied by William Rainforth. During the First World War Fosters built some of the first tanks for the British Army.
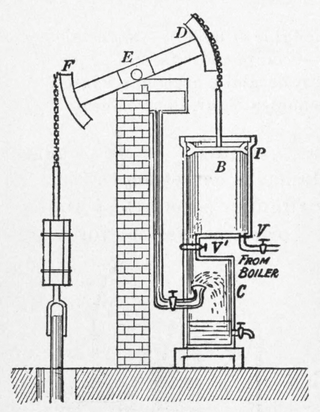
A beam engine is a type of steam engine where a pivoted overhead beam is used to apply the force from a vertical piston to a vertical connecting rod. This configuration, with the engine directly driving a pump, was first used by Thomas Newcomen around 1705 to remove water from mines in Cornwall. The efficiency of the engines was improved by engineers including James Watt, who added a separate condenser; Jonathan Hornblower and Arthur Woolf, who compounded the cylinders; and William McNaught, who devised a method of compounding an existing engine. Beam engines were first used to pump water out of mines or into canals but could be used to pump water to supplement the flow for a waterwheel powering a mill.

The Crossness Pumping Station is a former sewage pumping station designed by the Metropolitan Board of Works's chief engineer Sir Joseph Bazalgette and architect Charles Henry Driver. It is located at Crossness Sewage Treatment Works, at the eastern end of the Southern Outfall Sewer and the Ridgeway path in the London Borough of Bexley. Constructed between 1859 and 1865 by William Webster, as part of Bazalgette's redevelopment of the London sewerage system, it features spectacular ornamental cast ironwork, that Nikolaus Pevsner described as "a masterpiece of engineering – a Victorian cathedral of ironwork".
Haigh Foundry was an ironworks and foundry in Haigh, Lancashire, which was notable for the manufacture of early steam locomotives.

London Museum of Water & Steam is an independent museum founded in 1975 as the Kew Bridge Steam Museum. It was rebranded in early 2014 following a major investment project.

Snibston is an area and former civil parish east of Ravenstone, now in the parish of Ravenstone with Snibstone, in the North West Leicestershire district, in the county of Leicestershire, England. Originally rural, part of Snibston was transformed into a coal mining village by the opening of coal mines by the Snibston Colliery Company in the early 1830s. This industrial part of Snibston was subsequently subsumed into the developing town of Coalville, though small rural areas of Snibston survive within the civil parishes of Ravenstone with Snibston and Hugglescote and Donington le Heath. In the part of Snibston within the latter civil parish stands the 13th-century church of St Mary, noted as the smallest church still in use for regular worship in England. The main Snibston Colliery was sunk in 1831, and after its closure the Snibston Country Park with the Snibston Discovery Museum was built on part of the colliery site. Part of the park is Snibston Grange Local Nature Reserve.

Arthur Woolf was a Cornish engineer, most famous for inventing a high-pressure compound steam engine. In this way he made an outstanding contribution to the development and perfection of the Cornish engine.

Bolton Steam Museum is a museum in Bolton, Greater Manchester, England, which houses a variety of preserved steam engines. Based in the cotton store of the former Atlas Mill in Mornington Road, it is owned and run by the Northern Mill Engine Society (NMES).

The first recorded rudimentary steam engine was the aeolipile mentioned by Vitruvius between 30 and 15 BC and, described by Heron of Alexandria in 1st-century Roman Egypt. Several steam-powered devices were later experimented with or proposed, such as Taqi al-Din's steam jack, a steam turbine in 16th-century Ottoman Egypt, Denis Papin's working model of the steam digester in 1679 and Thomas Savery's steam pump in 17th-century England. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine became the first commercially successful engine using the principle of the piston and cylinder, which was the fundamental type of steam engine used until the early 20th century. The steam engine was used to pump water out of coal mines.

The Whitbread Engine preserved in the Powerhouse Museum in Sydney, Australia, built in 1785, is one of the first rotative steam engines ever built, and is the oldest surviving. A rotative engine is a type of beam engine where the reciprocating motion of the beam is converted to rotary motion, producing a continuous power source suitable for driving machinery.

A blowing engine is a large stationary steam engine or internal combustion engine directly coupled to air pumping cylinders. They deliver a very large quantity of air at a pressure lower than an air compressor, but greater than a centrifugal fan.

Forncett is a civil parish in the English county of Norfolk. It covers an area of 10.76 km2 (4.15 sq mi) and had a population of 1,000 in 381 households at the 2001 census, increasing to 1,126 at the 2011 census. For the purposes of local government, it falls within the district of South Norfolk.
A water-returning engine was an early form of stationary steam engine, developed at the start of the Industrial Revolution in the middle of the 18th century. The first beam engines did not generate power by rotating a shaft but were developed as water pumps, mostly for draining mines. By coupling this pump with a water wheel, they could be used to drive machinery.

Six-column beam engines are a type of beam engine, where the beam's central pivot is supported on a cast-iron frame or 'bedstead', supported on six iron columns.

The Nottingham Industrial Museum is a volunteer-run museum situated in part of the 17th-century stables block of Wollaton Hall, located in a suburb of the city of Nottingham. The museum won the Nottinghamshire Heritage Site of the Year Award 2012, a local accolade issued by Experience Nottinghamshire. The Museum collection closed in 2009 after Nottingham City Council withdrew funding, but has since reopened at weekends and bank holidays, helped by a £91,000 government grant, and run by volunteers. The museum contains a display of local textiles machinery, transport, telecommunications, mining and engineering technology. There is a display of cycles, motorcycles, and motor cars. There are examples of significant lace-making machinery. It also houses an operational beam engine, from the Basford, Nottingham pumping station.


















