Related Research Articles

Francesco I Sforza was an Italian condottiero who founded the Sforza dynasty in the duchy of Milan, ruling as its (fourth) duke from 1450 until his death.

The Republic of Florence, known officially as the Florentine Republic, was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany, Italy. The republic originated in 1115, when the Florentine people rebelled against the Margraviate of Tuscany upon the death of Matilda of Tuscany, who controlled vast territories that included Florence. The Florentines formed a commune in her successors' place. The republic was ruled by a council known as the Signoria of Florence. The signoria was chosen by the gonfaloniere, who was elected every two months by Florentine guild members.

The Guelphs and Ghibellines were factions supporting respectively the Pope and the Holy Roman Emperor in the Italian city-states of Central Italy and Northern Italy during the Middle Ages.

The Duchy of Milan was a state in Northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city since 1277.
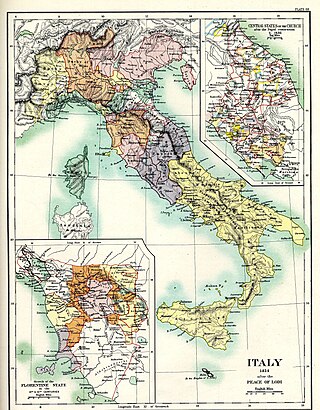
The Treaty of Lodi, or Peace of Lodi, was a peace agreement to put an end to the Wars in Lombardy between the Venetian Republic and the Duchy of Milan, signed in the city of Lodi on 9 April 1454.

The Golden Ambrosian Republic was a short-lived republic founded in Milan by members of the University of Pavia with popular support, during the first phase of the Milanese War of Succession. With the aid of Francesco Sforza they held out against the forces of the Republic of Venice, but after a betrayal Sforza defected and captured Milan to become Duke himself, abolishing the Republic.

The Castello Sforzesco is a medieval fortification located in Milan, Northern Italy. It was built in the 15th century by Francesco Sforza, Duke of Milan, on the remnants of a 14th-century fortification. Later renovated and enlarged, in the 16th and 17th centuries it was one of the largest citadels in Europe. Extensively rebuilt by Luca Beltrami in 1891–1905, it now houses several of the city's museums and art collections.

Bartolomeo Colleoni was an Italian condottiero, who became captain-general of the Republic of Venice. Colleoni "gained reputation as the foremost tactician and disciplinarian of the 15th century". He is also credited with having refurbished the Roman baths at Trescore Balneario.

Bianca Maria Visconti also known as Bianca Maria Sforza or Blanca Maria was Duchess of Milan from 1450 to 1468 by marriage to Francesco I Sforza. She was regent of Marche during the absence of her spouse in 1448. She served as Regent of the Duchy of Milan during the illness of her spouse in 1462, as well as in 1466, between the death of her spouse and until her son, the new Duke, who was absent, was able to return to Milan to assume power.

The Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy. They lasted from 1423 until the signing of the Treaty of Lodi in 1454. During their course, the political structure of Italy was transformed: out of a competitive congeries of communes and city-states emerged the five major Italian territorial powers that would make up the map of Italy for the remainder of the 15th century and the beginning of the Italian Wars at the turn of the 16th century. They were Venice, Milan, Florence, the Papal States and Naples. Important cultural centers of Tuscany and Northern Italy—Siena, Pisa, Urbino, Mantua, Ferrara—became politically marginalized.

Francesco (Cicco) Simonetta was an Italian Renaissance statesman who composed an early treatise on cryptography.

Vitaliano I Borromeo was an Italian Ghibelline nobleman from Milan, first Count of Arona. His father was Giacomo Vitaliani, ambassador of Padua to Venice, and his mother Margherita was of the prosperous family of Borromeo. He married Ambrosina Fagnani, and his only son was Filippo Borromeo. Many of his descendants took his name.
Carlo Gonzaga, Lord of Sabbioneta, was an Italian nobleman of the Mantuan House of Gonzaga who rose to the position of Captain of the People in the Ambrosian Republic of Milan, and eventually ruled practically as an autocrat. He was the younger son of Gianfrancesco Gonzaga and Paola Malatesta, as well as a friend of the humanist writer Francesco Filelfo. His brother was Ludovico III Gonzaga, Marquis of Mantua, and became a rival of his for Mantua and in the field of battle.
Filippo Borromeo (1419–1464) was the son of Vitaliano I Borromeo and Ambrosina Fagnini. He was second Count of Arona, and greatly expanded his father's banking trade throughout Europe. He married Francesca Visconti, the daughter of Count Lancillotto Visconti of Cicognola, through whom he had three sons and two daughters.

Francesco Piccinino was an Italian condottiero.
Luigi dal Verme (died 1449) was an Italian condottiero.

Milan, Italy is an ancient city in northern Italy first settled under the name Medhelanon in about 590 BC by a Celtic tribe belonging to the Insubres group and belonging to the Golasecca culture. The settlement was conquered by the Romans in 222 BC and renamed it Mediolanum. Diocletian divided the Roman Empire, choosing the eastern half for himself, making Milan the seat of the western half of the empire, from which Maximian ruled, in the late 3rd and early 4th century AD. In 313 AD Emperors Constantine and Licinius issued the Edict of Milan, which officially ended the persecution of Christians. In 774 AD, Milan surrendered to Charlemagne and the Franks.
The Milanese War of Succession was a war of succession over the Duchy of Milan from the death of duke Filippo Maria Visconti on 13 August 1447 to the Treaty of Lodi on 9 April 1454.

Guido Torelli was a condottiero. Through his military campaigns and diplomatic skills, he achieved the title of the first Count of Guastalla and Montechiarugolo.
References
- A History of Milan under the Sforza. Cecilia M. Ady, Edward Armstrong; Methuen & Co., 1907. Archived 2008-05-06 at the Wayback Machine