
The Pyrgi Tablets are three golden plates inscribed with a bilingual Phoenician–Etruscan dedicatory text. They are the oldest historical source documents from pre-Roman Italy and are rare examples of texts in these languages. They were discovered in 1964 during a series of excavations at the site of ancient Pyrgi,on the Tyrrhenian coast of Italy in Latium (Lazio). The text records the foundation of a temple and its dedication to the Phoenician goddess Astarte,who is identified with the Etruscan supreme goddess Uni in the Etruscan text. The temple's construction is attributed to Tiberius Velianas,ruler of the nearby city of Caere.

Palestrina is a modern Italian city and comune (municipality) with a population of about 22,000,in Lazio,about 35 kilometres east of Rome. It is connected to the latter by the Via Prenestina. It is built upon the ruins of the ancient city of Praeneste.
Mauro Cristofani was a linguist and researcher in Etruscan studies.

The Lemnian language was spoken on the island of Lemnos,Greece,in the second half of the 6th century BC. It is mainly attested by an inscription found on a funerary stele,termed the Lemnos stele,discovered in 1885 near Kaminia. Fragments of inscriptions on local pottery show that it was spoken there by a community. In 2009,a newly discovered inscription was reported from the site of Hephaistia,the principal ancient city of Lemnos. Lemnian is largely accepted as being a Tyrsenian language,and as such related to Etruscan and Rhaetic. After the Athenians conquered the island in the latter half of the 6th century BC,Lemnian was replaced by Attic Greek.
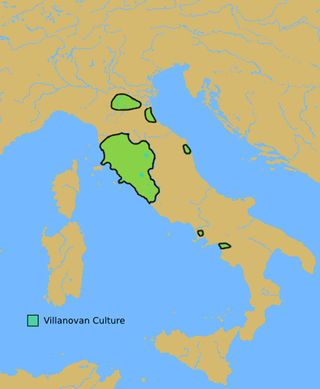
The Villanovan culture,regarded as the earliest phase of the Etruscan civilization,was the earliest Iron Age culture of Italy. It directly followed the Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture which branched off from the Urnfield culture of Central Europe. The name derives from the locality of Villanova,a fraction of the municipality of Castenaso in the Metropolitan City of Bologna where,between 1853 and 1855,Giovanni Gozzadini found the remains of a necropolis,bringing to light 193 tombs,of which there were 179 cremations and 14 inhumations.

Gian Rinaldo Carli (1720–1795),also known by other names,was an Italian economist,historian,and antiquarian.

The sanctuary of Minerva at Portonaccio is an archaeological site on the western side of the plateau on which the ancient Etruscan city of Veii,north of Rome,Italy,was located. The site takes its name from the locality within the village of Isola Farnese,part of Municipio XX,city of Rome.
Giovanni Becatti was an Italian Classical art historian and archaeologist.

Massimo Pallottino was an Italian archaeologist specializing in Etruscan civilization and art.
The Corpus Inscriptionum Etruscarum is a corpus of Etruscan texts,collected by Carl Pauli and his followers since 1885. After the death of Olof August Danielsson in 1933,this collection was passed on to the Uppsala University Library.

Pyrgi was originally an ancient Etruscan town and port in Latium,central Italy,to the north-west of Caere. Its location is now occupied by the borough of Santa Severa. It is notable for the discovery here of the gold tablets,an exceptional epigraphic document with rare texts in Phoenician and Etruscan languages,and also the exceptional terracotta pediment statues from the temple.

The National Etruscan Museum is a museum of the Etruscan civilization,housed in the Villa Giulia in Rome,Italy.

The Swedish Institute in Rome is a research institution that serves as the base for archaeological excavations and other scientific research in Italy. It also pursues academic instruction in archaeology and art sciences as well as arranging conferences with themes of interest to the institute. The Institute has at its disposal a building in central Rome with a relatively well-supplied library,archaeological laboratory and around twenty rooms and smaller apartments for the use of visiting researchers and holders of scholarships.
Corpus Speculorum Etruscorum is an international project with the goal to publish all existing Etruscan bronze mirrors. The first three volumes were published in 1981. A total of thirty-six fascicles has been produced.

Lur is an Etruscan underworld deity with not much known history. Lur does not have many depictions but the ones that have been found show the deity as a male. He has been noted to be associated with a prophetic nature,while also bearing oracular and martial characteristics. He has been linked to another deity by the name of Laran,which,it has been suggested,is where Lur derives his name from. The context of the name has been associated with darkness and the underworld. A fifth century vase found near a sanctuary in San Giovenale bears an inscription that translates:"I am Lurs,that of Laran." Another inscription has been found with the spelling lartla,noting relations to a Lar,which gives a label to Lur that describes features of protection. The name may be related to Latin luridus "pale".
Carlo De Simone is an Italian linguist,specializing in Ancient Greek and Latin texts and Etruscan epigraphs. He is best known for his research into Etruscan,Lemnian and Rhaetian languages.
Guglielmo Maetzke was an Italian archaeologist and etruscologist. A pupil of the Etruscologist Massimo Pallottino,he directed important excavation campaigns in Tuscany,Lazio,Campania and Sardinia.










