Mycoplasma hominis is a species of bacteria in the genus Mycoplasma. M. hominis has the ability to penetrate the interior of human cells. Along with ureaplasmas, mycoplasmas are the smallest free-living organisms known.

The Serb Volunteer Guard, also known as Arkan's Tigers or Arkan's men, was a Serbian volunteer paramilitary unit founded and led by Arkan that fought in Croatia (1991–93) and Bosnia (1992–95) during the Yugoslav Wars.
Staphylococcus hominis is a coagulase-negative member of the bacterial genus Staphylococcus, consisting of Gram-positive, spherical cells in clusters. It occurs very commonly as a harmless commensal on human and animal skin and is known for producing thioalcohol compounds that contribute to body odour. Like many other coagulase-negative staphylococci, S. hominis may occasionally cause infection in patients whose immune systems are compromised, for example by chemotherapy or predisposing illness.
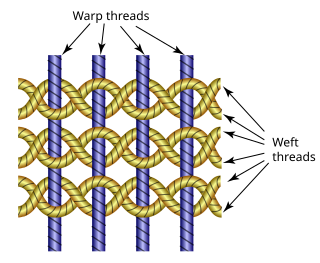
Gauze is a thin, translucent fabric with a loose open weave. In technical terms "gauze" is a weave structure in which the weft yarns are arranged in pairs and are crossed before and after each warp yarn keeping the weft firmly in place. This weave structure is used to add stability to fabric, which is important when using fine yarns loosely spaced. However, this weave structure can be used with any weight of yarn, and can be seen in some rustic textiles made from coarse hand-spun plant fiber yarns. Gauze is widely used for medical dressings.

The human botfly, Dermatobia hominis, is a species of botfly whose larvae parasitise humans. It is also known as the torsalo or American warble fly, though the warble fly is in the genus Hypoderma and not Dermatobia, and is a parasite on cattle and deer instead of humans.
The Nugent Score is a Gram stain scoring system for vaginal swabs to diagnose bacterial vaginosis. The Nugent score is calculated by assessing for the presence of large Gram-positive rods, small Gram-variable rods, and curved Gram-variable rods. A score of 7 to 10 is consistent with bacterial vaginosis without culture. The Nugent Score is now rarely used by physicians due to the time it takes to read the slides and requires the use of a trained microscopist. Bacterial vaginosis diagnosis is done by evaluating the pH, the presences of Lactobacillus spp. versus a mixed flora consisting of Gardnerella vaginalis, Bacteroides spp, Mobiluncus spp, and Mycoplasma hominis. The Amsel Criteria for bacterial vaginosis includes pH, evaluating the presence of clue cells, white discharge and an odor of amines after mixing with KOH.

Blastocystis is a genus of single-celled heterokont parasites belonging to a group of organisms that are known as the Stramenopiles that includes algae, diatoms, and water molds. Blastocystis consists of several species, living in the gastrointestinal tracts of species as diverse as humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, reptiles, amphibians, fish, and cockroaches. Blastocystis exhibits low host specificity, and many different species of Blastocystis can infect humans, and by current convention, any of these species would be identified as Blastocystis hominis.

Blastocystosis refers to a medical condition caused by infection with Blastocystis. Blastocystis is a protozoal, single-celled parasite that inhabits the gastrointestinal tracts of humans and other animals. Many different types of Blastocystis exist, and they can infect humans, farm animals, birds, rodents, amphibians, reptiles, fish, and even cockroaches. Blastocystosis has been found to be a possible risk factor for development of irritable bowel syndrome.

When the Gods Fall Asleep is a 1972 Brazilian film directed by José Mojica Marins. Marins is best known for the Zé do Caixão film series. The film is a sequel to Marins' 1971 film The End of Man, in which the character of Finis Hominis, an influential, messianic culture figure turns out to be an escaped mental patient. Rather than the horror themes which Marins was noted for, the film, like its predecessor, is low budget black humored social satire.

Cardiobacterium hominis is a Gram-negative bacillus (rod-shaped) bacterium commonly grouped with other bacteria into the HACEK group. It is one of several bacteria that is normally present in the mouth and upper part of the respiratory tract such as nose and throat. However, it may also rarely cause endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves.

Arcanobacterium is a genus of bacteria. They are gram-positive, non–acid fast, nonmotile, facultatively anaerobic, and non–endospore forming. They are widely distributed in nature in the microbiota of animals and are mostly innocuous. Some can cause disease in humans and other animals. As with various species of a microbiota, they usually are not pathogenic but can occasionally opportunistically capitalize on atypical access to tissues or weakened host defenses.
Roseburia hominis is a bacterium first isolated from human feces. It is anaerobic, Gram-negative or Gram-variable, slightly curved rod-shaped and motile. The cells range in size from 0.5-1.5 to 5.0 μm. A2-183(T) is the type strain.
The exact role of Mycoplasma hominis in regards to a number of conditions related to pregnant women and their (unborn) offspring is controversial. This is mainly because many healthy adults have genitourinary colonization with Mycoplasma, published studies on pathogenicity have important design limitations and the organisms are very difficult to detect. The likelihood of colonization with M. hominis appears directly linked to the number of lifetime sexual partners Neonatal colonization does occur, but only through normal vaginal delivery. Caesarean section appears protective against colonization and is much less common. Neonatal colonization is transient.
Chryseobacterium hominis is a Gram-negative bacteria from the genus of Chryseobacterium which has been isolated from blood from a patient in Belgium and from the fish Arothron hispidus.
Dietzia cinnamea is a Gram-positive and aerobic bacterium from the genus of Dietzia which has been isolated from a perianal swab from a patient in Germany.
Paenalcaligenes hominis is a bacterium from the genus Paenalcaligenes which has been isolated from human blood in Gothenburg in Sweden.
Tsukamurella hominis is a Gram-positive, non-spore-forming and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Tsukamurella which has been isolated from a conjunctival swab.
Candidatus Ornithobacterium hominis is a gram-negative bacterial species that colonises the human respiratory tract. Despite being related to the bird pathogen O. rhinotracheale, it is not a zoonosis. It has been detected in microbiome data from people around the world, including The Gambia, Madagascar and Central African Republic, Kenya, Mae La refugee camp in Thailand, rural Venezuela, Australia, and Fiji.
Ornithobacterium is a genus of Gram-negative, microaerophilic, rod-shaped bacteria from the family Weeksellaceae. It comprises two known species, O. hominis and O. rhinotracheale. Both species inhabit the respiratory tract: O. hominis is found in the human nasopharynx and O. rhinotracheale in the trachea of wild and domesticated birds
Gleimia coleocanis is a bacterium from the genus of Gleimia which has been isolated from the vagina of a dog.






