Customer relationship management (CRM) is a process in which a business or other organization administers its interactions with customers, typically using data analysis to study large amounts of information.
E-commerce is the activity of electronically buying or selling products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. E-commerce is the largest sector of the electronics industry and is in turn driven by the technological advances of the semiconductor industry.

In economics, a network effect is the phenomenon by which the value or utility a user derives from a good or service depends on the number of users of compatible products. Network effects are typically positive feedback systems, resulting in users deriving more and more value from a product as more users join the same network. The adoption of a product by an additional user can be broken into two effects: an increase in the value to all other users and also the enhancement of other non-users' motivation for using the product.

Marketing is the act of satisfying and retaining customers. It is one of the primary components of business management and commerce.
Personalized marketing, also known as one-to-one marketing or individual marketing, is a marketing strategy by which companies leverage data analysis and digital technology to deliver individualized messages and product offerings to current or prospective customers. Advancements in data collection methods, analytics, digital electronics, and digital economics, have enabled marketers to deploy more effective real-time and prolonged customer experience personalization tactics.
Marketing communications refers to the use of different marketing channels and tools in combination. Marketing communication channels focus on how businesses communicate a message to its desired market, or the market in general. It is also in charge of the internal communications of the organization. Marketing communication tools include advertising, personal selling, direct marketing, sponsorship, communication, public relations, social media, customer journey and promotion.

Customer service is the assistance and advice provided by a company through phone, online chat, and e-mail to those who buy or use its products or services. Each industry requires different levels of customer service, but towards the end, the idea of a well-performed service is that of increasing revenues. The perception of success of the customer service interactions is dependent on employees "who can adjust themselves to the personality of the customer". Customer service is often practiced in a way that reflects the strategies and values of a firm. Good quality customer service is usually measured through customer retention.

Online shopping is a form of electronic commerce which allows consumers to directly buy goods or services from a seller over the Internet using a web browser or a mobile app. Consumers find a product of interest by visiting the website of the retailer directly or by searching among alternative vendors using a shopping search engine, which displays the same product's availability and pricing at different e-retailers. As of 2020, customers can shop online using a range of different computers and devices, including desktop computers, laptops, tablet computers and smartphones.
In marketing, promotion refers to any type of marketing communication used to inform target audiences of the relative merits of a product, service, brand or issue, persuasively. It helps marketers to create a distinctive place in customers' mind, it can be either a cognitive or emotional route. The aim of promotion is to increase brand awareness, create interest, generate sales or create brand loyalty. It is one of the basic elements of the market mix, which includes the four Ps, i.e., product, price, place, and promotion.
The eCRM or electronic customer relationship management coined by Oscar Gomes encompasses all standard CRM functions with the use of the net environment i.e., intranet, extranet and internet. Electronic CRM concerns all forms of managing relationships with customers through the use of information technology (IT).
The digital economy is a portmanteau of digital computing and economy, and is an umbrella term that describes how traditional brick-and-mortar economic activities are being transformed by the Internet and World Wide Web technologies.

Digital marketing is the component of marketing that uses the Internet and online-based digital technologies such as desktop computers, mobile phones, and other digital media and platforms to promote products and services. Its development during the 1990s and 2000s changed the way brands and businesses use technology for marketing. As digital platforms became increasingly incorporated into marketing plans and everyday life, and as people increasingly used digital devices instead of visiting physical shops, digital marketing campaigns have become prevalent, employing combinations of search engine optimization (SEO), search engine marketing (SEM), content marketing, influencer marketing, content automation, campaign marketing, data-driven marketing, e-commerce marketing, social media marketing, social media optimization, e-mail direct marketing, display advertising, e-books, and optical disks and games have become commonplace. Digital marketing extends to non-Internet channels that provide digital media, such as television, mobile phones, callbacks, and on-hold mobile ringtones. The extension to non-Internet channels differentiates digital marketing from online marketing.
A touchpoint can be defined as any way consumers can interact with a business organization, whether person-to-person, through a website, an app or any form of communication. When consumers connect with these touchpoints they can consider their perceptions of the business and form an opinion.
Customer engagement is an interaction between an external consumer/customer and an organization through various online or offline channels. According to Hollebeek, Srivastava and Chen S-D logic-Definition of customer engagement is "a customer’s motivationally driven, volitional investment of operant resources, and operand resources into brand interactions," which applies to online and offline engagement.
A target market, also known as serviceable obtainable market (SOM), is a group of customers within a business's serviceable available market at which a business aims its marketing efforts and resources. A target market is a subset of the total market for a product or service.

Social media marketing is the use of social media platforms and websites to promote a product or service. Although the terms e-marketing and digital marketing are still dominant in academia, social media marketing is becoming more popular for both practitioners and researchers.
Customer to customer markets provide a way to allow customers to interact with each other. Traditional markets require business to customer relationships, in which a customer goes to the business in order to purchase a product or service. In customer to customer markets, the business facilitates an environment where customers can sell goods or services to each other. Other types of markets include business to business (B2B) and business to customer (B2C).
Online presence management is the process of creating and promoting traffic to a personal or professional brand online. This process combines web design, and development, blogging, search engine optimization, pay-per-click marketing, reputation management, directory listings, social media, link sharing, and other avenues to create a long-term positive presence for a person, organization, or product in search engines and on the web in general.
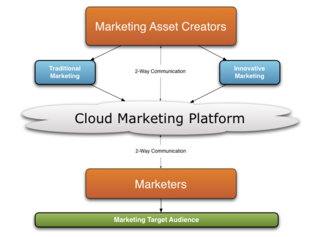
Cloud marketing is the process of an organization's efforts to market their goods and services online through integrated digital experiences, by which they are specialized for every end-user. It aims to use advertising methods to give tailor made adverts to customers based on their browsing history or interests via online applications through social media websites such as Facebook, Twitter and various online portals. Cloud marketing platforms could be supported by third party providers that maintain the platform.
Social media use by businesses includes a range of applications. Although social media accessed via desktop computers offer a variety of opportunities for companies in a wide range of business sectors, mobile social media, which users can access when they are "on the go" via tablet computers or smartphones, benefit companies because of the location- and time-sensitive awareness of their users. Mobile social media tools can be used for marketing research, communication, sales promotions/discounts, informal employee learning/organizational development, relationship development/loyalty programs, and e-commerce.






