Related Research Articles

In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.

Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that do not retain the crystal violet stain used in the gram-staining method of bacterial differentiation. They are characterized by their cell envelopes, which are composed of a thin peptidoglycan cell wall sandwiched between an inner cytoplasmic cell membrane and a bacterial outer membrane.

In cell biology, a vesicle is a structure within or outside a cell, consisting of liquid or cytoplasm enclosed by a lipid bilayer. Vesicles form naturally during the processes of secretion (exocytosis), uptake (endocytosis) and transport of materials within the plasma membrane. Alternatively, they may be prepared artificially, in which case they are called liposomes. If there is only one phospholipid bilayer, they are called unilamellar liposome vesicles; otherwise they are called multilamellar. The membrane enclosing the vesicle is also a lamellar phase, similar to that of the plasma membrane, and intracellular vesicles can fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell. Vesicles can also fuse with other organelles within the cell. A vesicle released from the cell is known as an extracellular vesicle.

Exocytosis is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules out of the cell by secreting them through an energy-dependent process. Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemical substances important to them are large polar molecules that cannot pass through the hydrophobic portion of the cell membrane by passive means. Exocytosis is the process by which a large amount of molecules are released; thus it is a form of bulk transport.

Membrane proteins are common proteins that are part of, or interact with, biological membranes. Membrane proteins fall into several broad categories depending on their location. Integral membrane proteins are a permanent part of a cell membrane and can either penetrate the membrane (transmembrane) or associate with one or the other side of a membrane. Peripheral membrane proteins are transiently associated with the cell membrane.

A transmembrane protein (TP) is a type of integral membrane protein that spans the entirety of the cell membrane. Many transmembrane proteins function as gateways to permit the transport of specific substances across the membrane. They frequently undergo significant conformational changes to move a substance through the membrane. They are usually highly hydrophobic and aggregate and precipitate in water. They require detergents or nonpolar solvents for extraction, although some of them (beta-barrels) can be also extracted using denaturing agents.
Secretion is the movement of material from one point to another, such as a secreted chemical substance from a cell or gland. In contrast, excretion, is the removal of certain substances or waste products from a cell or organism. The classical mechanism of cell secretion is via secretory portals at the cell plasma membrane called porosomes. Porosomes are permanent cup-shaped lipoprotein structure at the cell plasma membrane, where secretory vesicles transiently dock and fuse to release intra-vesicular contents from the cell.
Pore may refer to:

Porins are beta barrel proteins that cross a cellular membrane and act as a pore, through which molecules can diffuse. Unlike other membrane transport proteins, porins are large enough to allow passive diffusion, i.e., they act as channels that are specific to different types of molecules. They are present in the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria and some gram-positive mycobacteria, the outer membrane of mitochondria, and the outer chloroplast membrane.

The intermembrane space (IMS) is the space occurring between or involving two or more membranes. In cell biology, it is most commonly described as the region between the inner membrane and the outer membrane of a mitochondrion or a chloroplast. It also refers to the space between the inner and outer nuclear membranes of the nuclear envelope, but is often called the perinuclear space. The IMS of mitochondria plays a crucial role in coordinating a variety of cellular activities, such as regulation of respiration and metabolic functions. Unlike the IMS of the mitochondria, the IMS of the chloroplast does not seem to have any obvious function.

An eggshell is the outer covering of a hard-shelled egg and of some forms of eggs with soft outer coats.

The bacterial outer membrane is found in gram-negative bacteria. Its composition is distinct from that of the inner cytoplasmic cell membrane - among other things, the outer leaflet of the outer membrane of many gram-negative bacteria includes a complex lipopolysaccharide whose lipid portion acts as an endotoxin - and in some bacteria such as E. coli it is linked to the cell's peptidoglycan by Braun's lipoprotein.
The Transporter Classification Database is an International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB)-approved classification system for membrane transport proteins, including ion channels.
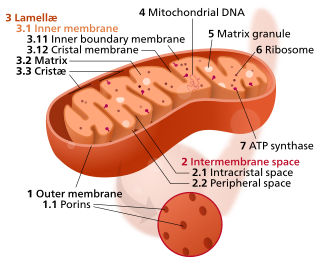
The inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) is the mitochondrial membrane which separates the mitochondrial matrix from the intermembrane space.
The vitelline membrane or vitelline envelope is a structure surrounding the outer surface of the plasma membrane of an ovum or, in some animals, the extracellular yolk and the oolemma. It is composed mostly of protein fibers, with protein receptors needed for sperm binding which, in turn, are bound to sperm plasma membrane receptors. The species-specificity between these receptors contributes to prevention of breeding between different species. It is called zona pellucida in mammals.
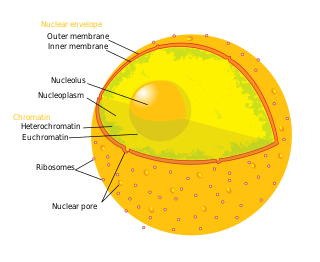
The nuclear envelope, also known as the nuclear membrane, is made up of two lipid bilayer membranes which in eukaryotic cells surrounds the nucleus, which encases the genetic material.

The translocase of the outer membrane (TOM) is a complex of proteins found in the outer mitochondrial membrane of the mitochondria. It allows movement of proteins through this barrier and into the intermembrane space of the mitochondrion. Most of the proteins needed for mitochondrial function are encoded by the nucleus of the cell. The outer membrane of the mitochondrion is impermeable to large molecules greater than 5000 Daltons. The TOM works in conjunction with the translocase of the inner membrane (TIM) to translocate proteins into the mitochondrion. Many of the proteins in the TOM complex, such as TOMM22, were first identified in Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
The outer mitochondrial membrane is made up of two essential proteins, Tom40 and Sam50.

The cuticle forms the major part of the integument of the Arthropoda. It includes most of the material of the exoskeleton of the insects, Crustacea, Arachnida, and Myriapoda.

The cell membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment which protects the cell from its environment. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer, including cholesterols that sit between phospholipids to maintain their fluidity at various temperatures. The membrane also contains membrane proteins, including integral proteins that go across the membrane serving as membrane transporters, and peripheral proteins that loosely attach to the outer (peripheral) side of the cell membrane, acting as enzymes shaping the cell. The cell membrane controls the movement of substances in and out of cells and organelles. In this way, it is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules. In addition, cell membranes are involved in a variety of cellular processes such as cell adhesion, ion conductivity and cell signalling and serve as the attachment surface for several extracellular structures, including the cell wall, the carbohydrate layer called the glycocalyx, and the intracellular network of protein fibers called the cytoskeleton. In the field of synthetic biology, cell membranes can be artificially reassembled.
References
- ↑ Kawaoka S, Katsuma S, Daimon T, Isono R, Omuro N, Mita K, Shimada T (February 2008). "Functional analysis of four Gloverin-like genes in the silkworm, Bombyx mori". Archives of Insect Biochemistry and Physiology. 67 (2): 87–96. doi:10.1002/arch.20223. PMID 18076111.