
Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains (glycans) covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycosylation. Secreted extracellular proteins are often glycosylated.
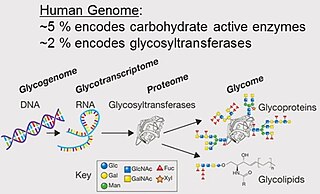
The glycome is the entire complement of sugars, whether free or present in more complex molecules, of an organism. An alternative definition is the entirety of carbohydrates in a cell. The glycome may in fact be one of the most complex entities in nature. "Glycomics, analogous to genomics and proteomics, is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology.

The Consortium for Functional Glycomics (CFG) is a large research initiative funded in 2001 by a glue grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences (NIGMS) to “define paradigms by which protein-carbohydrate interactions mediate cell communication”. To achieve this goal, the CFG studies the functions of:
Defined in the narrowest sense, glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, and biology of saccharides that are widely distributed in nature. Sugars or saccharides are essential components of all living things and aspects of the various roles they play in biology are researched in various medical, biochemical and biotechnological fields.

Fibrin is a fibrous, non-globular protein involved in the clotting of blood. It is formed by the action of the protease thrombin on fibrinogen which causes it to polymerize. The polymerized fibrin together with platelets forms a hemostatic plug or clot over a wound site.
Glycosylation is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule. In biology, glycosylation mainly refers in particular to the enzymatic process that attaches glycans to proteins, or other organic molecules. This enzymatic process produces one of the fundamental biopolymers found in cells. Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. It is an enzyme-directed site-specific process, as opposed to the non-enzymatic chemical reaction of glycation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the O-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five classes of glycans are produced:

Fucose is a hexose deoxy sugar with the chemical formula C6H12O5. It is found on N-linked glycans on the mammalian, insect and plant cell surface. Fucose is the fundamental sub-unit of the seaweed polysaccharide fucoidan. α(1→3) linked core fucose is a suspected carbohydrate antigen for IgE-mediated allergy.

KEGG is a collection of databases dealing with genomes, biological pathways, diseases, drugs, and chemical substances. KEGG is utilized for bioinformatics research and education, including data analysis in genomics, metagenomics, metabolomics and other omics studies, modeling and simulation in systems biology, and translational research in drug development.

Chi-Huey Wong is a Taiwanese-born American biochemist. He is a professor of chemistry and chemical biology at The Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla, California, and National Sun Yat-sen University in Taiwan. His expertise is bioorganic and synthetic chemistry, especially in carbohydrate chemistry and chemical biology.

Ovotransferrin (conalbumin) is a glycoprotein of egg white albumen. Egg white albumen is composed of multiple proteins, of which ovotransferrin is the most heat reliable. It has a molecular weight of 76,000 daltons and contains about 700 amino acids. Ovotransferrin makes up approximately 13% of egg albumen. As a member of the transferrin and metalloproteinase family, ovotransferrin has been found to produce heat shock proteins. When these heat shock proteins are induced in the skin, they provide protection against cold stress and other environmental stresses.

Viral neuraminidase is a type of neuraminidase found on the surface of influenza viruses that enables the virus to be released from the host cell. Neuraminidases are enzymes that cleave sialic acid groups from glycoproteins and are required for influenza virus replication.
Core 1 synthase, glycoprotein-N-acetylgalactosamine 3-beta-galactosyltransferase, 1, also known as C1GALT1, is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the C1GALT1 gene.
Glycopeptides are peptides that contain carbohydrate moieties (glycans) covalently attached to the side chains of the amino acid residues that constitute the peptide.
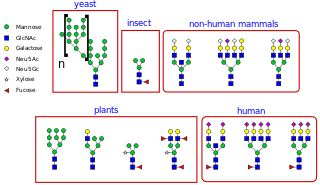
N-linked glycosylation, is the attachment of an oligosaccharide, a carbohydrate consisting of several sugar molecules, sometimes also referred to as glycan, to a nitrogen atom, in a process called N-glycosylation, studied in biochemistry. This type of linkage is important for both the structure and function of some eukaryotic proteins. The N-linked glycosylation process occurs in eukaryotes and widely in archaea, but very rarely in bacteria. The nature of N-linked glycans attached to a glycoprotein is determined by the protein and the cell in which it is expressed. It also varies across species. Different species synthesize different types of N-linked glycan.
EuroCarbDB was an EU-funded initiative for the creation of software and standards for the systematic collection of carbohydrate structures and their experimental data, which was discontinued in 2010 due to lack of funding. The project included a database of known carbohydrate structures and experimental data, specifically mass spectrometry, HPLC and NMR data, accessed via a web interface that provides for browsing, searching and contribution of structures and data to the database. The project also produces a number of associated bioinformatics tools for carbohydrate researchers:
Human milk oligosaccharides are sugar molecules, that are part of the oligosaccharides group and which can be found in high concentrations exclusively in human breast milk.
UniCarb-DB is a structural and mass spectrometric database used in glycomics. UniCarb-DB provides over 1000 LC-MS/MS spectra for N- and O-linked glycans released from glycoproteins that were manually annotated. Each entry contains reference to published work, information about structure, GlyToucan Accession Number, MS/MS fragmentation with complete peak lists, biological contexts and experimental metadata. The database was created by a collaboration between University of Gothenburg and Macquarie University and since November 2016 is hosted by Swiss Institute for Bioinformatics. The database is the first to implement the Minimum Information standard MIRAGE for submission of glycomic MS/MS data into the database.

Carbohydrate Structure Database (CSDB) is a free database and service platform in glycoinformatics, launched in 2005 by a group of Russian scientists from N.D. Zelinsky Institute of Organic Chemistry, Russian Academy of Sciences. CSDB stores published structural, taxonomical, bibliographic and NMR-spectroscopic data on natural carbohydrates and carbohydrate-related molecules.











