Related Research Articles

Microsoft Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Redmond, Washington. It is also incorporated in Washington. Microsoft's best-known software products are the Windows line of operating systems, the Microsoft 365 suite of productivity applications, and the Edge web browser. Its flagship hardware products are the Xbox video game consoles and the Microsoft Surface lineup of touchscreen personal computers. Microsoft ranked No. 14 in the 2022 Fortune 500 rankings of the largest United States corporations by total revenue; and it was the world's largest software maker by revenue in 2022 according to Forbes Global 2000. It is considered one of the Big Five American information technology companies, alongside Alphabet, Amazon, Apple, and Meta.

OS/2 is a series of computer operating systems, initially created by Microsoft and IBM under the leadership of IBM software designer Ed Iacobucci. As a result of a feud between the two companies over how to position OS/2 relative to Microsoft's new Windows 3.1 operating environment, the two companies severed the relationship in 1992 and OS/2 development fell to IBM exclusively. The name stands for "Operating System/2", because it was introduced as part of the same generation change release as IBM's "Personal System/2 (PS/2)" line of second-generation personal computers. The first version of OS/2 was released in December 1987 and newer versions were released until December 2001.
Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) is an implementation of Microsoft's event-driven programming language Visual Basic 6.0 built into most desktop Microsoft Office applications. Although based on pre-.NET Visual Basic, which is no longer supported or updated by Microsoft, the VBA implementation in Office continues to be updated to support new Office features. VBA is used for professional and end-user development due to its perceived ease-of-use, Office's vast installed userbase, and extensive legacy in business.
HPFS is a file system created specifically for the OS/2 operating system to improve upon the limitations of the FAT file system. It was written by Gordon Letwin and others at Microsoft and added to OS/2 version 1.2, at that time still a joint undertaking of Microsoft and IBM, and released in 1988.
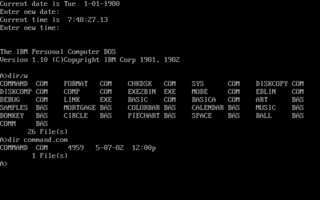
IBM PC DOS, an acronym for IBM Personal Computer Disk Operating System, is a discontinued disk operating system for the IBM Personal Computer, its successors, and IBM PC compatibles. It was manufactured and sold by IBM from the early 1980s into the 2000s. Developed by Microsoft, it was also sold by that company as MS-DOS. Both operating systems were identical or almost identical until 1993, when IBM began selling PC DOS 6.1 with new features. The collective shorthand for PC DOS and MS-DOS was DOS, which is also the generic term for disk operating system, and is shared with dozens of disk operating systems called DOS.
The taskbar is a graphical user interface element that has been part of Microsoft Windows since Windows 95, displaying and facilitating switching between running programs. The taskbar and the associated Start Menu were created and named in 1993 by Daniel Oran, a program manager at Microsoft who had previously collaborated on great ape language research with the behavioral psychologist B.F. Skinner at Harvard.

TopView is the first object-oriented, multitasking, and windowing, personal computer operating environment for PC DOS developed by IBM, announced in August 1984 and shipped in March 1985. TopView provided a text-mode operating environment that allowed users to run more than one application at the same time on a PC. IBM demonstrated an early version of the product to key customers before making it generally available, around the time they shipped their new PC AT computer.
Mark "Zibo" Joseph Zbikowski is a former Microsoft Architect and an early computer hacker. He started working at the company only a few years after its inception, leading efforts in MS-DOS, OS/2, Cairo and Windows NT. In 2006, he was honored for 25 years of service with the company, the third employee to reach this milestone, after Bill Gates and Steve Ballmer. He retired the same year from Microsoft.
Active Scripting is the technology used in Windows to implement component-based scripting support. It is based on OLE Automation and allows installation of additional scripting engines in the form of COM modules.

Charles Petzold is an American programmer and technical author on Microsoft Windows applications. He is also a Microsoft Most Valuable Professional and was named one of Microsoft's seven Windows Pioneers.
Marc B. McDonald is an American who was Microsoft's first salaried employee.
Microsoft is a multinational computer technology corporation. Microsoft was founded on April 4, 1975, by Bill Gates and Paul Allen in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Its current best-selling products are the Microsoft Windows operating system; Microsoft Office, a suite of productivity software; Xbox, a line of entertainment of games, music, and video; Bing, a line of search engines; and Microsoft Azure, a cloud services platform.

Everaldo Coelho is a Brazilian graphic designer and illustrator. He specializes in iconography, themes and user interface design. Everaldo's works include general illustrations, comics, children's books, corporate design and many other areas. He is known in Linux circles for his "Crystal" icon theme.
HDOS is an early microcomputer operating system, originally written for the Heathkit H8 computer system and later also available for the Heathkit H89 and Zenith Z-89 computers. The author was Heath Company employee Gordon Letwin, who later was an early employee of Microsoft and lead architect of OS/2.
In computing, sys is a command used in many operating system command-line shells and also in Microsoft BASIC.
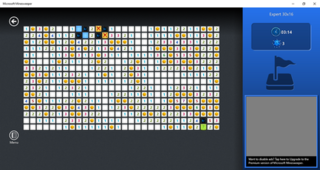
Microsoft Minesweeper is a minesweeper-type video game created by Curt Johnson, originally for IBM's OS/2, that was ported to Microsoft Windows by Robert Donner, both Microsoft employees at the time. First officially released as part of the Microsoft Entertainment Pack 1 in 1990, it was first included in the standard install of Windows 3.1 in 1992, replacing Reversi from Windows 3.0. Microsoft Minesweeper was included without major changes in all subsequent Windows releases until Windows Vista, at which time an updated version by Oberon Media replaced it. In Windows 8 and later the game is not included with a fresh Windows install, but Microsoft Studios has published an updated version of it, developed by Arkadium, on Microsoft Store.
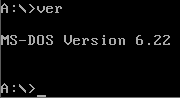
In computing, ver is a command in various command-line interpreters (shells) such as COMMAND.COM, cmd.exe and 4DOS/4NT. It prints the name and version of the operating system, the command shell, or in some implementations the version of other commands. It is roughly equivalent to the Unix command uname.

Heathkit's H8 is an Intel 8080A-based microcomputer sold in kit form starting in 1977. The H8 is similar to the S-100 bus computers of the era, and like those machines is often used with the CP/M operating system on floppy disk.

The .NET platform is a free and open-source, managed computer software framework for Windows, Linux, and macOS operating systems. The project is mainly developed by Microsoft employees by way of the .NET Foundation and is released under an MIT License.
Benton Harbor BASIC and Extended Benton Harbor BASIC were two versions of the BASIC programming language written by Heathkit for their H8 microcomputers. The BASICs were patterned on Dartmouth BASIC, and thus differ in some respects from the many Microsoft BASIC clones of the late-1970s era. The two differ from each other in that the former was able to run in machines with only 8 kB of main memory and only supported string constants, while Extended required 12 kB and added string variables and additional features. It is named after the town where Heathkit was located.
References
- ↑ "You searched: Gordon Letwin 19520702". Public Background Checks. Retrieved April 10, 2011.
- 1 2 3 "25 Years Ago At Microsoft". Time . May 1, 2000. Retrieved September 16, 2006.
- ↑ Shoemaker, D C (June 1981). "Treasures on Disk". Letters. Byte . p. 14.
- ↑ Zachary, G. Pascal (1994). Showstopper! The Breakneck Race to Create Windows NT and the Next Generation at Microsoft . Warner Books. ISBN 0-02-935671-7.
- ↑ "A look at Microsoft's first 11 employees". Boston Herald. Associated Press. April 12, 2000. Archived from the original on April 24, 2001. Retrieved February 21, 2007.