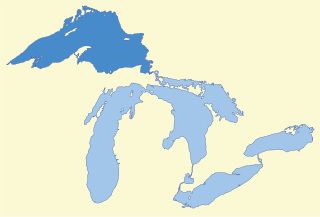
Lake Superior, the largest of the Great Lakes of North America, is also the world's largest freshwater lake by surface area, and the third largest freshwater lake by volume. The lake is shared by the Canadian province of Ontario to the north, the U.S. state of Minnesota to the west, and Wisconsin and the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to the south. The farthest north and west of the Great Lakes chain, Superior has the highest elevation of all five great lakes and drains into the St. Mary's River.

The SSM-N-8A Regulus or the Regulus I was a United States Navy-developed ship-and-submarine-launched, nuclear-capable turbojet-powered second generation cruise missile, deployed from 1955 to 1964. Its development was an outgrowth of U.S. Navy tests conducted with the German V-1 missile at Naval Air Station Point Mugu in California. Its barrel-shaped fuselage resembled that of numerous fighter aircraft designs of the era, but without a cockpit. Test articles of the Regulus were equipped with landing gear and could take off and land like an airplane. When the missiles were deployed they were launched from a rail launcher, and equipped with a pair of Aerojet JATO bottles on the aft end of the fuselage.

USS John A. Moore (FFG-19), eleventh ship of the Oliver Hazard Perry class of guided-missile frigates, was named for Commander John Anderson Moore (1910–1944). Ordered from Todd Pacific Shipyards, Los Angeles Division, San Pedro, California on 28 February 1977 as part of the FY77 program, John A. Moore was laid down on 19 September 1978, launched on 20 October 1979, and commissioned on 14 November 1981.

USS Grayback (SS/SSG/APSS/LPSS-574), the lead ship of her class of submarine, was the second ship of the United States Navy to be named for the grayback.

USS Growler (SSG-577) was an early attempt by the U.S. Navy to field a cruise missile submarine that would provide a nuclear deterrent using its second series of cruise missiles. Built to deliver the Regulus I cruise missile, Growler was the second and final submarine of the Grayback class, fourth ship of the United States Navy to be named after the growler. Since Regulus I and Regulus II programs had problems, Growler and Grayback were the only two submarines built in this class as instead, the U.S. Navy veered its nuclear deterrence efforts into submarine launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs)—the Polaris missile program.

USS Grampus (SS-207), a Tambor-class submarine, was the sixth ship of the United States Navy to be named for a member of the dolphin family (Delphinidae): Grampus griseus, also known as Risso's dolphin.

USS Grayback (SS-208), a Tambor-class submarine, was the first ship of the United States Navy to be named for the lake herring.
USS Grayback may refer to:

Oregon Route 46 is an Oregon state highway that runs between the city of Cave Junction and the Oregon Caves National Monument and Preserve. OR 46 traverses the Oregon Caves Highway No. 38 of the Oregon state highway system.

The Air Force Historical Research Agency is the repository for United States Air Force historical documents. The Agency's collection, begun during World War II in Washington, D.C. and moved in 1949 to Maxwell Air Force Base, the site of Air University, to provide research facilities for professional military education students, the faculty, visiting scholars, and the general public.

Battle Realms: Winter of the Wolf is the expansion pack of the real-time strategy video game Battle Realms, developed by Liquid Entertainment and Crave Entertainment and published by Ubisoft. The game was announced on July 7, 2002 and released on November 5, 2002.

The Grayback-class submarine was a class of two guided missile carrying submarines of the United States Navy. They carried the Regulus I and Regulus II nuclear cruise missiles, deployed 1957–64, that were phased out by Polaris Submarine Launched Ballistic Missiles (SLBMs). They and USS Halibut were the sole submarines designed specifically to carry Regulus missiles, and the only submarines capable of carrying Regulus II. However, USS Tunny and USS Barbero were modified earlier to carry two Regulus I missiles per boat.

The California Inland Empire Council (CIEC) of the Boy Scouts of America was formed in 1973 through the merger of the Arrowhead Area (#048) and Riverside Area Councils (#045). In 1974 Grayback Council (#024) also merged into the new council. In 2006, the council acquired the San Bernardino County portions of Old Baldy Council (#043). The council territory includes all of Riverside and San Bernardino Counties.
Operation Thunderhead was a highly classified combat mission conducted by U.S. Navy SEAL Team One and Underwater Demolition Team 11 (UDT-11) in 1972. The mission was conducted off the coast of North Vietnam during the Vietnam War to rescue two U.S. airmen said to be escaping from a prisoner of war prison in Hanoi. The prisoners, including Air Force Colonel John A. Dramesi were planning to steal a boat and travel down the Red River to the Gulf of Tonkin.
John Anderson Moore was a United States Navy submarine commander who was killed in action during World War II. He had been awarded three Navy Crosses and a Purple Heart Medal before his death. The U.S. Navy frigate USS John A. Moore (FFG-19) is named in his honor.

Tachopteryx thoreyi, commonly known as the gray petaltail and Thorey's grayback, is a species of dragonfly. It is native to the East Coast of the United States as far north as New York, as far south as Florida, and as far west as Texas. This species is the only member of the monotypic genus Tachopteryx.
There have been a number of 21 inch torpedoes in service with the United States. These have been used on ships and submarines of the US Navy. American "21 inch" torpedoes are actually 21 inch (533 mm) in diameter.

The Regulus missile submarines were a group of submarines operated by the United States Navy capable of carrying the Regulus cruise missile. Between 1959 and 1964, a total of five boats were used to undertake the first submarine-based nuclear deterrent patrols by the United States. Regulus submarines were used for this task until 1964, when sufficient ballistic missile submarines carrying the Polaris ballistic missile became available.

















