
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor that deposits onto a freezing surface. Frost forms when the air contains more water vapor than it can normally hold at a specific temperature. The process is similar to the formation of dew, except it occurs below the freezing point of water typically without crossing through a liquid state.

Ice is water that is frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 °C, 32 °F, or 273.15 K. It occurs naturally on Earth, on other planets, in Oort cloud objects, and as interstellar ice. As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral. Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque bluish-white color.

Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus and is heavily influenced by nearby bodies of water, topography, and wind conditions. In turn, fog affects many human activities, such as shipping, travel, and warfare.

Sea ice arises as seawater freezes. Because ice is less dense than water, it floats on the ocean's surface. Sea ice covers about 7% of the Earth's surface and about 12% of the world's oceans. Much of the world's sea ice is enclosed within the polar ice packs in the Earth's polar regions: the Arctic ice pack of the Arctic Ocean and the Antarctic ice pack of the Southern Ocean. Polar packs undergo a significant yearly cycling in surface extent, a natural process upon which depends the Arctic ecology, including the ocean's ecosystems. Due to the action of winds, currents and temperature fluctuations, sea ice is very dynamic, leading to a wide variety of ice types and features. Sea ice may be contrasted with icebergs, which are chunks of ice shelves or glaciers that calve into the ocean. Depending on location, sea ice expanses may also incorporate icebergs.

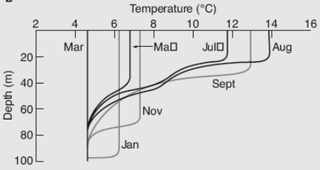
A thermocline is a distinct layer based on temperature within a large body of fluid with a high gradient of distinct temperature differences associated with depth. In the ocean, the thermocline divides the upper mixed layer from the calm deep water below.

The surface layer is the layer of a turbulent fluid most affected by interaction with a solid surface or the surface separating a gas and a liquid where the characteristics of the turbulence depend on distance from the interface. Surface layers are characterized by large normal gradients of tangential velocity and large concentration gradients of any substances transported to or from the interface.

Pancake ice is a form of sea ice that consists of round pieces of ice with diameters ranging from 30 centimetres to 3 metres and thicknesses up to 10 centimetres, depending on the local conditions. It forms as a result of wave action on slush or ice rind.

A polynya is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as a geographical term for an area of unfrozen seawater within otherwise contiguous pack ice or fast ice. It is a loanword from the Russian полынья, which refers to a natural ice hole and was adopted in the 19th century by polar explorers to describe navigable portions of the sea.

Frazil ice is a collection of loose, randomly oriented ice crystals a millimeter and sub-millimeter in size, with various shapes, e.g., elliptical disks, dendrites, needles and of an irregular nature. Frazil ice forms during the winter in open-water reaches of rivers as well as in lakes and reservoirs, where and when the water is in a turbulent state, which is, in turn, induced by the action of waves and currents. Turbulence causes the water column to become supercooled, as the heat exchange between the air and the water is such that the water temperature drops below its freezing point. The vertical mixing associated with that turbulence provides enough energy to overcome the crystals' buoyancy, thus keeping them from floating at the surface. Frazil ice also forms in oceans, where windy conditions, wave regimes and cold air also favor the establishment of a supercooled layer. Frazil ice can be found on the downwind side of leads and in polynyas. In these environments, that ice can eventually accumulate at the water surface into what is referred to as grease ice.
In oceanography, a halocline is a cline, a subtype of chemocline caused by a strong, vertical salinity gradient within a body of water. Because salinity affects the density of seawater, it can play a role in its vertical stratification. Increasing salinity by one kg/m3 results in an increase of seawater density of around 0.7 kg/m3.

A pycnocline is the cline or layer where the density gradient is greatest within a body of water. An ocean current is generated by the forces such as breaking waves, temperature and salinity differences, wind, Coriolis effect, and tides caused by the gravitational pull of celestial bodies. In addition, the physical properties in a pycnocline driven by density gradients also affect the flows and vertical profiles in the ocean. These changes can be connected to the transport of heat, salt, and nutrients through the ocean, and the pycnocline diffusion controls upwelling.

Anchor ice is defined by the World Meteorological Organization as "submerged ice attached or anchored to the bottom, irrespective of the nature of its formation". It may also be called bottom-fast ice. Anchor ice is most commonly observed in fast-flowing rivers during periods of extreme cold, at the mouths of rivers flowing into very cold seawater, in the shallow sub or intertidal during or after storms when the air temperature is below the freezing point of the water, and the subtidal in the Antarctic along ice shelves or near floating glacier tongues, and in shallow lakes.
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers.
Bottom water is the lowermost water mass in a water body, by its bottom, with distinct characteristics, in terms of physics, chemistry, and ecology.

A lead is a large fracture within an expanse of sea ice, defining a linear area of open water that can be used for navigation purposes. Leads vary in width from meters to hundreds of meters. As is the case for polynyas, leads allow the direct interaction between the atmosphere and the ocean, and are important for Arctic sea ice ecology. Additionally it has been lately found that ice leads contribute significantly to the amount of mercury deposited onto surface and leaked into the ocean. If the air is cold enough, the water within a lead quickly refreezes, such that in many cases, leads are partly or entirely covered by a thin layer of new ice.

Rotten ice is a loose term for ice that is melting or structurally disintegrating due to being honeycombed by liquid water, air, or contaminants trapped between the initial growth of ice crystals. It may appear transparent or splotchy grey, and it is generally found after spring or summer thaws, presenting a danger to those traveling or spending time in outdoor recreation. The increase of rotten ice vs. solid ice in the Arctic affects ocean-atmosphere heat transfer and year-to-year ice formation, as well as the lives of the Inuit, sea mammals such as walrus and polar bear, and the microorganisms that live inside the ice.

Frost flowers are ice crystals commonly found growing on young sea ice and thin lake ice in cold, calm conditions. The ice crystals are similar to hoar frost, and are commonly seen to grow in patches around 3–4 cm in diameter. Frost flowers growing on sea ice have extremely high salinities and concentrations of other sea water chemicals and, because of their high surface area, are efficient releasers of these chemicals into the atmosphere.
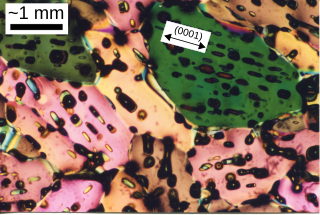
Sea ice is a complex composite composed primarily of pure ice in various states of crystallization, but including air bubbles and pockets of brine. Understanding its growth processes is important for climate modellers and remote sensing specialists, since the composition and microstructural properties of the ice affect how it reflects or absorbs sunlight.
Brine rejection is a process that occurs when salty water freezes. The salts do not fit in the crystal structure of water ice, so the salt is expelled.

This glossary of meteorology is a list of terms and concepts relevant to meteorology and atmospheric science, their sub-disciplines, and related fields.

















