Related Research Articles

Radiation therapy or radiotherapy, often abbreviated RT, RTx, or XRT, is a therapy using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer treatment to control or kill malignant cells and normally delivered by a linear accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor. Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist.

Skin cancers are cancers that arise from the skin. They are due to the development of abnormal cells that have the ability to invade or spread to other parts of the body. There are three main types of skin cancers: basal-cell skin cancer (BCC), squamous-cell skin cancer (SCC) and melanoma. The first two, along with a number of less common skin cancers, are known as nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC). Basal-cell cancer grows slowly and can damage the tissue around it but is unlikely to spread to distant areas or result in death. It often appears as a painless raised area of skin that may be shiny with small blood vessels running over it or may present as a raised area with an ulcer. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but may also form an ulcer. Melanomas are the most aggressive. Signs include a mole that has changed in size, shape, color, has irregular edges, has more than one color, is itchy or bleeds.

Psoriasis is a long-lasting, noncontagious autoimmune disease characterized by raised areas of abnormal skin. These areas are red, or purple on some people with darker skin, dry, itchy, and scaly. Psoriasis varies in severity from small, localized patches to complete body coverage. Injury to the skin can trigger psoriatic skin changes at that spot, which is known as the Koebner phenomenon.
Superficial X-rays are low-energy X-rays that do not penetrate very far before they are absorbed. They are produced by X-ray tubes operating at voltages in the 10–100 kV range, and therefore have peak energies in the 10–100 keV range. Precise naming and definitions of energy ranges may vary, and X-rays at the lower end of this range may also be known as Grenz rays. They are useful in radiation therapy for the treatment of various benign or malignant skin problems, including skin cancer and severe eczema. They have a useful depth of up to 5 mm. In some locations, orthovoltage treatment is being replaced by electron therapy or brachytherapy.

Keratinocytes are the primary type of cell found in the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. In humans, they constitute 90% of epidermal skin cells. Basal cells in the basal layer of the skin are sometimes referred to as basal keratinocytes. Keratinocytes form a barrier against environmental damage by heat, UV radiation, water loss, pathogenic bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses. A number of structural proteins, enzymes, lipids, and antimicrobial peptides contribute to maintain the important barrier function of the skin. Keratinocytes differentiate from epidermal stem cells in the lower part of the epidermis and migrate towards the surface, finally becoming corneocytes and eventually be shed off, which happens every 40-56 days in humans.
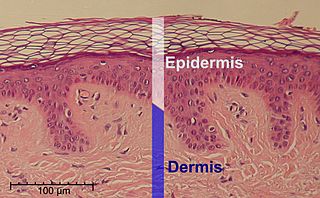
The epidermis is the outermost of the three layers that comprise the skin, the inner layers being the dermis and hypodermis. The epidermis layer provides a barrier to infection from environmental pathogens and regulates the amount of water released from the body into the atmosphere through transepidermal water loss.

Squamous-cell skin cancer, also known as cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma (cSCC), is one of the main types of skin cancer along with basal cell cancer and melanoma. It usually presents as a hard lump with a scaly top but can also form an ulcer. Onset is often over months. Squamous-cell skin cancer is more likely to spread to distant areas than basal cell cancer. When confined to the outermost layer of the skin, a precancerous or in situ form of cSCC is known as Bowen's disease.
Itch is a sensation that causes the desire or reflex to scratch. Itch has resisted many attempts to be classified as any one type of sensory experience. Itch has many similarities to pain, and while both are unpleasant sensory experiences, their behavioral response patterns are different. Pain creates a withdrawal reflex, whereas itch leads to a scratch reflex.

A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, hair, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment.

Pemphigus is a rare group of blistering autoimmune diseases that affect the skin and mucous membranes. The name is derived from the Greek root pemphix, meaning "pustule".

Actinic keratosis (AK), sometimes called solar keratosis or senile keratosis, is a pre-cancerous area of thick, scaly, or crusty skin. Actinic keratosis is a disorder of epidermal keratinocytes that is induced by ultraviolet (UV) light exposure. These growths are more common in fair-skinned people and those who are frequently in the sun. They are believed to form when skin gets damaged by UV radiation from the sun or indoor tanning beds, usually over the course of decades. Given their pre-cancerous nature, if left untreated, they may turn into a type of skin cancer called squamous cell carcinoma. Untreated lesions have up to a 20% risk of progression to squamous cell carcinoma, so treatment by a dermatologist is recommended.

Mycosis fungoides, also known as Alibert-Bazin syndrome or granuloma fungoides, is the most common form of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. It generally affects the skin, but may progress internally over time. Symptoms include rash, tumors, skin lesions, and itchy skin.
Aquagenic pruritus is a skin condition characterized by the development of severe, intense, prickling-like epidermal itching without observable skin lesions and evoked by contact with water.
Lentigo maligna is where melanocyte cells have become malignant and grow continuously along the stratum basale of the skin, but have not invaded below the epidermis. Lentigo maligna is not the same as lentigo maligna melanoma, as detailed below. It typically progresses very slowly and can remain in a non-invasive form for years.
Hailey–Hailey disease, or familial benign chronic pemphigus or familial benign pemphigus, was originally described by the Hailey brothers in 1939. It is a genetic disorder that causes blisters to form on the skin.

Extramammary Paget’s Disease (EMPD), is a rare and slow-growing malignancy which occurs within the epithelium and accounts for 6.5% of all Paget’s disease. The clinical presentation of this disease is similar to the characteristics of mammary Paget’s disease (MPD). However, unlike MPD, which occurs in large lactiferous ducts and then extends into the epidermis, EMPD originates in glandular regions rich in apocrine secretions outside the mammary glands. EMPD incidence is increasing by 3.2% every year, affecting hormonally-targeted tissues such as the vulva and scrotum. In women, 81.3% of EMPD cases are related to the vulva, while for men, 43.2% of the manifestations present at the scrotum.

The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to most of the other mammals' skin, and it is very similar to pig skin. Though nearly all human skin is covered with hair follicles, it can appear hairless. There are two general types of skin, hairy and glabrous skin (hairless). The adjective cutaneous literally means "of the skin".

Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout.
Corneocytes are terminally differentiated keratinocytes and compose most of the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the epidermis. They are regularly replaced through desquamation and renewal from lower epidermal layers and are essential for its function as a skin barrier.
The history of radiation therapy or radiotherapy can be traced back to experiments made soon after the discovery of X-rays (1895), when it was shown that exposure to radiation produced cutaneous burns. Influenced by electrotherapy and escharotics — the medical application of caustic substances — doctors began using radiation to treat growths and lesions produced by diseases such as lupus, basal cell carcinoma, and epithelioma. Radiation was generally believed to have bactericidal properties, so when radium was discovered, in addition to treatments similar to those used with x-rays, it was also used as an additive to medical treatments for diseases such as tuberculosis where there were resistant bacilli.
References
- 1 2 Lewis H: Grenz ray therapy: Regimens & Results.Chapter 15 in Physical Modalities in Dermatologic Therapy. Goldschmidt H (ed.) 1978 Springer-Verlag
- 1 2 Hollander MB : Grenz rays. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 21,15–26 July 1953.
- ↑ Olivo MP :Grenz ray treatment of Benign Skin Diseases Chapter 5 Radiation treatment and Radiation Reactions in Dermatology Panizzon R & Cooper J (ed.) 2004 Springer-Verlag Berlin.
- ↑ Lindelof B, Linden S, Ros A-M Effect of Grenz rays on Langerhans cells in human epidermis.Acta Dermatol.Venereol (Stockh)64:436-8 1984
- ↑ Beitner H, Nakatani T & Lindelof B An ultrastructural study of human epidermal Langerhans cells irradiated with Grenz rays and ultraviolet A Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 1990 : 7 : 266-8
- ↑ Burge SM, Graham-Brown RAC: "Hailey-Hailey Disease" in Treatment of Skin Disease: Comprehensive Therapeutic Strategies, 3rd Ed., edited by MG. Lebwohl, WR. Heymann, J. Berth-Jones, I. Coulson (Saunders Elsevier, 2010), pp. 287-288.