
A coenocyte is a multinucleate cell which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without their accompanying cytokinesis, in contrast to a syncytium, which results from cellular aggregation followed by dissolution of the cell membranes inside the mass. The word syncytium in animal embryology is used to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm of invertebrates. A coenocytic colony is referred to as a coenobium, and most coenobia are composed of a distinct number of cells, often as a multiple of two.
Struvea is a genus of green macroalgae in the family Boodleaceae.

Griffithsin is a protein isolated from the red algae Griffithsia. It has a 121-amino acid sequence which exhibits a Jacalin-like lectin fold. Several structures of this protein have been solved by X-ray crystallography and deposited in the PDB. It has been shown in vitro to be a highly potent HIV entry inhibitor. It is currently being investigated as a potential microbicide for use in the prevention of the transmission of HIV.

Calcinus elegans, also known as the blue line hermit crab, is a small, tropical hermit crab.

Naso elegans, the elegant unicornfish, the blonde naso tang, Indian orange-spine unicorn, lipstick surgeonfish, lipstick tang, orangespine unicornfish or smoothheaded unicornfish, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Acanthuridae, the surgeonfishes, unicornfishes and tangs. This species is found in the Indian and western Pacific Oceans.

Chaetophora elegans is the type species in the algae genus Chaetophora.

Gibbonsia elegans, the spotted kelpfish, is a species of clinid native to subtropical waters of the Pacific Ocean from central California, U.S. to southern Baja California, Mexico. It prefers subtidal rocky habitats with seaweed down to a depth of about 56 metres (184 ft). This species can reach a maximum length of 16 centimetres (6.3 in) TL. This species feeds on benthic crustaceans, gastropods, and polychaete worms. The genus Gibbonsia is named after William P. Gibbons who was a naturalist in the California Academy of Science. It is found in three different colors depending on their habitat. Males and females do not show sexual dimorphism.

Pocillopora is a genus of stony corals in the family Pocilloporidae occurring in the Pacific and Indian Oceans. They are commonly called cauliflower corals and brush corals.
Scytonema varium is a cultured cyanobacterium of the genus Scytonema. It is one of many anti viral protein producing algae. In a similar manner to Cyanovirin-N from Nostoc Ellipsosporum and griffithsin from the red algae Griffithsia, Scytonema varium secretes the broad-spectrum antiviral protein scytovirin which can inactivate both the HIV virus, and Ebola virus, offering hope of treatment for many diseases with viral etiology (cause). It is currently being investigated as a topical microbicide for HIV prophylaxis.

Draconichthys elegans a selenosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Frasnian Kellwasserkalk facies of the Anti-Atlas Mountains of what is now Morocco. During the Late Devonian, the region would have been a shallow, algae-dimmed sea.
Chondracanthus elegans is a red algae species in the genus Chondracanthus. The name elegans is Latin for 'elegant.'

Claudea is a marine red alga genus.
Cyanonephron elegans is a freshwater species of cyanobacteria in the family Synechococcaceae. It is described in the Netherlands, Siberia, Russia and Queensland, Australia.
Chromulina elegans is a species of golden algae in the family Chromulinaceae. It is found in freshwater, in Europe, South America and Asia.
Corythodinium elegans is a species of dinoflagellates in the family Oxytoxaceae. It is found Worldwide. The type locality is the Mediterranean. It is also found in Australian and New Zealand waters.
Spirogyra elegans is a species of green algae in the family Zygnemataceae.
Cruoriella elegans is a species of red algae in the family Peyssonneliaceae. It is found in the southern islands of Japan.
Clonophycus is a genus of fossil microalgae. The type species, C. elegans, was found in the Barney Creek Formation, of the Middle Proterozoic of Northern Australia. The authors are uncertain if the microalgae are prokaryotic cyanobacteria or eukaryotic green or red algae.
Pythium porphyrae, is a parasitic species of oomycete in the family Pythiaceae. It is the cause of red rot disease or red wasting disease, also called akagusare (赤ぐされ) in Japanese. The specific epithet porphyrae (πορφυρα) stems from the genus of one of its common hosts, Porphyra, and the purple-red color of the lesions on the thallus of the host. However, many of its hosts have been moved from the genus Porphyra to Pyropia.
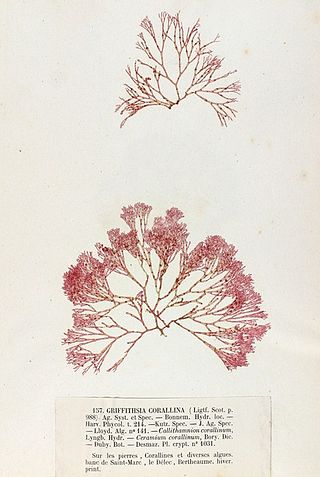
Griffithsia is a genus of red algae in the family Wrangeliaceae.









