Related Research Articles

The Caddo people comprise the Caddo Nation of Oklahoma, a federally recognized tribe headquartered in Binger, Oklahoma. They speak the Caddo language.

Etowah Indian Mounds (9BR1) are a 54-acre (220,000 m2) archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia, south of Cartersville. Built and occupied in three phases, from 1000–1550 CE, the prehistoric site is located on the north shore of the Etowah River.

The Mississippian culture was a Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from approximately 800 CE to 1600 CE, varying regionally. It was known for building large, earthen platform mounds, and often other shaped mounds as well. It was composed of a series of urban settlements and satellite villages linked together by loose trading networks. The largest city was Cahokia, believed to be a major religious center located in what is present-day southern Illinois.
Robert E. Bell, was an archaeologist. He was a Professor of Anthropology at the University of Oklahoma from 1947-1980, and Curator of Archaeology at the Stovall Museum of Science and History at the University of Oklahoma. He pioneered work on the Spiro Mounds archaeological site in eastern Oklahoma.

Moundville Archaeological Site, also known as the Moundville Archaeological Park, is a Mississippian culture archaeological site on the Black Warrior River in Hale County, near the modern city of Tuscaloosa, Alabama. Extensive archaeological investigation has shown that the site was the political and ceremonial center of a regionally organized Mississippian culture chiefdom polity between the 11th and 16th centuries. The archaeological park portion of the site is administered by the University of Alabama Museums and encompasses 185 acres (75 ha), consisting of 29 platform mounds around a rectangular plaza.

Spiro Mounds is an archaeological site located in present-day eastern Oklahoma that remains from an indigenous Indian culture that was part of the major northern Caddoan Mississippian culture. The 80-acre site is located within a floodplain on the southern side of the Arkansas River. The modern town of Spiro developed approximately seven miles to the south.
Big Mound City (8PB48) is a prehistoric site near Canal Point, Florida, United States. It is located 10 miles east of Canal Point, off U.S. Route 98. On May 24, 1973, it was added to the U.S. National Register of Historic Places. It is located inside the J.W. Corbett Wildlife Management Area.
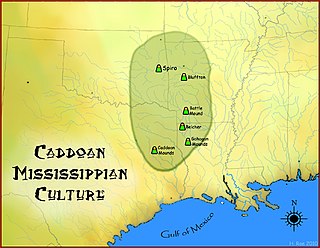
The Caddoan Mississippian culture was a prehistoric Native American culture considered by archaeologists as a variant of the Mississippian culture. The Caddoan Mississippians covered a large territory, including what is now Eastern Oklahoma, Western Arkansas, Northeast Texas, Southwest Missouri and Northwest Louisiana of the United States.
The Antelope Creek Phase was an American Indian culture in the Texas Panhandle and adjacent Oklahoma dating from AD 1200 to 1450. The two most important areas where the Antelope Creek people lived were in the Canadian River valley centered on present-day Lake Meredith near the city of Borger, Texas and the Buried City complex in Wolf Creek valley near the town of Perryton, Texas. Settlements are also found in Oklahoma near the town of Guymon and along the Beaver River.

Plum Bayou culture is a Pre-Columbian Native American culture that lived in what is now east-central Arkansas from 650–1050 CE, a time known as the Late Woodland Period. Archaeologists defined the culture based on the Toltec Mounds site and named it for a local waterway.

Foster's Mound is a Plaquemine culture archaeological site located in Adams County, Mississippi northeast of Natchez off US 61. It is the type site for the Foster Phase of the Natchez Bluffs Plaquemine culture chronology. It was added to the NRHP on September 2, 1982 as NRIS number 82003091. The mounds are listed on the Mississippi Mound Trail.

Caddo Mounds State Historic Site (41CE19) is an archaeological site in Weeping Mary, Texas. This Caddoan Mississippian culture site is composed of a village and ceremonial center that features two earthwork platform mounds and one burial mound. Located on an ancient Native American trail later named by the Spanish as El Camino Real de los Tejas, the settlement developed hundreds of years before the arrival of Europeans to the region. Archaeologists believe the site was created in approximately 800 CE, with most major construction taking place between 1100 and 1300 CE.
The Hughes Mound Site, (3SA11), is an archeological site in Saline County, Arkansas near Benton. The 4.5-acre (1.8 ha) is an important Caddoan Mississippian culture village center, at the northeastern frontier of that civilization. It is the only known platform mound site south of Benton on the Saline River. The site has not been dated, but artifacts found there are consistent with the Caddoan period; no contact-period artifacts have been found.
The Keller Site is a prehistoric ceremonial center located on a former plantation property in Calhoun County, Arkansas. It consists of a group of burial mounds that were apparently first established by the Coles Creek culture, and the area also saw use in the Caddoan period, c. 1200AD. The site was partially excavated in 1909 by Clarence B. Moore. The site, which was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979, is primarily notable because it is relatively undisturbed, providing the potential for further fruitful research.
The Edwards Archaeological Site is an archaeological site in Beckham County, Oklahoma, near the town of Carter. The site is part of the Edwards Complex, a culture which flourished in this area from about 1400 to 1650. The site was a Native American (Indian) village and included dwellings surrounded by a round fortification. Large amounts of waste material, such as tools and bones, have been collected from the site, indicating prolonged inhabitation by a large group. Pottery fragments and obsidian and turquoise artifacts found at the site suggest that its inhabitants traded with Puebloan peoples.
The Goforth-Saindon Mound Group is a prehistoric archaeological site near Siloam Springs, Arkansas. The site, which is one of the only known Caddoan Mississippian culture mound sites in the western Ozark highlands, is significant for providing a series of datable strata encompassing the entire period of that culture in the region. The connection between this site and other sites further southwest is exemplified by similarities in the layout of their features.
References
- 1 2 "National Register Information System". National Register of Historic Places . National Park Service. March 13, 2009.
- ↑ Robert L. Brooks. "Grobin Davis Site". The Encyclopedia of Oklahoma History and Culture. Retrieved March 22, 2018.