Description
The Gruta do Lago Azul has a main hall with a floor that slopes to a subterranean lake over 50 metres (160 ft) long. The entrance is circular, about 40 metres (130 ft) in diameter, illuminating the lake with sunshine. Between the months of September and February the waters take on an intense blue color, for which the lake is named. Fossil bones have been found of large mammals that inhabited the region for more than 12,000 years in the Pleistocene. These include giant sloths, armadillos and sabre-toothed tigers.
The Gruta de Nossa Senhora Aparecida does not contain water and has little natural light. It has a single, large hall with a sloping floor 100 metres (330 ft) at its widest. The hall contains speleothems, some of which are called "angels" since they resemble humans with wings. The Gruta de Nossa Senhora Aparecida is closed to visitors for safety reasons.

Mato Grosso is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.

Mato Grosso do Sul is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and Bolivia, to the west. The economy of the state is largely based on agriculture and cattle-raising. Crossed in the south by the Tropic of Capricorn, Mato Grosso do Sul generally has a warm, sometimes hot, and humid climate, and is crossed by numerous tributaries of the Paraná River. The state has 1,3% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1,5% of the Brazilian GDP.
In Brazil, public holidays may be legislated at the federal, statewide and municipal levels. Most holidays are observed nationwide.

The Gruta Rei do Mato (MG-3653) is a cave located at the edge of the BR-040 highway, close to the off ramp to the city of Sete Lagoas, in Minas Gerais, Brazil. From Sete Lagoas the cave can easily be reached by bus, taxi or car. Sete Lagoas is 70 km (43.5 mi) from Belo Horizonte, the capital of the state.
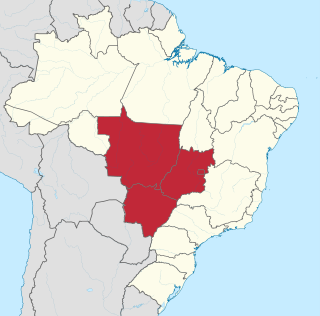
The Central-West or Center-West Region of Brazil is composed of the states of Goiás, Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul; along with Distrito Federal, where Brazil's national capital, Brasília, is situated. This Region is right in the heart of Brazil, representing 18.86% of the national territory.

Rio de Contas is a municipality in the Bahia state, in the eastern part of Brazil. Its estimated population as of 2020 was 12,932.

The Cathedral of Brasília is the Roman Catholic cathedral serving Brasília, Brazil, and serves as the seat of the Archdiocese of Brasília. It was designed by Brazilian architect Oscar Niemeyer and projected by Brazilian structural engineer Joaquim Cardozo, and was completed and dedicated on May 31, 1970. The cathedral is a hyperboloid structure constructed from 16 concrete columns, weighing 90 tons each.

Nobres is a city in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It is located approximately 140 kilometers from Cuiabá on the south slopes of the Serra Azul.

Bonito is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Mato Grosso do Sul. As of 2020 its population was 22,190, and it has an area of 4,934 square kilometres (1,905 sq mi).

The Federal University of Mato Grosso do Sul, is a public university located in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul in Brazil. It has, in addition to the main campus in Campo Grande, nine campuses located in the following inland cities: Aquidauana, Chapadão do Sul, Corumbá, Coxim, Naviraí, Nova Andradina, Paranaíba, Ponta Porã e Três Lagoas.
Bonito is a name given to various species of fish of the genus Sarda.

Alto Garças is a municipality) in the south-east of the Brazilian State of Mato Grosso with a population of about 12,000 on an area of 3672 km. The distance to the state capital Cuiabá is approximately 350 km². In 1933 Alto Garças became a district of the municipality of Santa Rita do Araguaia and on 10 December 1953 it was separated as an independent entity. Alto Garças is part of the micro-region Alto Araguaia.

Gruta das Torres, is a lava cave, a geological formation of volcanic origin formed from the flow and cooling of subterranean magma rivers. This formation is located outside the parish of Criação Velha, in the municipality of Madalena, on the western flanks of the island of Pico. The cave system formed from a series of pāhoehoe lava flows which originating from the Cabeço Bravo parasitic cone about 500 to 1500 years ago. The caves are a group of interconnected lava tubes between 0.5–22 metres (2–72 ft) width, created from both pāhoehoe and ʻaʻā types of lavas generated during different geological periods. It has a height between 1.1 and 15 metres (3.6–49 ft) and is located at an elevation of 300 metres (980 ft). With an estimated length of over 5.2 km (3.2 mi) it is the longest lava cave in the Azores. Access to the cave was managed by the Mountaineering Association. Starting in 2011, AZORINA, SA took over the management and organization of the cave.

Palmeiras-Barra Funda Intermodal Terminal is the second largest intermodal transportation hub in São Paulo, Brazil. The terminal has access to the São Paulo Metro, CPTM commuter rail, and numerous bus lines.

The Gruta da Lagoa Azul State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. Its primary attraction is a limestone cave with a pool of blue water and unusual cave formations. These have suffered from vandalism, causing the cave to be closed until measures to protect it could be implemented.

The Serra Azul State Park is a state park in the state of Mato Grosso, Brazil. It protects a mountainous area of cerrado forest and contains slopes that are used for paragliding. The park contains the geodetic center of Brazil.

The Campinhos State Park is a state park in the state of Paraná, Brazil. The environment has been much degraded by human activity and is in the process of regeneration, but there are areas of the original Araucaria Forest. The main attraction is the 500 metres (1,600 ft) long Jesuits Cave, with many speleothems such as stalagmites and stalactites.
Habeastrum is a genus of minute diplommatinid pulmonate gastropods, endemic to limestone caves in Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil. It is represented by two sympatric species, Habeastrum omphalium and Habeastrum parafusum.
















