
The Guelphic Legion (German : Welfenlegion) was an irregular, volunteer military unit founded and maintained at the expense of the deposed Welf king George V of Hanover, after the annexation of the Kingdom of Hanover by Prussia in 1866.

The Guelphic Legion (German : Welfenlegion) was an irregular, volunteer military unit founded and maintained at the expense of the deposed Welf king George V of Hanover, after the annexation of the Kingdom of Hanover by Prussia in 1866.
After the Austro-Prussian War, in the autumn of 1866, victorious Prussia annexed four former allies of the defeated Austrian forces north of the Main line: Hanover as well as Hesse-Kassel, Nassau, and the Free City of Frankfurt. While the former kingdom was incorporated as the Province of Hanover without any referendum or consultation; protests by the affected population led to the foundation of the anti-Prussian German-Hanoverian Party.
Upon the Hanoverian surrender after the Battle of Langensalza on 29 June 1866, the kingdom was occupied by Prussian troops and formally annexed on 20 September. During the Luxembourg Crisis between Prussia and France in spring 1867, a rising number of Hanoverian soldiers gathered at Arnhem in the Netherlands at the behest of exiled King George V and his newly established court at the Villa Hügel in Hietzing near Vienna. However, when a war was once again averted by the Treaty of London signed on 11 May, the Dutch government ordered all foreign troops to leave the country. After being raised as a sizeable force, the Legion migrated to Switzerland, where its numbers swelled to 700. [1]
King George V, who never abandoned his claim to the Hanoverian throne, continued to maintain the Legion at his own expense while in exile in France. In February 1868 the unit moved from Switzerland to France at the same time as George V and Marie of Saxe-Altenburg celebrated their silver wedding anniversary in Paris. In 1869 the Prussian House of Representatives passed a law sequestering the funds of the former King of Hanover (Welfenfonds) in retaliation for his enmity and deployment of the Guelphic Legion. [2]
The Guelphic Legion was formally dissolved on 15 April 1870. Each of the 1,400 legionnaires received 400 francs upon discharge and additional traveling expenses as needed. Many returned to Hanover, but some migrated to the United States or to other parts of Europe. [1] George V, unreconciled and embittered, died in Paris on 12 June 1878.

The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as Deutscher Krieg, Deutsch-Deutscher Krieg, Deutscher Bruderkrieg and by a variety of other names, was fought in 1866 between the Austrian Empire and the Kingdom of Prussia, with each also being aided by various allies within the German Confederation. Prussia had also allied with the Kingdom of Italy, linking this conflict to the Third Independence War of Italian unification. The Austro-Prussian War was part of the wider rivalry between Austria and Prussia, and resulted in Prussian dominance over the German states.

The House of Hanover is a European royal house with roots tracing back to the 17th century. Its members, known as Hanoverians, ruled Hanover, Great Britain, Ireland, and the British Empire at various times during the 17th to 20th centuries. Originating as a cadet branch of the House of Welf in 1635, also known then as the House of Brunswick-Lüneburg, the Hanoverians ascended to prominence with Hanover's elevation to an Electorate in 1692. In 1714 George I, prince-elector of Hanover and a descendant of King James VI and I, assumed the throne of Great Britain and Ireland, marking the beginning of Hanoverian rule over the British Empire. At the end of his line, Queen Victoria's death in 1901, the throne of the United Kingdom passed to her eldest son Edward VII, a member of the House of Saxe-Coburg and Gotha, through his father Albert, Prince Consort. The last reigning members of the House of Hanover lost the Duchy of Brunswick in 1918 when Germany became a republic and abolished royalty and nobility.

The Kingdom of Prussia constituted the German state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. It was the driving force behind the unification of Germany in 1866 and was the leading state of the German Empire until its dissolution in 1918. Although it took its name from the region called Prussia, it was based in the Margraviate of Brandenburg. Its capital was Berlin.

Prince Adolphus, Duke of Cambridge was the tenth child and seventh son of King George III of the United Kingdom and Queen Charlotte. He held the title of Duke of Cambridge from 1801 until his death. He served as Viceroy of the Kingdom of Hanover successively on behalf of his elder brothers King George IV and King William IV.

George V was the last king of Hanover, reigning from 18 November 1851 to 20 September 1866. The only child of King Ernest Augustus and Queen Frederica, he succeeded his father in 1851. George's reign was ended by the Austro-Prussian War, after which Prussia annexed Hanover.

Ernest Augustus, Crown Prince of Hanover, 3rd Duke of Cumberland and Teviotdale, was the eldest child and only son of George V of Hanover and his wife, Marie of Saxe-Altenburg. Ernest Augustus was deprived of the throne of Hanover upon its annexation by Prussia in 1866 and later the Duchy of Brunswick in 1884. Ernest Augustus was deprived of his British peerages and honours for having sided with Germany in World War I.
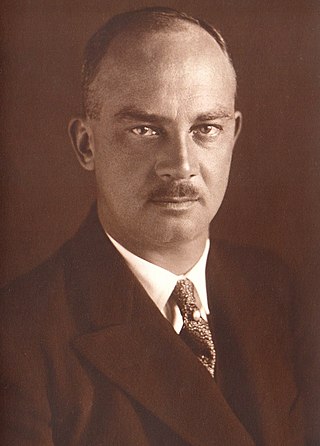
Ernest Augustus ; 17 November 1887 – 30 January 1953) was Duke of Brunswick from 2 November 1913 to 8 November 1918. He was a grandson of George V of Hanover, thus a Prince of Hanover and a Prince of the United Kingdom. He was also a maternal grandson of Christian IX of Denmark and the son-in-law of German Emperor Wilhelm II. The Prussians had deposed King George from the Hanoverian throne in 1866, but his marriage ended the decades-long feud between the Prussians and the Hanoverians.
Hanover is a territory that was at various times a principality within the Holy Roman Empire, an Electorate within the same, an independent Kingdom, and a subordinate Province within the Kingdom of Prussia. The territory was named after its capital, the city of Hanover, which was the principal town of the region from 1636. In contemporary usage, the name is used only for the city. Most of the historical territory of Hanover forms the greater part of the German state of Lower Saxony but excludes certain areas.

Princess Thyra of Denmark was the youngest daughter and fifth child of Christian IX of Denmark and Louise of Hesse-Kassel. In 1878, she married Ernest Augustus, the exiled heir to the Kingdom of Hanover. As the Kingdom of Hanover had been annexed by Prussia in 1866, she spent most of her life in exile with her husband in Austria.

The Kingdom of Hanover was established in October 1814 by the Congress of Vienna, with the restoration of George III to his Hanoverian territories after the Napoleonic era. It succeeded the former Electorate of Hanover, and joined 38 other sovereign states in the German Confederation in June 1815. The kingdom was ruled by the House of Hanover, a cadet branch of the House of Welf, in personal union with Great Britain between 1714 and 1837. Since its monarch resided in London, a viceroy, usually a younger member of the British royal family, handled the administration of the Kingdom of Hanover.

The Royal Guelphic Order, sometimes referred to as the Hanoverian Guelphic Order, is a Hanoverian order of chivalry instituted on 28 April 1815 by the Prince Regent. It takes its name from the House of Guelph, of which the House of Hanover was a branch. Since Hanover and the United Kingdom shared a monarch until 1837, the order was frequently bestowed upon British subjects.

The King of Hanover was the official title of the head of state and hereditary ruler of the Kingdom of Hanover, beginning with the proclamation of King George III of the United Kingdom, as "King of Hanover" during the Congress of Vienna, on 12 October 1814 at Vienna, and ending with the kingdom's annexation by Prussia on 20 September 1866.

The Electorate of Hanover was an electorate of the Holy Roman Empire located in northwestern Germany that arose from the Principality of Calenberg. Although formally known as the Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, it made Hanover its capital city. For most of its existence, the electorate was ruled in personal union with Great Britain and Ireland following the Hanoverian Succession.
The German-Hanoverian Party, also known as the Guelph Party, was an agrarian, federalist political party in the German Empire and the Weimar Republic. It represented the interests of Hanoverian separatists and regionalists that sought to restore the overthrown House of Welf and separate from Prussia to either become a kingdom within Germany or to become independent outright. The party was a part of the anti-Prussian faction in the Reichstag and closely cooperated with the Catholic Centre Party, including opposing Kulturkampf and centralization legislations.

The Battle of Langensalza was fought on 27 June 1866, during the Austro-Prussian War, near Bad Langensalza in what is now modern Germany, between the Kingdom of Hanover and the Kingdom of Prussia. The Hanoverians won the battle but were then surrounded by a larger and reinforced Prussian army. Unable to link up with their Bavarian allies to the south, the Hanoverians surrendered.

Marie of Saxe-Altenburg was Queen of Hanover from 18 November 1851 until 20 September 1866 as the wife of King George V. George V was a grandson of George III of the United Kingdom and his wife, Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz.

The Hanoverian Army was the standing army of the Electorate of Hanover from the seventeenth century onwards. From 1692 to 1803 it acted in defence of the electorate. Following the Hanoverian Succession of 1714, this was in conjunction with the British Army with which it shared a monarch. Hanoverian troops fought in the War of the Austrian Succession, Seven Years' War and American War of Independence during the eighteenth century.

Georg Herbert Fürst zu Münster von Derneburg , also known by his earlier title of Count of Münster-Ledenburg, was a Hanoverian and later German diplomat and politician. He served as ambassador to London 1873–1885 and Paris (1885–1900).

The Invasion of Hanover in 1803 during the Napoleonic Wars saw a French army under Édouard Mortier invade and occupy the Electorate of Hanover in Northern Germany following the breakdown of the Peace of Amiens. Hanover was under the rule of George III in a personal union with Britain, the principal enemy of Napoleon's French Empire. One consequence was the formation of the exiled King's German Legion in British service. Hanover remained under French control until its liberation in 1813.
The Liberation of Hanover took place in November 1813 as part of the War of the Sixth Coalition during the larger Napoleonic Wars. The Electorate of Hanover had been invaded and occupied in 1803 and since then had been divided between the First French Empire and the Kingdom of Westphalia ruled by Napoleon's younger brother Jerome. The historic House of Guelph headed by George III, but by 1813 under the control of the Prince Regent, were restored to their historic territories.