
Marfan syndrome (MFS) is a multi-systemic genetic disorder that affects the connective tissue. Those with the condition tend to be tall and thin, with long arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They also typically have exceptionally flexible joints and abnormally curved spines. The most serious complications involve the heart and aorta, with an increased risk of mitral valve prolapse and aortic aneurysm. The lungs, eyes, bones, and the covering of the spinal cord are also commonly affected. The severity of the symptoms is variable.

Ehlers–Danlos syndromes (EDS) are a group of 13 genetic connective-tissue disorders in the current classification, with the latest type discovered in 2018. Symptoms often include loose joints, joint pain, stretchy velvety skin, and abnormal scar formation. These may be noticed at birth or in early childhood. Complications may include aortic dissection, joint dislocations, scoliosis, chronic pain, or early osteoarthritis.

Pectus excavatum is a structural deformity of the anterior thoracic wall in which the sternum and rib cage are shaped abnormally. This produces a caved-in or sunken appearance of the chest. It can either be present at birth or develop after puberty.

Pectus carinatum, also called pigeon chest, is a malformation of the chest characterized by a protrusion of the sternum and ribs. It is distinct from the related malformation pectus excavatum.

The sternocostal joints, also known as sternochondral joints or costosternal articulations, are synovial plane joints of the costal cartilages of the true ribs with the sternum. The only exception is the first rib, which has a synchondrosis joint since the cartilage is directly united with the sternum. The sternocostal joints are important for thoracic wall mobility.

SCARF syndrome is a rare syndrome characterized by skeletal abnormalities, cutis laxa, craniostenosis, ambiguous genitalia, psychomotor retardation, and facial abnormalities. These characteristics are what make up the acronym SCARF. It shares some features with Lenz-Majewski hyperostotic dwarfism. It is a very rare disease with an incidence rate of approximately one in a million newborns. It has been clinically described in two males who were maternal cousins, as well as a 3-month-old female. Babies affected by this syndrome tend to have very loose skin, giving them an elderly facial appearance. Possible complications include dyspnea, abdominal hernia, heart disorders, joint disorders, and dislocations of multiple joints. It is believed that this disease's inheritance is X-linked recessive.
Restrictive lung diseases are a category of extrapulmonary, pleural, or parenchymal respiratory diseases that restrict lung expansion, resulting in a decreased lung volume, an increased work of breathing, and inadequate ventilation and/or oxygenation. Pulmonary function test demonstrates a decrease in the forced vital capacity.
Sydney A. Haje was a Brazilian orthopedist, known internationally for his pioneering work on chest wall deformities including the creation of a conservative treatment protocol for the pectus carinatum and pectus excavatum conditions.
7p22.1 microduplication syndrome is a genetic disorder which is characterized by cranial and facial dysmorphisms, intellectual disability, and motor-speech delays. It is caused by a duplication of the p22.1 region of chromosome 7.
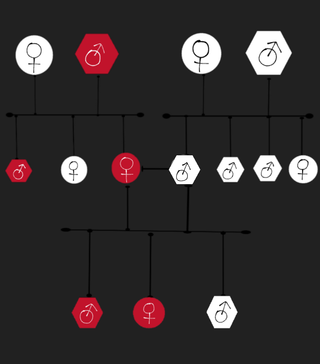
Familial thoracic aortic aneurysm and aortic dissection is a very rare vascular genetic disorder, it's characterized by recurrent thoracic aortic aneurysms and aortic dissections within a family, these mentioned complications affect one or more aortic segments without any other disease being associated with them. People with this disorder have a higher chance of having a potentially fatal aortic rupture. This disorder is the cause of 20% of thoracic aortic aneurysms
Brachydactyly-long thumb syndrome is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by symmetric brachydactyly of the fingers accompanied by an abnormally long thumb, hypomobility of the shoulder and metacarpo-phalangeal joints, and heart conduction defects. Small feet and hands, small shoulders accompanied with short clavicles, clinodactyly, pectus excavatum, mild limb shortening, cardiomegaly, and pulmonic stenosis murmur have also been reported. It was first discovered when D W Hollister et al. described 4 affected members belonging to a 3-generation family. No new cases have been reported since 1981. This disorder is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.

Gustavson syndrome, also known as Severe X-linked intellectual disability, Gustavson type, is a rare genetic disorder which is characterized by severe intellectual disabilities, microcephaly, developmental delay, optic atrophy-induced severe vision impairment/loss, severe hearing loss, spasticity, epilepsy, hypomobility of major joints, facial dysmorphisms, and premature death. Some other frequent symptoms include severe postnatal growth retardation, infantile apnea, brain atrophy, dilation of the fourth cerebral ventricle, recurrent upper respiratory tract infections, and a small fontanelle. This disorder was first discovered in 1993, by Gustavson et al., when they described 7 male children from a 2-generation family, these children had the symptoms mentioned above, they came to the conclusion that this case was part of a novel X-linked recessive syndrome. No new cases have been reported since then (1993).
Blepharophimosis intellectual disability syndromes are a group of rare genetic disorders which are characterized by blepharophimosis, ptosis, and intellectual disabilities. These disorders usually follow either autosomal recessive, autosomal dominant, x-linked recessive, or mitochondrial inheritance patterns.

Tranebjaerg–Svejgaard syndrome, also known as X-linked mental retardation associated with psoriasis is a very rare genetic disorder which is characterized by intellectual disabilities, psychomotor development delays, seizures, psoriasis, and cranio-facial dysmorphisms. It is a type of X-linked syndromic intellectual disability. Only 4 cases have been described in medical literature.

Acrocraniofacial dysostosis, also known as Kaplan Plauchu Fitch syndrome is a very rare hereditary disorder which is characterized by cranio-facial dysmorphisms, hearing loss, digital clubbing, and osseous anomalies. Only 2 cases have been described in medical literature.

McDonough syndrome, also known as Mental retardation, peculiar facies, kyphoscoliosis, diastasis recti, cryptorchidism, and congenital heart defect is a very rare multi-systemic genetic disorder which is characterized by facial dysmorphisms, psychomotor delays, intellectual disabilities, and congenital heart defects. Additional findings include either pectus excavatum or pectus carinatum, kyphoscoliosis, diastasis recti and cryptorchidism.

Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia-short limb-abnormal calcification syndrome is a rare genetic disorder which is characterized by osseous anomalies resulting in short stature and other afflictions.

Faciocardiorenal syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by facial dysmorphisms, congenital heart defects, and the presence of a horseshoe kidney, alongside intellectual disabilities. Facial dysmorphisms include protruding ears, narrowing of the mouth, cleft palate, hypertelorism, etc. Only 4 cases from the United States, Northern Ireland, and Mexico have been described in the medical literature. Transmission is, presumably, autosomal recessive.

Lymphedema-posterior choanal atresia syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the early-onset appearance of lymphedemas and congenital choanal atresia, which might be accompanied by other features such as pectus excavatum, hypoplasia of the nipples, and facial dysmorphisms such as hypertelorism, frontal bossing, etc. Only 7 cases from Yemen and Iran have been described in the medical literature. This condition is caused by homozygous mutations in the PTPN14 gene, located in chromosome 1.









