The Coral Sea Islands Territory is an external territory of Australia which comprises a group of small and mostly uninhabited tropical islands and reefs in the Coral Sea, north-east of Queensland, Australia. The only inhabited island is Willis Island. The territory covers 780,000 km2 (301,160 sq mi), most of which is ocean, extending east and south from the outer edge of the Great Barrier Reef and includes Heralds Beacon Island, Osprey Reef, the Willis Group and fifteen other reef/island groups. Cato Island is the highest point in the Territory.

The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuelan coastline to the Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The geopolitical region centered around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean.

The Bay of Pigs is an inlet of the Gulf of Cazones, located on the southern coast of Cuba. By 1910 it was included in Santa Clara Province, and then to Las Villas Province by 1961, but in 1976, it was reassigned to Matanzas Province, when the original six provinces of Cuba were re-organized into 14 new Provinces of Cuba.

A cay, also spelled caye or key, is a small, low-elevation, sandy island on the surface of a coral reef. Cays occur in tropical environments throughout the Pacific, Atlantic, and Indian oceans, including in the Caribbean and on the Great Barrier Reef and Belize Barrier Reef.
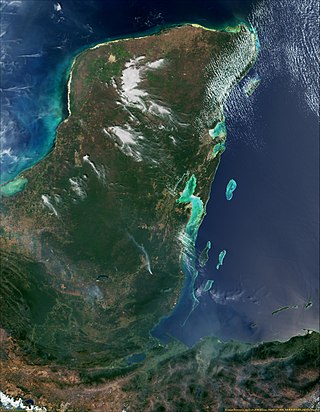
The Gulf or Bay of Honduras is a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea, indenting the coasts of Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. From north to south, it runs for approximately 200 km from Dangriga, Belize, to La Ceiba, Honduras.

Roatán is an island in the Caribbean, about 65 kilometres (40 mi) off the northern coast of Honduras. The largest of the Bay Islands of Honduras, it is located between the islands of Utila and Guanaja. It is approximately 77 kilometres (48 mi) long, and less than 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) across at its widest point. The island consists of two municipalities: José Santos Guardiola in the east and Roatán, including the Cayos Cochinos, in the west. The island was formerly known in English as Ruatan and Rattan.

Utila is the smallest of Honduras' major Bay Islands, after Roatán and Guanaja, in a region that marks the south end of the Mesoamerican Barrier Reef System, the second-largest in the world. It has been documented in history since Columbus' fourth voyage.

The Cayos Cochinos or Cochinos Cays consist of two small islands and 13 smaller coral cays situated 30 kilometres (19 mi) northeast of La Ceiba on the northern shores of Honduras. Although geographically separate, they belong to the Bay Islands department and are part of the Roatán municipality. The population numbered 108 at the 2001 census. The total land area measures about 2 km2 (0.8 sq mi).

The Cayos Arcas is a chain of three tiny sand cays and an accompanying reef system in the Gulf of Mexico, 128 kilometres from the mainland. It is located approximately 130 kilometres from the mainland, west of Campeche. Their aggregate land area is 22.8 hectares. They belong to the municipality of Campeche in the state of Campeche.

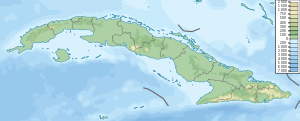
Cayo Largo del Sur, or simply Cayo Largo, is a small resort island in Cuba, off the south coast of the northwestern part of the main island in the Caribbean Sea. The cay is about 25 kilometers (16 mi) long and 3 kilometers (1.9 mi) wide and is the second largest island in the Canarreos Archipelago. Cayo Largo is part of the special municipality of Isla de la Juventud.
Jardines de la Reina is an archipelago in the southern part of Cuba, in the provinces of Camagüey and Ciego de Ávila.

Cay Sal Bank is the third largest and the westernmost of the Bahama Banks. It is located between 23º27'N - 24º10'N and 079º25'W – 080º35'W. In a geographical sense, it is separate from the Bahamas proper as it is much closer to Cuba than to the closest Bahamian island. It is separated by Santaren Channel from the Great Bahama Bank, the western rim of which is 50 km (31 mi) to the east. The Straits of Florida separate it from the United States mainland and the Florida Keys.

The Miskito Cays are an archipelago of small cays and reefs with an area of 27 km2 located off Mosquito Coast in the Caribbean exclusive economic zones of Honduras and Nicaragua. They are part of the Bay Islands Department in Honduras and the North Caribbean Coast Autonomous Region in Nicaragua. The Miskito Cays are composed of 76 formations that include estuaries, coral reefs, cays, seagrass beds, and islets, of which 12 of the formations are covered with vegetation and consequently form islands which are lined with white sand beaches.
The Colorados Archipelago is a chain of isles and cays on Cuba's north-western coast.
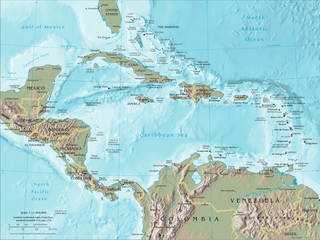
The Caribbean, is a subregion in the middle of the Americas centered around the Caribbean Sea in the North Atlantic Ocean. Bordered by North America to the north, Central America to the west, and South America to the south, it comprises numerous islands, cays, islets, reefs, and banks. It includes the Lucayan Archipelago, Greater Antilles, and Lesser Antilles of the West Indies; the Quintana Roo islands and Belizean islands of the Yucatán Peninsula; and the Bay Islands, Miskito Cays, Archipelago of San Andrés, Providencia, and Santa Catalina, and Corn Islands of Central America. It also includes the coastal areas on the continental mainland of the Americas bordering the region from the Yucatán Peninsula in North America through Central America to the Guianas in South America.

San Andrés is a coral island in the Caribbean Sea. Politically part of Colombia, and historically tied to the United Kingdom, San Andrés and the nearby islands of Providencia and Santa Catalina form part of the department of San Andrés, Providencia and Santa Catalina; or The Raizal Islands. San Andrés, in the southern group of islands, is the largest of Colombia. The official languages of the department are Spanish, English, and San Andrés–Providencia Creole.

The Prickly Pear Cays, sometimes spelt as Prickley Pear Cays, are a small pair of uninhabited islands about six miles from Road Bay, Anguilla, in the Leeward Islands of the Caribbean. They are divided by a narrow boat channel between Prickly Pear East and Prickly Pear West. Prickly Pear Cays were classified as 'wildlands' by the "Eastern Caribbean Natural Area Management Programme" (ECNAMP). In addition, Prickly Pear Cays are one of six marine protected areas of Anguilla.

Cayo Levisa is a cay in Pinar del Río Province, Cuba. Accessible only through boats from Palma Rubia, the white sand beaches on its north coast attract tourism. It has several snorkeling and diving sites. It is part of the Colorados Archipelago coral reef and well known for its black coral.

Lighthouse Reef is an atoll in the Caribbean Sea, the easternmost part of the Belize Barrier Reef and one of its three atolls, the other two being Turneffe Atoll and Glover's Reef. Lighthouse Reef is located about 80 kilometres (50 mi) southeast of Belize City. The atoll is of oblong shape, approximately 35 kilometres (22 mi) long from north to south, and about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) wide. It forms a shallow sandy lagoon with an area of 120 square kilometres (46 sq mi) and a depth between 2 and 6 metres deep.

The Elbow Cays are uninhabited cays in the Cay Sal Bank, Bahamas. It is the most Western point in the Bahamas. They are part of a reef shelf located at the northwestern end of the bank about 80 km (50 mi) off the Cuban coast and 130 km (80 mi) southeast of Key West, Florida. These cays are an excellent scuba diving spot.