Related Research Articles
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes."
The International Federation for Information Processing (IFIP) is a global organisation for researchers and professionals working in the field of computing to conduct research, develop standards and promote information sharing.

Enterprise integration is a technical field of enterprise architecture, which is focused on the study of topics such as system interconnection, electronic data interchange, product data exchange and distributed computing environments.

Computer-integrated manufacturing (CIM) is the manufacturing approach of using computers to control the entire production process. This integration allows individual processes to exchange information with each part. Manufacturing can be faster and less error-prone by the integration of computers. Typically CIM relies on closed-loop control processes based on real-time input from sensors. It is also known as flexible design and manufacturing.
Business process interoperability (BPI) is a property referring to the ability of diverse business processes to work together, to so called "inter-operate". It is a state that exists when a business process can meet a specific objective automatically utilizing essential human labor only. Typically, BPI is present when a process conforms to standards that enable it to achieve its objective regardless of ownership, location, make, version or design of the computer systems used.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.

Generalised Enterprise Reference Architecture and Methodology (GERAM) is a generalised enterprise architecture framework for enterprise integration and business process engineering. It identifies the set of components recommended for use in enterprise engineering.
François B. Vernadat is a French and Canadian computer scientist, who has contributed to Enterprise Modelling, Enterprise Integration and Networking over the last 40 years specialising in Enterprise Architectures, business process modelling, information systems design and analysis, systems integration and interoperability and systems analysis using Petri nets.
Peter Bernus is a Hungarian Australian scientist and Associate Professor of Enterprise Architecture at the School of Information and Communication Technology, Griffith University, Brisbane, Australia.

James G. "Jim" Nell is an American engineer. He was the principal investigator of the Manufacturing Enterprise Integration Project at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), and is known for his work on enterprise integration.
Enterprise interoperability is the ability of an enterprise—a company or other large organization—to functionally link activities, such as product design, supply chains, manufacturing, in an efficient and competitive way.
The GRAI method, GRAI is short for Graphs with Results and Actions Inter-related, and the further developed GRAI Integrated Methodology (GIM) is a modeling method of Enterprise modelling.

Federated architecture (FA) is a pattern in enterprise architecture that allows interoperability and information sharing between semi-autonomous de-centrally organized lines of business (LOBs), information technology systems and applications.
Model Driven Interoperability (MDI) is a methodological framework, which provides a conceptual and technical support to make interoperable enterprises using ontologies and semantic annotations, following model driven development (MDD) principles.
Kurt Kosanke is a German engineer, retired IBM manager, director of the AMICE Consortium and consultant, known for his work in the field of enterprise engineering, Enterprise integration and CIMOSA.
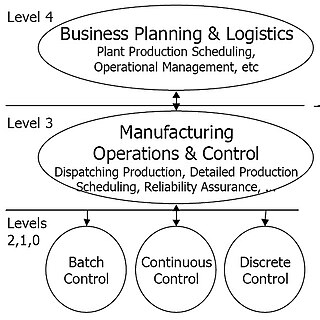
Purdue Enterprise Reference Architecture (PERA), or the Purdue model, is a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture, developed by Theodore J. Williams and members of the Industry-Purdue University Consortium for Computer Integrated Manufacturing.
The INTEROP V-Lab is a network of organizations, which links scientists, research centers, representatives of industry, and small and medium-sized enterprises. The members come from several European countries as well as China and represent 250 scientists and 70 organizations.
Bruno Vallespir is a French engineer, and Professor of Enterprise Modelling at the University of Bordeaux, working in the fields of production management, performance evaluation and enterprise modeling.
The history of business architecture has its origins in the 1980s. In the next decades business architecture has developed into a discipline of "cross-organizational design of the business as a whole" closely related to enterprise architecture. The concept of business architecture has been proposed as a blueprint of the enterprise, as a business strategy, and also as the representation of a business design.
Gregory Zacharewicz is Full Professor at École des mines d'Alès in Alès, France. He recently joined the LGI2P laboratory in 2018 to develop research based on simulation. He was previously Associate Professor at the University of Bordeaux (2007-2018), where he conducted research on modeling, interoperability and simulation of business and social organization. He worked with Bruno Vallespir and Guy Doumeingts and under the direction of Claudia Frydman and Norbert Giambiasi.
References
- ↑ Doumeingts, G. (1984) La Méthode GRAI. PhD. Thesis, University of Bordeaux I, Bordeaux, France. (In French).
- ↑ Doumeingts, Guy. "GEM: GRAI evolution method: a case study." International Journal of Technology Management 22.1 (2001): 189-211.
- 1 2 Guy Doumeingts, Jörg Müller, Gérard Morel, and Bruno Vallespir. Enterprise Interoperability. Springer-Verlag London Limited, 2007. p. v.
- ↑ Guy Doumeingts at DBLP Bibliography Server