Related Research Articles

Sonic hedgehog protein(SHH) is encoded for by the SHH gene. The protein is named after the character Sonic the Hedgehog.
Ras, from "Rat sarcoma virus", is a family of related proteins that are expressed in all animal cell lineages and organs. All Ras protein family members belong to a class of protein called small GTPase, and are involved in transmitting signals within cells. Ras is the prototypical member of the Ras superfamily of proteins, which are all related in three-dimensional structure and regulate diverse cell behaviours.
The Hedgehog signaling pathway is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper cell differentiation. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway also has roles in the adult. Diseases associated with the malfunction of this pathway include cancer.
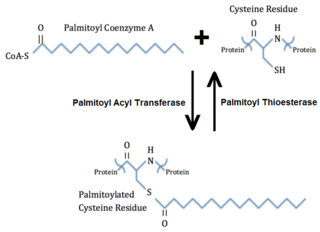
Palmitoylation is the covalent attachment of fatty acids, such as palmitic acid, to cysteine (S-palmitoylation) and less frequently to serine and threonine (O-palmitoylation) residues of proteins, which are typically membrane proteins. The precise function of palmitoylation depends on the particular protein being considered. Palmitoylation enhances the hydrophobicity of proteins and contributes to their membrane association. Palmitoylation also appears to play a significant role in subcellular trafficking of proteins between membrane compartments, as well as in modulating protein–protein interactions. In contrast to prenylation and myristoylation, palmitoylation is usually reversible (because the bond between palmitic acid and protein is often a thioester bond). The reverse reaction in mammalian cells is catalyzed by acyl-protein thioesterases (APTs) in the cytosol and palmitoyl protein thioesterases in lysosomes. Because palmitoylation is a dynamic, post-translational process, it is believed to be employed by the cell to alter the subcellular localization, protein–protein interactions, or binding capacities of a protein.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(q) subunit alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNAQ gene. Together with GNA11, it functions as a Gq alpha subunit.

Gap junction beta-6 protein (GJB6), also known as connexin 30 (Cx30) — is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GJB6 gene. Connexin 30 (Cx30) is one of several gap junction proteins expressed in the inner ear. Mutations in gap junction genes have been found to lead to both syndromic and nonsyndromic deafness. Mutations in this gene are associated with Clouston syndrome.

Indian hedgehog homolog (Drosophila), also known as IHH, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the IHH gene. This cell signaling protein is in the hedgehog signaling pathway. The several mammalian variants of the Drosophila hedgehog gene (which was the first named) have been named after the various species of hedgehog; the Indian hedgehog is honored by this one. The gene is not specific to Indian hedgehogs.
Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG2 gene.

Sterol O-acyltransferase 1, also known as SOAT1, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOAT1 gene.

Sterol O-acyltransferase 2, also known as SOAT2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SOAT2 gene.

Synaptobrevin homolog YKT6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the YKT6 gene.

Cytoskeleton-associated protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CKAP4 gene.

Cellular nucleic acid-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CNBP gene.

Ribosomal protein S6 kinase alpha-4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RPS6KA4 gene.

Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(I)/G(S)/G(O) subunit gamma-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GNG3 gene.

Glycerol-3-phosphate acyltransferase 1, mitochondrial is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GPAM gene.

Palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC17 is an enzyme that contains a DHHC domain that in humans is encoded by the ZDHHC17 gene.

Kinesin-like protein KIF2A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KIF2A gene.
In molecular biology the DHHC domain is a protein domain that acts as an enzyme, which adds a palmitoyl chemical group to proteins in order to anchor them to cell membranes. The DHHC domain was discovered in 1999 and named after a conserved sequence motif found in its protein sequence. Roth and colleagues showed that the yeast Akr1p protein could palmitoylate Yck2p in vitro and inferred that the DHHC domain defined a large family of palmitoyltransferases. In mammals twenty three members of this family have been identified and their substrate specificities investigated. Some members of the family such as ZDHHC3 and ZDHHC7 enhance palmitoylation of proteins such as PSD-95, SNAP-25, GAP43, Gαs. Others such as ZDHHC9 showed specificity only toward the H-Ras protein. However, a recent study questions the involvement of classical enzyme-substrate recognition and specificity in the palmitoylation reaction. Several members of the family have been implicated in human diseases.

Zinc finger, also known as ZDHHC2, is a human gene.
References
- ↑ Kawakami Y, Wang X, Shofuda T, Sumimoto H, Tupesis J, Fitzgerald E, Rosenberg S (February 2001). "Isolation of a new melanoma antigen, MART-2, containing a mutated epitope recognized by autologous tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes". J. Immunol. 166 (4): 2871–7. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.166.4.2871 . PMID 11160356.
- ↑ "OMIM Entry - * 605743 - HEDGEHOG ACYLTRANSFERASE; HHAT". www.omim.org. Retrieved 2017-02-20.
- ↑ Chamoun Z, Mann RK, Nellen D, von Kessler DP, Bellotto M, Beachy PA, Basler K (September 2001). "Skinny hedgehog, an acyltransferase required for palmitoylation and activity of the hedgehog signal". Science. 293 (5537): 2080–4. Bibcode:2001Sci...293.2080C. doi: 10.1126/science.1064437 . PMID 11486055. S2CID 39594965.