
Edward Hawke, 1st Baron Hawke,, of Scarthingwell Hall in the parish of Saxton with Scarthingwell, near Tadcaster, Yorkshire, was an English Royal Navy officer. As captain of the third-rate HMS Berwick, he took part in the Battle of Toulon in February 1744 during the War of the Austrian Succession. He also captured six ships of a French squadron in the Bay of Biscay in the Second Battle of Cape Finisterre in October 1747.

HMS Vanguard was a 70-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 16 April 1748. She was built by Philemon Ewer at his East Cowes yard on the Isle of Wight to the draught specified by the 1745 Establishment, at a cost of £8,009. She was the fourth vessel of the Royal Navy to bear the name Vanguard.
There were a number of shipbuilders and shipwrights called Philemon Ewer in the villages of Bursledon and Hamble in the River Hamble area of Hampshire, England during the 18th century.

Bursledon is a village on the River Hamble in Hampshire, England. It is located within the borough of Eastleigh. Close to the city of Southampton, Bursledon has a railway station, a marina, dockyards and the Bursledon Windmill. Nearby villages include Swanwick, Hamble-le-Rice, Netley and Sarisbury Green.

HMS Leviathan was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the British Royal Navy, launched on 9 October 1790.

HMS Elephant was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She was built by George Parsons in Bursledon, Hampshire, and launched on 24 August 1786.

Sir Thomas Slade was an English naval architect best known for designing the Royal Navy warship HMS Victory, which served as Lord Nelson's flagship at the Battle of Trafalgar in 1805.

HMS Anson was a ship of the Royal Navy, launched at Plymouth on 4 September 1781. Originally a 64-gun third rate ship of the line, she fought at the Battle of the Saintes.
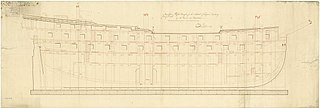
The Crown-class ships of the line were a class of three 64-gun third rates, designed for the Royal Navy by Sir Edward Hunt.
HMS Ardent was a Royal Navy 64-gun third rate. This ship of the line was launched on 21 December 1782 at Bursledon, Hampshire. She disappeared in 1794, believed lost to a fire and explosion.

HMS Anson was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 11 May 1812 at Hull.
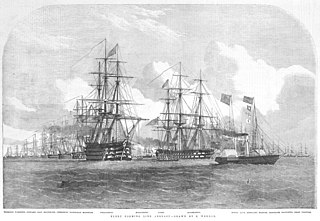
HMS Wellington was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 21 September 1816 at Deptford Dockyard.

HMS Falkland was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built by Holland of New Castle, New Hampshire, and purchased by the navy in 1696.

HMS Devonshire was an 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 5 April 1692.

HMS Lancaster was an 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 3 April 1694.

HMS Cumberland was a 80-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 12 November 1695.
HMS Winchester was a 60-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the English Royal Navy, launched at Bursledon on 11 April 1693.

HMS Gloucester was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line built at Deptford by Joseph Allin the elder for the Royal Navy in 1710/11. She participated in the War of the Spanish Succession. The ship was burned to prevent capture after she was damaged in a storm during Commodore George Anson's voyage around the world in 1742.

HMS Eagle was a 58-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy built at King's Yard in Harwich by John Barnard and launched in 1745.

HMS Ruby was a 50-gun fourth rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, built at Bursledon in Hampshire to the dimensions specified in the 1741 proposals of the 1719 Establishment, and launched on 3 August 1745.

















