Related Research Articles
Several ships and one submarine of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Dreadnought in the expectation that they would "dread nought", i.e. "fear nothing". The 1906 ship was one of the Royal Navy's most famous vessels; battleships built after her were referred to as 'dreadnoughts', and earlier battleships became known as pre-dreadnoughts.

Several ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Resolution. However, the first English warship to bear the name Resolution was actually the first rate Prince Royal, which was renamed Resolution in 1650 following the inauguration of the Commonwealth, and continued to bear that name until 1660, when the name Prince Royal was restored. The name Resolution was bestowed on the first of the vessels listed below:
Six ships and a shore establishment of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Europa, after the Greek mythological character Europa.
Five ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Hebe, after the Greek goddess Hebe.
Eighteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Eagle, after the eagle.
Eight vessels of the British Royal Navy have been named HMS Terrible:
Twelve ships and two shore establishments of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Defiance. Others have borne the name whilst serving as depot ships and tenders to the establishments:

The Gunboat War was a naval conflict between Denmark–Norway and the British during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Navy. In Scandinavia it is seen as the later stage of the English Wars, whose commencement is accounted as the First Battle of Copenhagen in 1801.
Ten ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Fury, whilst another was planned but later cancelled:

HMS Apollo, the fifth ship of the Royal Navy to be named for the Greek god Apollo, was a fifth-rate frigate of the Lively class, carrying 38 guns, launched in 1805 and broken up in 1856.

HMS Armada was a Royal Navy 74-gun third-rate ship of the line, launched in 1810. She was the first ship to carry the name. After a relatively undistinguished career, Armada was sold out of the Navy in 1863 and broken up at Marshall's ship breaking yard in Plymouth.
Six ships of the Royal Navy, and one shore establishment, have borne the name HMS Nimrod, after the biblical figure of Nimrod:
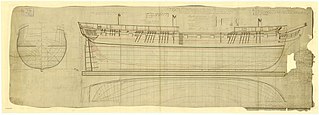
HMS Havannah was a Royal Navy 36-gun fifth-rate frigate. She was launched in 1811 and was one of twenty-seven Apollo-class frigates. She was cut down to a 24-gun sixth rate in 1845, converted to a training ship in 1860, and sold for breaking up in 1905.

Furieuse was a 38-gun frigate of the French Navy. The Royal Navy captured her in 1809 and took her into service as the fifth rate HMS Furieuse. She spent most of her British career in the Mediterranean Sea, though towards the end of the War of 1812 she served briefly on the North American station. She was laid up in 1815 and sold for breaking up in 1816.
William Mounsey CB was a British officer of the Royal Navy. He served during the American Revolutionary, the French Revolutionary and the Napoleonic Wars, rising to the rank of Captain.

The action of 19 January 1799 was a minor naval battle of the French Revolutionary Wars fought in waters of the Strait of Gibraltar, off Punta Europa. A Spanish squadron of 14 gunboats with a mistico as flagship, commanded by Francisco Mourelle de la Rua, attacked a British merchant convoy escorted by several Royal Navy warships, among them a 74-gun ship of the line. The British warships failed to defend the convoy, losing a gunboat sunk and another captured. The convoy also lost a ship and two brigs. For this action Mourelle de la Rua was promoted to frigate captain.

Grinder was a gunboat serving as a tender, rather than a commissioned warship, to HMS Anholt, the British garrison on the island of Anholt during the Gunboat War. Grinder's origins are obscure, but the Danes captured her in 1810 and the British recaptured her in 1811. She was sold in 1832.

HMS Prince William was a 64-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy. She had previously been Nuestra Señora de la Asunción, but was better known as Guipuzcoano, an armed merchantmen of the Spanish Basque Guipuzcoan Company of Caracas.

HMS Grasshopper was a Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1806, captured several vessels, and took part in two notable actions before the Dutch captured her in 1811. She then served The Netherlands navy until she was broken up in 1822.

The Siege of Zara, also known as the Blockade of Zara, was a military event that took place between 22 November and 5 December 1813, during the Adriatic Campaign of the Napoleonic Wars. During the siege, an Anglo-Austrian force under command of George Cadogan in HMS Havannah blockaded and bombarded Zara which was then held by a French garrison. Within two weeks, the garrison surrendered to the attackers.
References
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.