Related Research Articles
Sixteen different ships of the British Royal Navy have been named HMS Greyhound, after the greyhound, a breed of dog notable for its speed.
Twelve ships of the Royal Navy have been called HMS Jason, after the Greek mythological character Jason:

HMS Thetis was a 38-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy launched in 1782.

HMS Diadem was a 64-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 19 December 1782 at Chatham. She participated in the Battle of Cape St Vincent in 1797 under Captain George Henry Towry.
Eleven ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Blonde:
Sixteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Alert, while another was planned:
Twelve ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Mosquito, or the archaic HMS Musquito, after the tropical insect, the Mosquito:

HMS Amphion was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate, the lead ship of her class, built for the Royal Navy during the 1790s. She served during the Napoleonic Wars.
Eight ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Espiegle

HMS Inconstant was a 36-gun Perseverance-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had a successful career serving in the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars, capturing three French warships during the French Revolutionary naval campaigns, Curieux, Unité, and the former British ship HMS Speedy.

HMS Thisbe was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy.
Six ships of the Royal Navy and one naval base have borne the name HMS Stag:

HMS Alligator was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was originally ordered during the American War of Independence but was completed too late to see service during the conflict. Instead she had an active career during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars.

HMS Santa Dorothea was a Royal Navy 34-gun fifth-rate. This frigate had previously served in the Spanish Navy under the name Santa Dorotea. Built in Spain in 1775, she served during the early years of the French Revolutionary Wars until being captured while sailing as part of a squadron off Cartagena. Taken into British service, she spent the rest of the French Revolutionary and most of the Napoleonic Wars under the white ensign until being broken up in 1814.
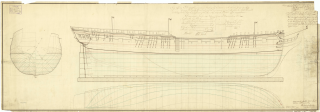
HMS Diana was a 38-gun Artois-class fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1794.
HMS Resource was a 28-gun Enterprise-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1778 and sold for breaking up in 1816.

HMS Venus was the name ship of the 36-gun Venus-class fifth-rate frigates of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1758 and served for more than half a century until 1809. She was reduced from 36 to 32 guns in 1792. She was sold in 1822.
HMS Orpheus was a 32–gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1780, and served for more than a quarter of a century, before she was wrecked in 1807.

Hébé was a 38-gun warship of the French Navy, and lead ship of the Hébé-class frigate. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1782 and took her into service as HMS Hebe, before renaming her HMS Blonde in 1805.
Sir Henry Peake (1753–1825) was a shipbuilder and designer to the Royal Navy who rose to be Surveyor of the Navy.
References
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- Winfield, Rif (2008). British Warships in the Age of Sail 1793–1817: Design, Construction, Careers and Fates. London: Seaforth. ISBN 1-86176-246-1.
- Swinford, Sally (2018) Veteran Diver, Peter Manchee, discusses shipwrecks near Georgetown. Georgetown: South Carolina Maritime Museum.
- Wiberg, Eric (2013) SS Astrea, Dutch, sunk by Italian sub Enrico Tazzoli SE of Bermuda March 1942, rescued by Hebe & Rio Iguazu. Boston: Eric Wiberg