
Royal Charles was an 80-gun first-rate three-decker ship of the line of the English Navy. She was built by Peter Pett and launched at Woolwich Dockyard in 1655, for the navy of the Commonwealth of England. She was originally called Naseby, named in honour of Sir Thomas Fairfax's decisive 1645 victory over the Royalist forces during the English Civil Wars. She was ordered in 1654 as one of a programme of four second rates, intended to carry 60 guns each. However, she was altered during construction to mount a complete battery of guns along the upper deck, and so was reclassed as a first rate.
Bristol was a 44-gun fourth rate vessel of the Commonwealth of England built under the 1651 Programme. She arrived too late for the First Anglo-Dutch War, however, was an active participant in the Second Anglo-Dutch War though in the Third she was no longer used as a line-of battle vessel and reverted to a role of cruising against privateers. She was lost in this role in the English Channel when she was captured by the French. Two weeks she was recaptured by the English and sank in 1709.
HMS Ruby was a 40-gun frigate of the Commonwealth of England, built by Peter Pett at Deptford. She took part in actions during all three of the Anglo-Dutch Wars of 1652–1654, 1665–1667 and 1672–1674. She later served in the West Indies, and in 1683 was sent to the Leeward Islands to protect British settlements against Caribbean pirate raids. In 1687, the English pirate Joseph Bannister was captured by the crew of Ruby and brought to Port Royal for trial. She was rebuilt in 1687. She was captured by the French in October 1707.
HMS Royal Oak was a 100-gun first rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched in 1664 at Portsmouth Dockyard. Royal Oak was built by John Tippetts, Master-Shipwright at Portsmouth 1660-8, who later became Navy Commissioner and subsequently Surveyor of the Navy.

Victory was a great ship of the English Navy, launched in 1620 and in active service during the seventeenth century's Anglo-Dutch Wars. After an seventy-year naval career, she was broken up at Woolwich Dockyard in 1691 and her timbers reused in other vessels.

HMS Triumph was a 42-gun great ship or second rate of the English Royal Navy, built by William Burrell at Deptford Royal Dockyard and launched in 1623. Like many major warships in the 17th century, she was modified at various times during her life, so that her dimensions and tonnage grew during her 65 years of service.

HMS Assurance was a 32-gun fourth-rate of the English Navy, built by Peter Pett I at Deptford Dockyard and launched in 1646. She was in the Parliamentary force during the English Civil War, then the Commonwealth Navy and was incorporated into the Royal Navy after the Restoration in 1660. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the Battles of Dover, Portland, Gabbard and Texel. She foundered in a gale at Woolwich in 1660 and was salved. After the Restoration she partook in the Battle of Lowestoffe, the Four Days Fight and the Texel (1673). She was reduced to a Fifth Rate in 1690 before being sold in 1698.
HMS Dragon was a 38-gun fourth rate of the English Navy, she became part of the Royal Navy after the Restoration, built by the Master Shipwright Henry Goddard at Chatham and launched in 1647. She was the first frigate to be built at Chatham.
Essex was a 48-gun third rate frigate built for the navy of the Commonwealth of England by Phineas Pett II at Deptford, and launched in 1653. Following the restoration of the English monarchy in 1660, she was commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Essex.

The frigate Gloucester was a Speaker-class third rate, commissioned into the Royal Navy as HMS Gloucester after the restoration of the English monarchy in 1660. The ship was ordered in December 1652, built at Limehouse in East London, and launched in 1654. The warship was conveying James Stuart, Duke of York to Scotland, when on 6 May 1682 she struck a sandbank off the Norfolk coast, and quickly sank. The Duke was among those saved, but as many as 250 people drowned, including members of the royal party; it is thought that James's intransigence delayed the evacuation of the passengers and crew.
Bridgewater was a 52-gun third rate Speaker-class frigate built for the navy of the Commonwealth of England at Deptford, and launched in 1654.

Foresight was a 40-gun fourth-rate of the Commonwealth of England, after the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660 she was incorporated into the Navy of the Kingdom of England. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch war being present in the battles of Dungeness, Kentish Knock, Portland, The Gabbard and Scheveningen. She was also present at the Battle of Santa Cruz and the bombardment of Porto Farina, In the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was involved in the Battle of Vagen and the St James Day Fight. During the Third Anglo-Dutch War she participated in the battles of Schooneveld and Texel. For the remainder of her career she was in the West Indies, the Mediterranean and North American waters. She was wrecked south of Cuba in July 1698.
HMS Assistance was one of six 40-gun fourth-rate frigates, built for the Commonwealth of England under the 1650 Programme, after the Restoration of the monarchy in 1660 she was incorporated into the navy of the Kingdom of England. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she partook in the First Anglo-Dutch war being present in the battles of Kentish Knock, Portland and The Gabbard. In the Mediterranean she was present at the Battle of Santa Cruz and the bombardment of Porto Farina, In the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was involved in the Battle of Lowestoft, Battle of Vagen and the St James Day Fight. She did not participate in fleet actions after this. She spent the rest of her service life undergoing several rebuilds and plying the waters as a cruiser protecting British trade and projecting British sovereignty. After nearly 95 years of Service she was sunk as a break water at Sheerness at the end of 1745.
The English ship Kentish was a 40-gun fourth-rate frigate of the Commonwealth of England Navy, built by contract at Deptford and launched in November 1652.
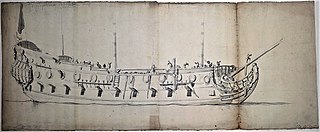
The English ship Winsby was a 44-gun fourth-rate frigate, built for the navy of the Commonwealth of England at Great Yarmouth, and launched in February 1654. Winsby was named for the Parliamentarian victory at the Battle of Winceby (1643).

The Richard was a 70-gun second-rate ship of the line of the navy of the Commonwealth of England, built by the Master Shipwright Christopher Pett at Woolwich Dockyard, and launched in 1658. She was named after Richard Cromwell, to honour his appointment as the Protector in succession to his late father Oliver Cromwell.

Admiral Sir Richard Haddock was an officer of the Royal Navy. He served during the Anglo-Dutch Wars, eventually rising to the rank of Admiral in August 1690. In Herge's Adventures of Tintin, Richard Haddock was one of the inspirations for Captain Haddock's 17th century ancestor, Sir Francis Haddock.
The English ship Drake was a 14-gun sixth rate vessel built under the 1651 Programme at Deptford Dockyard for the Commonwealth of England in 1651/52. During her time in the Commonwealth Navy she spent her time patrolling Home Waters and did not participate actively in the First Anglo-Dutch War. On the restoration she was incorporated into the Royal Navy as HMS Drake. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she fought in the Battle of Lowestoft. She spent the rest of her career patrolling Home Waters before going to Jamaica. She was sold in Jamaica in 1691.
The English ship Martin was a 14-gun sixth rate vessel built under the 1651 Programme at Portsmouth Dockyard for the Commonwealth of England in 1651/52. Her service in the Commonwealth Navy was very active. She participated in the Battles of Dover, Portland and the Gabbard. She was with Robert Blake at Porto Farina. She was the main vessel at the Capture of Jamaica in 1655. With the Restoration she became HMS Martin. During the Second Anglo-Dutch War she was in the initial battle of Lowestoft then the Battle of Vagen. She was sold in February 1667.









