Related Research Articles
Sixteen ships of the Royal Navy have been named HMS Mermaid after the mermaid:

HMS Hannibal was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 15 April 1786, named after the Carthaginian general Hannibal. She is best known for having taken part in the Algeciras Campaign, and for having run aground during the First Battle of Algeciras on 5 July 1801, which resulted in her capture. She then served in the French Navy until she was broken up in 1824.

HMS Majestic was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line launched on 11 December 1785 at Deptford.

HMS Cornwallis was a 74-gun third rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 12 May 1813 at Bombay. She was built of teak. The capture of Java by USS Constitution delayed the completion of Cornwallis as Java had been bringing her copper sheathing from England.

HMS Gloucester was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line built at Deptford by Joseph Allin the elder for the Royal Navy in 1710/11. She participated in the War of the Spanish Succession. The ship was burned to prevent capture after she was damaged in a storm during Commodore George Anson's voyage around the world in 1742.
HMS Rover was a 16-gun sloop-of-war that the Royal Navy purchased in 1796, commissioned in 1798, and that was wrecked in early 1798. In her brief career she captured one French privateer.

HMS Santa Margarita was a 36-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had been built for service with the Spanish Navy, but was captured after five years in service, eventually spending nearly 60 years with the British.
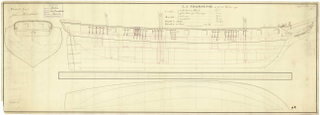
HMS Trompeuse was the French privateer Mercure, captured in 1799. She foundered in the English Channel in 1800.
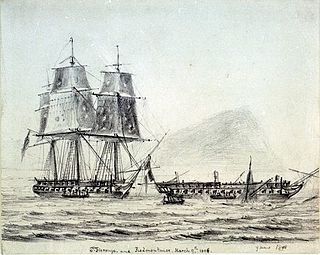
Minerve was a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. She operated in the Mediterranean during the French Revolutionary Wars. Her crew scuttled her at Saint-Florent to avoid capture when the British invaded Corsica in 1794, but the British managed to raise her and recommissioned her in the Royal Navy as the 38-gun fifth rate HMS St Fiorenzo.

HMS Pique was a 38-gun fifth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She had formerly served with the French Navy, initially as the Fleur-de-Lys, and later as the Pique. HMS Blanche captured her in 1795 in a battle that left the Blanche's commander, Captain Robert Faulknor, dead. HMS Pique was taken into service under her only British captain, David Milne, but served for just three years with the Royal Navy before being wrecked in an engagement with the French ship Seine in 1798. The Seine had been spotted heading for a French port and Pique and another British ship gave chase. All three ships ran aground after a long and hard-fought pursuit. The arrival of a third British ship ended French resistance, but while the Seine and Jason were both refloated, attempts to save Pique failed; she bilged and had to be abandoned.
HMS Drake was a 14-gun brig-sloop of the Royal Navy. She was bought from a commercial builder during the early years of the American War of Independence, and went on to support operations in the English Channel and the Caribbean. At one stage she assisted an attack on a French-held island, an expedition commanded by a young Horatio Nelson. Laid up for a time after the end of the American War of Independence, she returned to service shortly before the outbreak of the French Revolutionary Wars. Drake spent most of her time in Caribbean waters, until being declared unfit for service in 1800 and deleted from the navy lists.

L'Espoir was a French brig-sloop that served for 9½ years in the French Navy before HMS Thalia captured her in September 1797. In her subsequent short career in British service as HMS Espoir she captured three prizes, with the capture in 1798 of the more heavily armed Genoese pirate Liguria earning her crew a clasp to the Naval General Service Medal. Espoir was laid up in 1799 and sold in 1804.

HMS Peterel was a 16-gun Pylades-class ship-sloop of the Royal Navy. She was launched in 1794 and was in active service until 1811. Her most famous action was the capture of the French brig Ligurienne when shortly after Peterel captured two merchant ships and sent them off with prize crews, three French ships attacked her. She drove two on shore and captured the largest, the 14-gun Ligurienne. The Navy converted Peterel to a receiving ship at Plymouth in 1811 and sold her in 1827.
HMS Teazer was a schooner purchased in Honduras in 1798 for local use. She was armed with six 4-pounder guns and had a crew of 25 men from the "Colonial Troops".
HMS Towzer was a gunvessel purchased in the West Indies in 1798 for the colony at Honduras. She was a sloop armed with one 18-pounder gun and had a crew of 25 men. Like Tickler, she was under the command of a merchant captain, in Towzer's case a Mr. Gelston, who brought with him some of his crew.
HMS Tickler was a gunvessel purchased in Honduras for local use. She was a sloop armed with one 18-pounder gun and had a crew of 25 men. Like Towzer, she was under the command of a merchant captain, in Tickler's case a Mr. Hosmer, who brought with him some of his crew.
HMS Swinger was a schooner purchased in Honduras in 1798 for local use. She had a crew of 25 men from the "Colonial Troops".
HMS Zenobia was a schooner of the Adonis class of the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic War. She was built and completed at Bermuda using Bermuda cedar in 1806 and commissioned under Lieutenant Archibald Hamilton. She sailed for Norfolk, Virginia, on 22 October 1806.
HMS Matilda was the French privateer Matilde, which HMS Cambrian captured in 1805. The British Royal Navy used her briefly that year. She is last listed in 1805.
HMS George was a sloop that the Royal Navy acquired in 1796, probably as the acquisition of a prize. She was captured by two Spanish privateers of superior force on 3 January, 1798. in a bloody engagement.
References
- Colledge, J. J.; Warlow, Ben (2006) [1969]. Ships of the Royal Navy: The Complete Record of all Fighting Ships of the Royal Navy (Rev. ed.). London: Chatham Publishing. ISBN 978-1-86176-281-8.
- James, William (1837). The Naval History of Great Britain, from the Declaration of War by France in 1793, to the Accession of George IV. R. Bentley.