
The Gunboat War was a naval conflict between Denmark–Norway and the British during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Navy. In Scandinavia it is seen as the later stage of the English Wars, whose commencement is accounted as the First Battle of Copenhagen in 1801.

HMS Hannibal was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line of the Royal Navy, launched on 15 April 1786, named after the Carthaginian general Hannibal. She is best known for having taken part in the Algeciras Campaign, and for having run aground during the First Battle of Algeciras on 5 July 1801, which resulted in her capture. She then served in the French Navy until she was broken up in 1824.
Fifteen ships of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMS Ranger

Minerve was a 40-gun Minerve-class frigate of the French Navy. The British captured her twice and the French recaptured her once. She therefore served under four names before being broken up in 1814:

HMS Majestic was a 74-gun third-rate ship of the line launched on 11 December 1785 at Deptford. She fought at the Battle of the Nile, where she engaged the French ships Tonnant and Heureux, helping to force their surrenders. She was captained by George Blagdon Westcott, who was killed in the battle.
Six vessels of the Royal Navy have borne the name HMSRoyal Charlotte, after Charlotte of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, consort of King George III.

HMS Amphion was a 32-gun fifth rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the Napoleonic Wars.

HMS Gloucester was a 50-gun fourth-rate ship of the line built for the Royal Navy in the 1710s. She participated in the 1701–15 War of the Spanish Succession. The ship was burned to prevent capture after she was damaged in a storm during Commodore George Anson's voyage around the world in 1742.
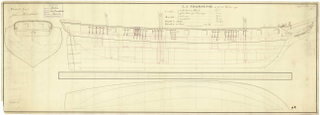
HMS Trompeuse was the French privateer Mercure, captured in 1799. She foundered in the English Channel in 1800.

HMS Epervier was an 18-gun Cruizer-class brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, built by Ross at Rochester, England, and launched on 2 December 1812. USS Peacock captured her in 1814 and took her into service. USS Epervier disappeared in 1815 while carrying dispatches reporting the signing of a treaty with the Dey of Algiers.

HMS Assistance was an Arctic discovery barque of the Royal Navy, and the sixth vessel to carry the name. She began in 1834 as the India-built merchant vessel Acorn. Her name was changed to Baboo. Under that name she transported coolies between Mauritius and India, and immigrants to South Australia. The Royal Navy purchased her in 1850 and named her HMS Assistance. Assistance participated in two Arctic expeditions before her crew abandoned her in the ice in 1854.

HMS Carysfort was a 28-gun Coventry-class sixth-rate frigate of the Royal Navy. She served during the American War of Independence, the French Revolutionary and the Napoleonic Wars in a career that spanned over forty years.
The French lugger Affronteur was launched in 1795 and in 1796-7 participated in the Expédition d'Irlande. In 1803, HMS Doris captured her and she subsequently served the Royal Navy either as a commissioned vessel or, more probably, as His Majesty's hired armed brig Caroline. In 1807 she was either broken up, or became a letter of marque.
HMS Mermaid was a gunvessel purchased in Honduras in 1798 for local use. She was sloop-rigged, armed with one long 9-pounder gun and had a crew of 25 men from the "Colonial Troops".
HMS Teazer was a schooner purchased in Honduras in 1798 for local use. She was armed with six 4-pounder guns and had a crew of 25 men from the "Colonial Troops".
}}
HMS Swinger was a schooner purchased in Honduras in 1798 for local use. She had a crew of 25 men from the "Colonial Troops".
HMS Zenobia was a schooner of the Adonis class of the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic War. She was built and completed at Bermuda using Bermuda cedar in 1806 and commissioned under Lieutenant Archibald Hamilton. She sailed for Norfolk, Virginia, on 22 October 1806.
HMS Spencer was a 16-gun brig-sloop of the Royal Navy, formerly the civilian Sir Charles Grey. The Admiralty purchased her in 1795, after having hired her in 1793-94, and renamed her HMS Lilly in 1800. The French privateer Dame Ambert captured her in 1804 and Lilly became the French privateer Général Ernouf. She blew up in 1805 while in an engagement with HMS Renard.
HMS Matilda was the French privateer Matilde, which HMS Cambrian captured in 1805. The British Royal Navy used her briefly that year. She is last listed in 1805.