
The Courageous class consisted of three battlecruisers known as "large light cruisers" built for the Royal Navy during the First World War. The class was nominally designed to support the Baltic Project, a plan by Admiral of the Fleet Lord Fisher that was intended to land troops on the German Baltic Coast. Ships of this class were fast but very lightly armoured, with only a few heavy guns. They were given a shallow draught, in part to allow them to operate in the shallow waters of the Baltic but also reflecting experience gained earlier in the war. To maximize their speed, the Courageous-class battlecruisers were the first capital ships of the Royal Navy to use geared steam turbines and small-tube boilers.
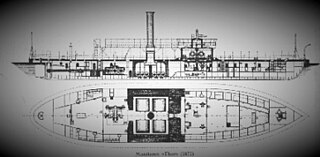
HNoMS Thor was a monitor built for the Royal Norwegian Navy in 1871, named after the Norse god Thor. She was decommissioned in 1918, long after her heavy guns were outdated. She was considered an improvement on the Skorpionen class of monitors, with heavier armour and a wider beam.

HNoMS Thrudvang was a monitor built for the Royal Norwegian Navy in 1869. She was scrapped in 1918, well after her muzzle-loading guns were outdated. The slightly later Thor can be seen as an improvement of the Skorpionen class.

The two Scorpion-class ironclads, HMS Scorpion and HMS Wivern, were ironclad warships ordered by the Confederate States Navy in 1862 and seized in 1863 by the British to prevent their delivery. This would have violated the Foreign Enlistment Act, which forbade British subjects to build or arm any ships for governments at war with governments friendly to Great Britain. The Scorpion class were masted turret ships, each with two gun turrets that were designed to mount a pair of heavy muzzle-loading guns. They were purchased for service in the Royal Navy in 1864 and served briefly with the Channel Fleet before they became guard ships at Bermuda and Hong Kong. Scorpion was sold in 1903 and sank under tow to be scrapped, while Wivern was sold for scrap in 1922.

HMS Magdala was a Cerberus-class breastwork monitor of the Royal Navy, built specifically to serve as a coastal defence ship for the harbour of Bombay in the late 1860s. She was ordered by the India Office for the Bombay Marine. The original specifications were thought to be too expensive and a cheaper design was ordered. While limited to harbour defence duties, the breastwork monitors were described by Admiral George Alexander Ballard as being like "full-armoured knights riding on donkeys, easy to avoid but bad to close with." Aside from gunnery practice Magdala remained in Bombay Harbour for her entire career. The ship was sold for scrap in 1903.

HMS Neptune was an ironclad turret ship originally designed and built in Britain for Brazil, but acquired for the Royal Navy in 1878. Modifications to suit the Royal Navy took three years to complete and the ship did not begin her first commission until 1883 with the Channel Fleet. She was transferred to the Mediterranean Fleet in 1885, but refitted in Portsmouth in 1886–87. Neptune then became the coastguard ship for the 1st Class Reserve at Holyhead until 1893 when she was placed in reserve in Portsmouth. While she was being towed to the breakers in 1903, Neptune unintentionally rammed HMS Victory, then serving as a training hulk for the Naval Signal School, collided with HMS Hero, and narrowly missed several other ships. She was scrapped in Germany in 1904.

The Gorgon-class monitors were a class of monitors in service with the Royal Navy during World War I. Gorgon and her sister ship Glatton were originally built as coastal defence ships for the Royal Norwegian Navy, as HNoMS Nidaros and HNoMS Bjørgvin respectively but requisitioned for British use. Gorgon commissioned first, in June 1918 and bombarded German positions and other targets in Occupied Flanders. She fired the last shots of the war by the Royal Navy into Belgium on 15 October 1918. She was offered for sale after the war, but was used as a target ship when there were no takers. She was sold for scrap in 1928. Glatton was destroyed by a magazine explosion only days after she was completed in September 1918 while in Dover Harbour. She remained a hazard to shipping until the wreck was partially salvaged and the remains moved out of the way during 1925–26.

The John Ericsson-class monitors were a group of five iron-hulled monitors; four were built for the Royal Swedish Navy and one for the Royal Norwegian Navy in the mid to late 1860s. They were designed under the supervision of the Swedish-born inventor, John Ericsson, and built in Sweden. Generally the monitors were kept in reserve for the majority of the year and were only commissioned for several during the year. The ships made one foreign visit to Russia in 1867, but remained in Swedish or Norwegian waters for the rest of their careers. Two of the monitors, Thordon and Mjølner, ran aground, but were salvaged and repaired. Most of the monitors were reconstructed between 1892 and 1905 with more modern guns, but one was scrapped instead as it was not thought cost-effective to rebuild such an old ship. The surviving ships were mobilized during World War I and sold for scrap afterwards.

HSwMS John Ericsson was the lead ship of the John Ericsson-class monitors built for the Royal Swedish Navy in the mid-1860s. She was designed under the supervision of the Swedish-born inventor, John Ericsson, and built in Sweden. John Ericsson made one foreign visit to Russia in 1867, but remained in Swedish or Norwegian waters for the rest of her career. The ship was reconstructed between 1892 and 1895, but generally remained in reserve. She was mobilized during World War I and sold in 1919 for conversion to a barge.

HNoMS Mjølner, named after the hammer of the god Thor, was the fourth of five ships of the John Ericsson-class monitors built for the Royal Swedish Navy and the Royal Norwegian Navy in the mid-1860s. Influenced by the use of ironclads during the American Civil War, the design was based on that of USS Monitor. They were designed under the supervision of the Swedish-born inventor John Ericsson—coincidentally designer of Monitor—and built in Sweden. Mjølner was delivered in 1868. She ran aground the following year, without serious damage, and reconstructed in 1897 with later breech-loading guns. Mjølner was sold for scrap in 1909.

The Cyclops-class monitor was a group of four ironclad breastwork monitors built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s. They were slightly modified versions of the Cerberus-class monitors. The ships were ordered to satisfy demands for local defence during the war scare of 1870, but the pace of construction slowed tremendously as the perceived threat of war declined. The Cyclops-class monitors spent most of their careers in reserve and were finally sold off in 1903.

HMS Gorgon was the first ship commissioned of the four Cyclops-class breastwork monitors built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s.

HMS Hecate was the last ship completed of the four Cyclops-class breastwork monitors built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s.

HMS Hydra was the second ship completed of the four Cyclops-class breastwork monitors built for the Royal Navy during the 1870s. The ships were ordered to satisfy demands for local defence during the war scare of 1870, but the pace of construction slowed tremendously as the perceived threat of war declined. The ship spent most of her career in reserve; her only sustained period in commission was four months during the Russo-Turkish War in 1878 when the British were trying to force the Russians to end the war without seizing Constantinople. Hydra was sold for scrap in 1903.

Smerch was a monitor built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the early 1860s. She was designed by the British shipbuilder Charles Mitchell and built in Saint Petersburg. The ship spent her entire career with the Baltic Fleet. She ran aground and sank shortly after she entered service in 1865. Smerch was refloated and repaired shortly afterwards. She became a training ship sometime after 1892 and was stricken from the Navy List in 1904. The ship was hulked five years later and renamed Blokshiv No. 2. She was in Finland when that country declared its independence in 1918, but was returned to the Soviets after the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk was signed. Blokshiv No. 1, as the ship was now known, was sunk by German artillery fire in 1941. She was salvaged the following year and remained in service until she was stricken in 1959 and subsequently broken up.

Bronenosets was a Uragan-class monitor built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the mid-1860s. The design was based on the American Passaic-class monitor, but was modified to suit Russian engines, guns and construction techniques. The ship was only active when the Gulf of Finland was not frozen, but very little is known about her service. She was stricken in 1900 from the Navy List, converted into a coal barge in 1903 and renamed Barzha No. 324. The ship was lost in a storm sometime during World War I.
Strelets is an Uragan-class monitor built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the mid-1860s. The design was based on the American Passaic-class monitor, but was modified to suit Russian engines, guns and construction techniques. Spending her entire career with the Baltic Fleet, the ship was only active when the Gulf of Finland was not frozen, but very little is known about her service. She was struck from the Navy List in 1900, converted into a floating workshop the following year and renamed Plavmasterskaia No. 1. The ship served as such through 1955. The ship was identified as still afloat in St. Petersburg, Russia in 2015, and attempts are being made by the Foundation for Historic Boats and the Russian Central Military History Museum to restore her.

Perun was an Uragan-class monitor built for the Imperial Russian Navy in the mid-1860s. The design was based on the American Passaic-class monitor, but was modified to suit Russian engines, guns and construction techniques. Spending her entire career with the Baltic Fleet, the ship was only active when the Gulf of Finland was not frozen, but very little is known about her service. Perun was struck from the Navy List in 1900 and became a pilot ship. Renamed Lotsiia (Pilot) in 1915, the ship was damaged during the Kronstadt rebellion of 1921 and laid up afterwards. She was run aground by a flood three years later and then her wreck was scrapped.

The two British Devastation-class battleships of the 1870s, HMS Devastation and HMS Thunderer, were the first class of ocean-going capital ship that did not carry sails, and the first which mounted the entire main armament on top of the hull rather than inside it.













