
A microprocessor is a computer processor for which the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit (IC), or a small number of ICs. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit (CPU). The IC is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, clock-driven, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and provides results as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system.

A minicomputer, or colloquially mini, is a type of smaller general-purpose computer developed in the mid-1960s and sold at a much lower price than mainframe and mid-size computers from IBM and its direct competitors. In a 1970 survey, The New York Times suggested a consensus definition of a minicomputer as a machine costing less than US$25,000, with an input-output device such as a teleprinter and at least four thousand words of memory, that is capable of running programs in a higher level language, such as Fortran or BASIC.

The Motorola 68020 is a 32-bit microprocessor from Motorola, released in 1984. A lower-cost version was also made available, known as the 68EC020. In keeping with naming practices common to Motorola designs, the 68020 is usually referred to as the "020", pronounced "oh-two-oh" or "oh-twenty".

Precision Architecture RISC (PA-RISC) or Hewlett Packard Precision Architecture, is a general purpose computer instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hewlett-Packard from the 1980s until the 2000s.

In computer science, a reduced instruction set computer (RISC) is a computer architecture designed to simplify the individual instructions given to the computer to accomplish tasks. Compared to the instructions given to a complex instruction set computer (CISC), a RISC computer might require more instructions in order to accomplish a task because the individual instructions are written in simpler code. The goal is to offset the need to process more instructions by increasing the speed of each instruction, in particular by implementing an instruction pipeline, which may be simpler to achieve given simpler instructions.
Symbolics, Inc., was a privately held American computer manufacturer that acquired the assets of the former company and continues to sell and maintain the Open Genera Lisp system and the Macsyma computer algebra system.

VAX is a series of computers featuring a 32-bit instruction set architecture (ISA) and virtual memory that was developed and sold by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) in the late 20th century. The VAX-11/780, introduced October 25, 1977, was the first of a range of popular and influential computers implementing the VAX ISA. The VAX family was a huge success for DEC, with the last members arriving in the early 1990s. The VAX was succeeded by the DEC Alpha, which included several features from VAX machines to make porting from the VAX easier.
Very long instruction word (VLIW) refers to instruction set architectures that are designed to exploit instruction level parallelism (ILP). A VLIW processor allows programs to explicitly specify instructions to execute in parallel, whereas conventional central processing units (CPUs) mostly allow programs to specify instructions to execute in sequence only. VLIW is intended to allow higher performance without the complexity inherent in some other designs.
Tandem Computers, Inc. was the dominant manufacturer of fault-tolerant computer systems for ATM networks, banks, stock exchanges, telephone switching centers, 911 systems, and other similar commercial transaction processing applications requiring maximum uptime and zero data loss. The company was founded by Jimmy Treybig in 1974 in Cupertino, California. It remained independent until 1997, when it became a server division within Compaq. It is now a server division within Hewlett Packard Enterprise, following Hewlett-Packard's acquisition of Compaq and the split of Hewlett-Packard into HP Inc. and Hewlett Packard Enterprise.

The HP 2100 is a series of 16-bit minicomputers that were produced by Hewlett-Packard (HP) from the mid-1960s to early 1990s. Tens of thousands of machines in the series were sold over its twenty-five year lifetime, making HP the fourth largest minicomputer vendor during the 1970s.

The HP 3000 series is a family of 16-bit and 32-bit minicomputers from Hewlett-Packard. It was designed to be the first minicomputer with full support for time-sharing in the hardware and the operating system, features that had mostly been limited to mainframes, or retrofitted to existing systems like Digital's PDP-11, on which Unix was implemented. First introduced in 1972, the last models reached end-of-life in 2010, making it among the longest-lived machines of its generation.

HP 9000 is a line of workstation and server computer systems produced by the Hewlett-Packard (HP) Company. The native operating system for almost all HP 9000 systems is HP-UX, which is based on UNIX System V.
Bit slicing is a technique for constructing a processor from modules of processors of smaller bit width, for the purpose of increasing the word length; in theory to make an arbitrary n-bit central processing unit (CPU). Each of these component modules processes one bit field or "slice" of an operand. The grouped processing components would then have the capability to process the chosen full word-length of a given software design.

Am2900 is a family of integrated circuits (ICs) created in 1975 by Advanced Micro Devices (AMD). They were constructed with bipolar devices, in a bit-slice topology, and were designed to be used as modular components each representing a different aspect of a computer control unit (CCU). By using the bit slicing technique, the Am2900 family was able to implement a CCU with data, addresses, and instructions to be any multiple of 4 bits by multiplying the number of ICs. One major problem with this modular technique was that it required a larger number of ICs to implement what could be done on a single CPU IC. The Am2901 chip included an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and 16 4-bit processor register slices, and was the "core" of the series. It could count using 4 bits and implement binary operations as well as various bit-shifting operations. The Am2909 was a 4-bit-slice address sequencer that could generate 4-bit addresses on a single chip, and by using n of them, it was able to generate 4n-bit addresses. It had a stack that could store a microprogram counter up to 4 nest levels, as well as a stack pointer.

The NEC V60 is a CISC microprocessor manufactured by NEC starting in 1986. Several improved versions were introduced with the same instruction set architecture (ISA), the V70 in 1987, and the V80 and AFPP in 1989. They were succeeded by the V800 product families, which is currently produced by Renesas Electronics.

The HP 64000 Logic Development System, introduced 17 September 1979, is a tool for developing hardware and software for products based on commercial microprocessors from a variety of manufacturers. The systems assisted software development with assemblers and compilers for Pascal and C, provided hardware for in-circuit emulation of processors and memory, had debugging tools including logic analysis hardware, and a programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip programmer. A wide variety of optional cards and software were available tailored to particular microprocessors. When introduced the HP 64000 had two distinguishing characteristics. First, unlike most microprocessor development systems of the day, such as the Intel Intellec and Motorola EXORciser, it was not dedicated to a particular manufacturer's microprocessors, and second, it was designed such that up to six workstations would be connected via the HP-IB (IEEE-488) instrumentation bus to a common hard drive and printer to form a tightly integrated network.
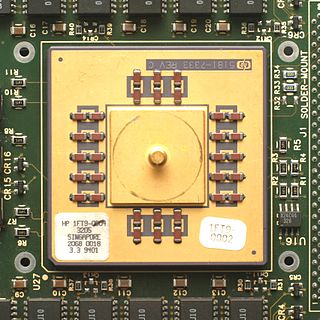
The PA-7100 is a microprocessor developed by Hewlett-Packard (HP) that implemented the PA-RISC 1.1 instruction set architecture (ISA). It is also known as the PCX-T and by its code name Thunderbird. It was introduced in early 1992 and was the first PA-RISC microprocessor to integrate the floating-point unit (FPU) on-die. It operated at 33 – 100 MHz and competed primarily with the Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) Alpha 21064 in the workstation and server markets. PA-7100 users were HP in its HP 9000 workstations and Stratus Computer in its Continuum fault-tolerant servers.
In computer architecture, 16-bit integers, memory addresses, or other data units are those that are 16 bits wide. Also, 16-bit central processing unit (CPU) and arithmetic logic unit (ALU) architectures are those that are based on registers, address buses, or data buses of that size. 16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
The Capricorn family of microprocessors was developed by Hewlett-Packard in the late 1970s for the HP series 80 scientific microcomputers. Capricorn was first used in the HP-85 desktop BASIC computer, introduced in January 1980. Steve Wozniak was inspired to build the Apple to be a computer like the HP 9830, and in 1976, he offered HP rights to the Apple computer. He was turned down and was given a release. When the calculator division started an 8-bit computer project called Capricorn, he left for Apple when he wasn't allowed to work on that project.

The HP 9845C from Hewlett Packard was one of the first desktop computers to be equipped with a color display and light pen for design and illustration work. It was used to create the color war room graphics in the 1983 movie WarGames.














