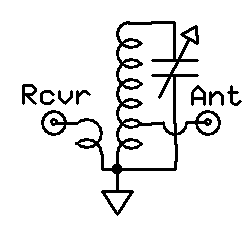Software-defined radio (SDR) is a radio communication system where components that conventionally have been implemented in analog hardware are instead implemented by means of software on a personal computer or embedded system. While the concept of SDR is not new, the rapidly evolving capabilities of digital electronics render practical many processes which were once only theoretically possible.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electromagnetic interrogation pulse from a nearby RFID reader device, the tag transmits digital data, usually an identifying inventory number, back to the reader. This number can be used to track inventory goods.
A low-noise amplifier (LNA) is an electronic component that amplifies a very low-power signal without significantly degrading its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Any electronic amplifier will increase the power of both the signal and the noise present at its input, but the amplifier will also introduce some additional noise. LNAs are designed to minimize that additional noise, by choosing special components, operating points, and circuit topologies. Minimizing additional noise must balance with other design goals such as power gain and impedance matching.

SMA connectors are semi-precision coaxial RF connectors developed in the 1960s as a minimal connector interface for coaxial cable with a screw-type coupling mechanism. The connector has a 50 Ω impedance. SMA was originally designed for use from DC (0 Hz) to 12 GHz, however this has been extended over time and variants are available to 18 GHz and 26.5 GHz. There are also mechanically compatible connectors such as the K-connector which operate up to 40 GHz. The SMA connector is most commonly used in microwave systems, hand-held radio and mobile telephone antennas and, more recently, with WiFi antenna systems and USB software-defined radio dongles. It is also commonly used in radio astronomy, particularly at higher frequencies (5 GHz+).

MCX are coaxial RF connectors developed in the 1980s. They have the same inner contact and insulator dimensions as the SMB connector but are 30% smaller. MCX is standardized in European CECC 22220.

An S meter is an indicator often provided on communications receivers, such as amateur radio or shortwave broadcast receivers. The scale markings are derived from a system of reporting signal strength from S1 to S9 as part of the R-S-T system. The term S unit refers to the amount of signal strength required to move an S meter indication from one marking to the next.
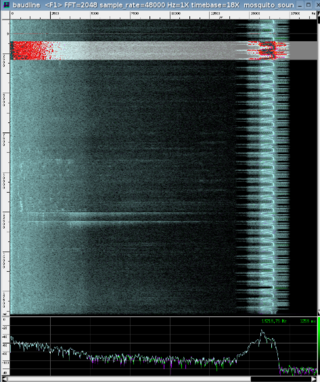
The baudline time-frequency browser is a signal analysis tool designed for scientific visualization. It runs on several Unix-like operating systems under the X Window System. Baudline is useful for real-time spectral monitoring, collected signals analysis, generating test signals, making distortion measurements, and playing back audio files.
The low-rate picture transmission (LRPT) is a digital transmission system, intended to deliver images and data from an orbital weather satellite directly to end users via a VHF radio signal. It is used aboard polar-orbiting, near-Earth weather satellite programs such as MetOp and NPOESS.
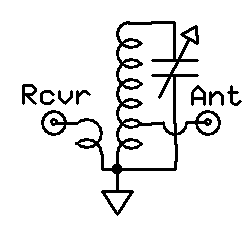
A preselector is a name for an electronic device that connects between a radio antenna and a radio receiver. The preselector is a band-pass filter that blocks troublesome out-of-tune frequencies from passing through from the antenna into the radio receiver that otherwise would be directly connected to the antenna.

The OpenHPSDR project dates from 2005 when Phil Covington, Phil Harman, and Bill Tracey combined their separate projects to form the HPSDR group. It is built around a modular concept which encourages experimentation with new techniques and devices without the need to replace the entire set of boards. The project has expanded from the original group, and several additional people have been involved in recent HPSDR module designs.
A software GNSS receiver is a Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) receiver that has been designed and implemented using software-defined radio.

A baseband processor is a device in a network interface controller that manages all the radio functions ; however, this term is generally not used in reference to Wi-Fi and Bluetooth radios. A baseband processor typically uses its own RAM and firmware. Baseband processors are typically fabricated using CMOS or RF CMOS technology, and are widely used in radio-frequency (RF) and wireless communications.
Encoder receiver transmitter (ERT) is a packet radio protocol developed by Itron for automatic meter reading. The technology is used to transmit data from utility meters over a short range so a utility vehicle can collect meter data without a worker physically inspecting each meter.
The field-programmable RF (FPRF) is a class of radio frequency transceiver microchip that mimics the concept of an FPGA in the radio frequency domain to deliver a multi-standard, multi frequency device.

FT8 or Franke & Taylor 8 is a frequency shift keying digital mode of radio communication used by amateur radio operators worldwide. Following release on June 29, 2017, by its creators Joe Taylor, K1JT, and Steve Franke, K9AN, along with the software package WSJT, FT8 was adopted rapidly and, in little over two years, it became the most popular digital mode recorded by automatic spotting networks such as PSK Reporter. FT8DMC is the most important club dedicated to this mode of digital communication.
The Frontier Radio is a family of software-defined radios developed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory. Four variants have been developed: the Frontier Radio (FR), the Frontier Radio Lite, and the Frontier Radio Multi Lingual, and the Next-Gen Frontier Radio. In addition, the Frontier-S and Frontier-X are licensed derivatives manufactured by commercial aerospace company Rocket Lab.
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.
Osmocom is an open-source software project that implements multiple mobile communication standards, including GSM, DECT, TETRA and others.

Proxmark3 is a multi-purpose hardware tool for radio-frequency identification (RFID) security analysis, research and development. It supports both high frequency and low frequency proximity cards and allows users to read, emulate, fuzz, and brute force the majority of RFID protocols.