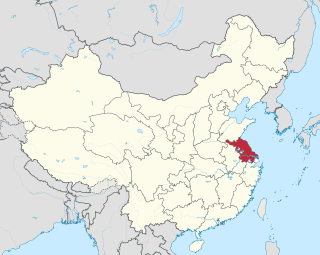
Haizhou or Hai Prefecture (海州) was a zhou (prefecture) in imperial China seated in modern Lianyungang, Jiangsu, China. It existed (intermittently) from 549 to 1912.
Zhou were historical political divisions of China. Formally established during the Han dynasty, zhou exist continuously until the establishment of the Republic of China in 1912—a period of over 2000 years. Zhou were also previously used in Korea, Vietnam, and Japan.

The earliest known written records of the history of China date from as early as 1250 BC, from the Shang dynasty, during the king Wu Ding's reign, who was recorded as the twenty-first Shang king by the written records of Shang dynasty unearthed. Ancient historical texts such as the Records of the Grand Historian and the Bamboo Annals describe a Xia dynasty before the Shang, but no writing is known from the period, and Shang writings do not indicate the existence of the Xia. The Shang ruled in the Yellow River valley, which is commonly held to be the cradle of Chinese civilization. However, Neolithic civilizations originated at various cultural centers along both the Yellow River and Yangtze River. These Yellow River and Yangtze civilizations arose millennia before the Shang. With thousands of years of continuous history, China is one of the world's oldest civilizations, and is regarded as one of the cradles of civilization.

Lianyungang is a prefecture-level city in northeastern Jiangsu province, China. It borders Yancheng to its southeast, Huai'an and Suqian to its south, Xuzhou to its southwest, and the province of Shandong to its north. Its name derives from Lian Island the largest island in Jiangsu Province which lies off its coastline, and Yuntai Mountain (Jiangsu), the highest peak in Jiangsu Province, a few miles from the town center, and the fact that it is a port.
During the Yuan dynasty it was briefly named Haizhou Route (海州路).

The Yuan dynasty, officially the Great Yuan, was the empire or ruling dynasty of China established by Kublai Khan, leader of the Mongolian Borjigin clan. It followed the Song dynasty and preceded the Ming dynasty. Although the Mongols had ruled territories including modern-day North China for decades, it was not until 1271 that Kublai Khan officially proclaimed the dynasty in the traditional Chinese style, and the conquest was not complete until 1279. His realm was, by this point, isolated from the other khanates and controlled most of modern-day China and its surrounding areas, including modern Mongolia. It was the first foreign dynasty to rule all of China and lasted until 1368 which ended in Ming dynasty defeating the Yuan dynasty, the rebuked Genghisid rulers retreated to their Mongolian homeland and continued to rule the Northern Yuan dynasty. Some of the Mongolian Emperors of the Yuan mastered the Chinese language, while others only used their native language and the 'Phags-pa script.
The modern Haizhou District in Lianyungang City retains its name.

Haizhou District is one of three urban districts of Lianyungang, Jiangsu province, China.