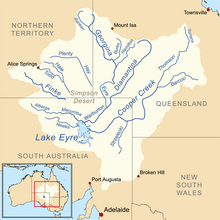
The Simpson Desert is a large area of dry, red sandy plain and dunes in Northern Territory, South Australia and Queensland in central Australia. It is the fourth-largest Australian desert, with an area of 176,500 km2 (68,100 sq mi).

West MacDonnell is a national park in the Northern Territory (Australia) due west of Alice Springs and 1234 km south of Darwin. It extends along the MacDonnell Ranges west of Alice Springs.

Alice Springs is the third-largest town in the Northern Territory of Australia. Known as Stuart until 31 August 1933, the name Alice Springs was given by surveyor William Whitfield Mills after Alice, Lady Todd, wife of the telegraph pioneer Sir Charles Todd. Now colloquially known as The Alice or simply Alice, the town is situated roughly in Australia's geographic centre. It is nearly equidistant from Adelaide and Darwin.

The Lake Eyre basin is a drainage basin that covers just under one-sixth of all Australia. It is the largest endorheic basin in Australia and amongst the largest in the world, covering about 1,200,000 square kilometres (463,323 sq mi), including much of inland Queensland, large portions of South Australia and the Northern Territory, and a part of western New South Wales. The basin is also one of the largest, least-developed arid zone basins with a high degree of variability anywhere. It supports about 60,000 people and a large amount of wildlife, and has no major irrigation, diversions or flood-plain developments. Low density grazing is the major land use, occupying 82% of the total land within the basin.

Lake Disappointment, or Kumpupintil/Kumpupirntily in the Western Desert Language, is an endorheic salt lake located in the Pilbara region of Western Australia.

The Cooper Creek is one of the most famous rivers in Australia because it was the site of the death of the explorers Burke and Wills in 1861. It is sometimes known as the Barcoo River from one of its tributaries and is one of three major Queensland river systems that flow into the Lake Eyre basin. The flow of the creek depends on monsoonal rains falling months earlier and many hundreds of kilometres away in eastern Queensland. At 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) in length it is the second longest inland river system in Australia after the Murray-Darling system.

The Walker River is a river in west-central Nevada in the United States, approximately 62 miles (100 km) long. Fed principally by snowmelt from the Sierra Nevada mountains of California, it drains an arid portion of the Great Basin southeast of Reno and flows into the endorheic basin of Walker Lake. The river is an important source of water for irrigation in its course through Nevada; water diversions have reduced its flow such that the level of Walker Lake has fallen 160 feet (49 m) between 1882 and 2010. The river was named for explorer Joseph Reddeford Walker.

The Liard River of the North American boreal forest flows through Yukon, British Columbia and the Northwest Territories, Canada. Rising in the Saint Cyr Range of the Pelly Mountains in southeastern Yukon, it flows 1,115 kilometres (693 mi) southeast through British Columbia, marking the northern end of the Rocky Mountains and then curving northeast back into Yukon and Northwest Territories, draining into the Mackenzie River at Fort Simpson, Northwest Territories. The river drains approximately 277,100 square kilometres (107,000 sq mi) of boreal forest and muskeg.

The Finke River, or Larapinta (Arrernte), is a river in central Australia, one of four main rivers of the Lake Eyre Basin and thought to be the oldest riverbed in the world. It flows for only a few days a year and when this happens, its water usually disappears into the sands of the Simpson Desert, rarely if ever reaching Lake Eyre.

The Todd River is an ephemeral river in the southern Northern Territory, central Australia. The origins of the Todd River are in the MacDonnell Ranges, where it flows past the Telegraph Station, almost through the centre of Alice Springs, through Heavitree Gap at the southern end of Alice Springs and continuing on for some distance, passing through the western part of the Simpson Desert, as it becomes a tributary of the Hale River, and eventually flowing into Lake Eyre in South Australia.
The MacDonnell Ranges, or Tjoritja in Arrernte, is a mountain range and an interim Australian bioregion located in southern Northern Territory and has an area of 3,929,444 hectares. The range is a 644 km (400 mi) long series of mountains in central Australia, consisting of parallel ridges running to the east and west of Alice Springs. The mountain range contains many spectacular gaps and gorges as well as areas of Aboriginal significance.
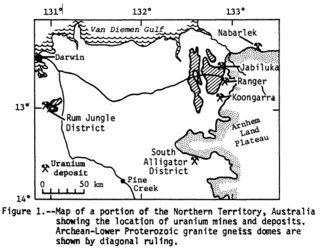
Alligator Rivers is the name of an area in an Arnhem Land region of the Northern Territory of Australia, containing three rivers, the East, West, and South Alligator Rivers. It is regarded as one of the richest biological regions in Australia, with part of the region in the Kakadu National Park. It is an Important Bird Area (IBA), lying to the east of the Adelaide and Mary River Floodplains IBA. It also contains mineral deposits, especially uranium, and the Ranger Uranium Mine is located there. The area is also rich in Australian Aboriginal art, with 1500 sites. The Kakadu National Park is one of the few World Heritage sites on the list because of both its natural and human heritage values. They were explored by Lieutenant Phillip Parker King in 1820, who named them in the mistaken belief that the crocodiles in the estuaries were alligators.

The Larapinta Trail is an extended walking track in the Northern Territory of Australia. Its total length covers 223 kilometres (139 mi) from east to west, with the eastern end at Alice Springs and the western end at Mount Sonder, one of the territory's highest mountains. It follows the West MacDonnell Ranges, sometimes along the ridge line, other times on the plain below, in the West MacDonnell National Park.

The Georgina River is the north-westernmost of the three major rivers of the Channel Country in Central West Queensland, that also flows through a portion of the Northern Territory, in central Australia. Part of the Lake Eyre basin, the Georgina flows in extremely wet years into Lake Eyre.

John Ross was a Scottish Australian drover and explorer.

Brunswick River is an open mature wave dominated barrier estuary, located in the Northern Rivers region of New South Wales, Australia.
The geography of South Australia incorporates the south central part of the continent of Australia. It is one of the six states of Australia. South Australia is bordered on the west by Western Australia, to the north by the Northern Territory, Queensland to the northeast, and both New South Wales and Victoria to the east. South Australia's south coast is flanked by the Great Australian Bight and the Indian Ocean, although it is referred to locally as the Southern Ocean.

The Northern Territory (NT) occupies the north central part of the continent of Australia. The Northern Territory borders are to the west with Western Australia, the Western Australia border being near the 129° east longitude. The NT to the south with the South Australian border being the 26th parallel south latitude. To the east the NT with the Queensland border along the 138° east longitude.

The Bulloo RiverBUUL-oo is an isolated drainage system in western Queensland, central Australia. Its floodplain, which extends into northern New South Wales, is an important area for waterbirds when inundated. It comprises most of the Bulloo-Bancannia drainage basin.

Newcastelia cephalantha is a species of plant belonging to the mint family, Lamiaceae, and native to several Australian states: Queensland, South Australia, Western Australia and the Northern Territory