
A pension is a fund into which amounts are paid regularly during an individual's working career, and from which periodic payments are made to support the person's retirement from work. A pension may be:

In the United States, Social Security is the commonly used term for the federal Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) program and is administered by the Social Security Administration (SSA). The Social Security Act was passed in 1935, and the existing version of the Act, as amended, encompasses several social welfare and social insurance programs.

The Social Security Act of 1935 is a law enacted by the 74th United States Congress and signed into law by U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt. The law created the Social Security program as well as insurance against unemployment. The law was part of Roosevelt's New Deal domestic program.

Lionel Robert Jospin is a French politician who served as Prime Minister of France from 1997 to 2002.

Einar Henry Gerhardsen was a Norwegian politician who served as the 22nd prime minister of Norway from 1945 to 1951, 1955 to 1963 and 1963 to 1965. With a total of 16 years in office, he is the longest serving Prime Minister in Norway since the introduction of parliamentarism. He was the leader of the Labour Party from 1945 to 1965.
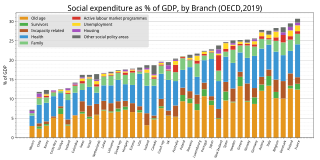
A welfare state is a form of government in which the state protects and promotes the economic and social well-being of its citizens, based upon the principles of equal opportunity, equitable distribution of wealth, and public responsibility for citizens unable to avail themselves of the minimal provisions for a good life.

Welfare spending is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifically to social insurance programs which provide support only to those who have previously contributed, as opposed to social assistance programs which provide support on the basis of need alone. The International Labour Organization defines social security as covering support for those in old age, support for the maintenance of children, medical treatment, parental and sick leave, unemployment and disability benefits, and support for sufferers of occupational injury.

End Poverty in California (EPIC) was a political campaign started in 1934 by socialist writer Upton Sinclair. The movement formed the basis for Sinclair's campaign for Governor of California in 1934. The plan called for a massive public works program, sweeping tax reform, and guaranteed pensions. It gained major popular support, with thousands joining End Poverty Leagues across the state. EPIC never came to fruition due to Sinclair's defeat in the 1934 election, but is seen as an influence on New Deal programs enacted by President Franklin D. Roosevelt.

Francis Everett Townsend was an American physician and political activist in California. In 1933, he devised an old-age pension scheme to help alleviate the Great Depression. Known as the "Townsend Plan", this proposal would pay every person over age 60 $200 per month, with the requirement it all be spent quickly. It was never enacted but the popularity of the Plan influenced Congress to start the Social Security system, which involved much smaller amounts. The Plan was organized by real estate salesman Robert Clements, who made Townsend only a figurehead while the Plan expanded to thousands of clubs in many states. Townsend was born just outside Fairbury, Illinois, where he is memorialized by a post office named in his honor.

Irving Fisher was an American economist, statistician, inventor, eugenicist and progressive social campaigner. He was one of the earliest American neoclassical economists, though his later work on debt deflation has been embraced by the post-Keynesian school. Joseph Schumpeter described him as "the greatest economist the United States has ever produced", an assessment later repeated by James Tobin and Milton Friedman.

The Progressive Era (1901–1929) was a period in the United States during the early 20th century of widespread social activism and political reform across the country. Progressives sought to address the problems caused by rapid industrialization, urbanization, immigration, and political corruption as well as the enormous concentration of industrial ownership in monopolies. Progressive reformers were alarmed by the spread of slums, poverty, and the exploitation of labor. Multiple overlapping progressive movements fought perceived social, political, and economic ills by advancing democracy, scientific methods, and professionalism; regulating business; protecting the natural environment; and improving working and living conditions of the urban poor.

Sheridan Downey was an American lawyer and a Democratic politician from Wyoming and California. In 1934, he ran for Lieutenant Governor of California as Upton Sinclair's running mate in the "End Poverty in California" campaign. In 1938 he was elected U.S. Senator from California, and he served from 1939 to 1950.
The Townsend Plan, officially the Old-Age Revolving Pensions (OARP) plan, was a September 1933 proposal by California physician Francis Townsend for an old-age pension in response to the Great Depression, leading to a social and political movement. At its peak, the OARP advocacy group claimed more than 750,000 members. The movement demonstrated nationwide demand for old-age pensions, leading Congress and President Franklin D. Roosevelt to adopt a national Social Security policy, though Townsend's original plan called for greater benefits to a greater number of people than Social Security provided.
The history of Illinois may be defined by several broad historical periods, namely, the pre-Columbian period, the era of European exploration and colonization, its development as part of the American frontier, its early statehood period, growth in the 19th and 20th centuries, and contemporary Illinois of today.
Liberalism in the United States is based on concepts of unalienable rights of the individual. The fundamental liberal ideals of consent of the governed, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, freedom of religion, the separation of church and state, the right to due process, and equality before the law are widely accepted as a common foundation of liberalism. It differs from liberalism worldwide because the United States has never had a resident hereditary aristocracy, and avoided much of the class warfare that characterized Europe. According to American philosopher Ian Adams, "all U.S. parties are liberal and always have been. Essentially they espouse classical liberalism, that is a form of democratised Whig constitutionalism plus the free market. The point of difference comes with the influence of social liberalism and the proper role of government."

Ham and eggs is a dish combining various preparations of those two ingredients. It has been described as a staple of "an old-fashioned American breakfast". It is also served as a lunch and dinner dish. Some notable people have professed an affinity for the dish, such as American entrepreneur Duncan Hines and the Manchurian Emperor Puyi. Similar dishes include bacon and eggs, Spanish eggs, the Denver omelette and eggs Benedict.
Unreported employment, also known as money under the table, working under the table, off the books, cash-in-the-claw, money-in-the-paw, or illicit work is illegal employment that is not reported to the government. The employer or the employee often does so for tax evasion or avoiding and violating other laws such as obtaining unemployment benefits while being employed. The working contract is made without social security costs and does typically not provide health insurance, paid parental leave, paid vacation or pension funds. It is a part of what has been called the underground economy, shadow economy, black market or the non-observed economy.

The 1924 United States presidential election in California took place on November 4, 1924, as part of the 1924 United States presidential election. State voters chose 13 electors, or representatives to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

William Harvey Kindig, was a candidate for California state controller in 1934, Los Angeles City Council member from 1935 to 1937 and a sponsor of the Ham and Eggs movement for old-age pensions in California in 1939.
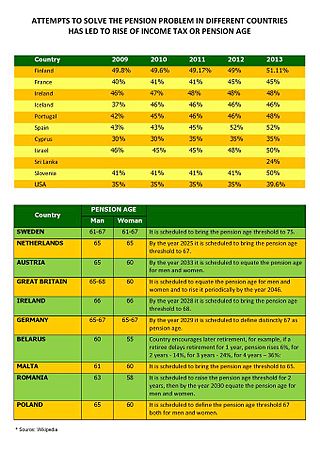
There are various types of Pensions in Armenia, including social pensions, mandatory funded pensions, or voluntary funded pensions. Currently, Amundi-ACBA and Ampega act as the mandatory pension fund managers within Armenia.
















