
The Egyptian language, or Ancient Egyptian, is an extinct branch of the Afro-Asiatic languages that was spoken in ancient Egypt. It is known today from a large corpus of surviving texts, which were made accessible to the modern world following the decipherment of the ancient Egyptian scripts in the early 19th century.

Egyptian hieroglyphs were the formal writing system used in Ancient Egypt for writing the Egyptian language. Hieroglyphs combined logographic, syllabic and alphabetic elements, with more than 100 distinct characters. Cursive hieroglyphs were used for religious literature on papyrus and wood. The later hieratic and demotic Egyptian scripts were derived from hieroglyphic writing, as was the Proto-Sinaitic script that later evolved into the Phoenician alphabet. Through the Phoenician alphabet's major child systems, the Egyptian hieroglyphic script is ancestral to the majority of scripts in modern use, most prominently the Latin and Cyrillic scripts and the Arabic script, and possibly the Brahmic family of scripts.

Seshat was the ancient Egyptian goddess of writing, wisdom, and knowledge. She was the daughter of Thoth. She was seen as a scribe and record keeper; her name means "female scribe". She is credited with inventing writing. She also became identified as the goddess of sciences, accounting, architecture, astronomy, astrology, building, mathematics, and surveying.
A determinative, also known as a taxogram or semagram, is an ideogram used to mark semantic categories of words in logographic scripts which helps to disambiguate interpretation. They have no direct counterpart in spoken language, though they may derive historically from glyphs for real words, and functionally they resemble classifiers in East Asian and sign languages. For example, Egyptian hieroglyphic determinatives include symbols for divinities, people, parts of the body, animals, plants, and books/abstract ideas, which helped in reading, but none of which were pronounced.
The Hand drill is a hieroglyph,, used in ancient Egypt from the earliest dynasties. As a hieroglyph, it can also be used as a determinative for words related to the profession of vase, bowl, pot-making, etc., typically from fine-grained, colorful rare stone, for example unguent jars. The size of drills was small-to-large, small for small unguent jars, and large for more massive, grain-storing pottery. The original jars found in tombs were more often used for ceremonial usages, presumably the reason they are found as grave goods or tomb offerings.

The ancient Egyptian Mast hieroglyph is one of the oldest language hieroglyphs from Ancient Egypt. It is used on a famous label of Pharaoh Den of the First dynasty, but forms part of the location hieroglyph: Emblem of the East.
The ancient Egyptian Shuti, a two-feather adornment for crowns, is part of a series of hieroglyphs for "crowns"; usage as a hieroglyph is not as common as the actual crown represented in Egyptian art, and artworks.
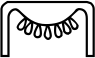
The ancient Egyptian Censer pot, is most commonly seen in Ancient Egyptian iconography as an offering, held in hand by the offering person or god. Many pots are offered in hands, or a single hand with offerings of oils, a liquid-(water), or other item in the pot.

The ancient Egyptian Hill-country or "Foreign land" hieroglyph (𓈉) is a member of the sky, earth, and water hieroglyphs. A form of the hieroglyph in color, has a green line-(banding) at the base of the hieroglyph. The hieroglyph refers to the hills, and mountains, on both sides of the Nile River, and thus the green references the verdant black farming land adjacent to the river proper. It is coded N25 in Gardiner's sign list, and U+13209 in Unicode. It is a determinative hieroglyph, simply conveying a meaning, and has no phonetic value.

The pectorals of ancient Egypt were a form of jewelry, often in the form of a brooch. They are often also amulets, and may be so described. They were mostly worn by richer people and the pharaoh.
The Egyptian hieroglyph representing gold, phonetic value nb, is important due to its use in the Horus-of-Gold name, one of the Fivefold Titulary names of the Egyptian pharaoh.

The ancient Egyptian Bone-with-meat hieroglyph represented: "ancestry, inherit", and phonetic isw, iw' ; a determinative for the femur, (iw'); and swt, for the tibia.

The ancient Egyptian Sky hieroglyph,, is Gardiner sign listed no. N1, within the Gardiner signs for sky, earth, and water.

The ancient Egyptian Pick hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed nos. U17, U18 is a portrayal of a 'pick upon the side view of a block'; it is in the Gardiner subset for agriculture, crafts, and professions.

The Egyptian hieroglyph ndj (nḏ) has the shape of a cross. It presumably depicts some type of tool such as a mill. It is often written alongside the nu "pot" hieroglyph (W24). It is used as an ideogram or determinative in the context of "grains", "grinding stone", "grind", "to rub out".

The ancient Egyptian knot hieroglyph, or girdle knot, Gardiner sign listed no. S24, portrays a reef knot. Besides its use as a hieroglyph, it has usage in statuary and reliefs. The knot hieroglyph is also an amulet, typically made of worked stone, or as jewellery elements.

The ancient Egyptian Scribe equipment hieroglyph 𓏞, or its reversed form 𓏟, portrays the equipment of the scribe. Numerous scribes used the hieroglyph in stating their name, either on papyrus documents, but especially on statuary or tomb reliefs.

The ancient Egyptian Obelisk hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. O25 is a portrayal of the obelisk. The hieroglyph is commonly used on erected Egyptian obelisks, as there is often a discussion of the event of its erection: a historical event, as well as an accomplishment of the pharaoh, and the Egyptian Kingdom.

The ancient Egyptian Arms-in-embrace hieroglyph, Gardiner sign listed no. D32 is a portrayal of the embracing human arms. The hieroglyph is in the large Gardiner sign list category of Parts of the Human Body.


















