Related Research Articles
In mathematics, the term "almost all" means "all but a negligible quantity". More precisely, if is a set, "almost all elements of " means "all elements of but those in a negligible subset of ". The meaning of "negligible" depends on the mathematical context; for instance, it can mean finite, countable, or null.
The P versus NP problem is a major unsolved problem in theoretical computer science. Informally, it asks whether every problem whose solution can be quickly verified can also be quickly solved.
In computer science, the computational complexity or simply complexity of an algorithm is the amount of resources required to run it. Particular focus is given to computation time and memory storage requirements. The complexity of a problem is the complexity of the best algorithms that allow solving the problem.
Discrete mathematics is the study of mathematical structures that can be considered "discrete" rather than "continuous". Objects studied in discrete mathematics include integers, graphs, and statements in logic. By contrast, discrete mathematics excludes topics in "continuous mathematics" such as real numbers, calculus or Euclidean geometry. Discrete objects can often be enumerated by integers; more formally, discrete mathematics has been characterized as the branch of mathematics dealing with countable sets. However, there is no exact definition of the term "discrete mathematics".
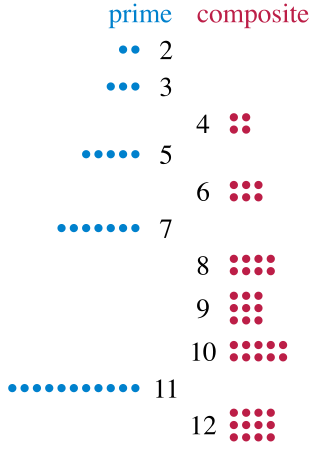
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways of writing it as a product, 1 × 5 or 5 × 1, involve 5 itself. However, 4 is composite because it is a product (2 × 2) in which both numbers are smaller than 4. Primes are central in number theory because of the fundamental theorem of arithmetic: every natural number greater than 1 is either a prime itself or can be factorized as a product of primes that is unique up to their order.
A computer algebra system (CAS) or symbolic algebra system (SAS) is any mathematical software with the ability to manipulate mathematical expressions in a way similar to the traditional manual computations of mathematicians and scientists. The development of the computer algebra systems in the second half of the 20th century is part of the discipline of "computer algebra" or "symbolic computation", which has spurred work in algorithms over mathematical objects such as polynomials.

In mathematics, an expression is a written arrangement of symbols following the context-dependent, syntactic conventions of mathematical notation. Symbols can denote numbers, variables, operations, and functions. Other symbols include punctuation marks and brackets, used for grouping where there is not a well-defined order of operations.

Øystein Ore was a Norwegian mathematician known for his work in ring theory, Galois connections, graph theory, and the history of mathematics.

Hendrik Pieter (Henk) Barendregt is a Dutch logician, known for his work in lambda calculus and type theory.
In computer science, termination analysis is program analysis which attempts to determine whether the evaluation of a given program halts for each input. This means to determine whether the input program computes a total function.
David Alan Plaisted is a computer science professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
In mathematics, arithmetic combinatorics is a field in the intersection of number theory, combinatorics, ergodic theory and harmonic analysis.
Dexter Campbell Kozen is an American theoretical computer scientist. He is Professor Emeritus and Joseph Newton Pew, Jr. Professor in Engineering at Cornell University.

Jacob Alexander Lurie is an American mathematician who is a professor at the Institute for Advanced Study. In 2014, Lurie received a MacArthur Fellowship. Lurie's research interests are algebraic geometry, topology, and homotopy theory.
Jan Willem Klop is a professor of applied logic at Vrije Universiteit in Amsterdam. He holds a Ph.D. in mathematical logic from Utrecht University. Klop is known for his work on the algebra of communicating processes, co-author of TeReSe and his fixed point combinator

Samuel R. (Sam) Buss is an American computer scientist and mathematician who has made major contributions to the fields of mathematical logic, complexity theory and proof complexity. He is currently a professor at the University of California, San Diego, Department of Computer Science and Department of Mathematics.
Henderik Alex (Erik) Proper is a Dutch computer scientist, an FNR PEARL Laureate, and a senior research manager within the Computer Science (ITIS) department of the Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology (LIST). He is also adjunct professor in data and knowledge engineering at the University of Luxembourg. He is known for work on conceptual modeling, enterprise architecture and enterprise engineering.
Nachum Dershowitz is an Israeli computer scientist, known e.g. for the Dershowitz–Manna ordering and the multiset path ordering used to prove termination of term rewrite systems.
Deepak Kapur is a Distinguished Professor in the Department of Computer Science at the University of New Mexico.
References
- ↑ Arts, Thomas, and Jürgen Giesl. "Termination of term rewriting using dependency pairs." Theoretical Computer Science 236.1 (2000): 133-178.
- ↑ Ohlebusch, Enno. Advanced topics in term rewriting. Springer, 2002.
- ↑ Hans Zantema at the Mathematics Genealogy Project
- ↑ Thierry Coquand and Henrik Persson. A proof-theoretical investigation of Zantema's problem. Computer Science Logic. Lecture Notes in Computer Science Volume 1414, pp. 177-188, Springer, 1988.
- ↑ Hans Zantema. Playing with Infinity: Turtles, Patterns and Pictures, CRC Press, 2024.