
The Battle of Marais des Cygnes took place on October 25, 1864, in Linn County, Kansas, during Price's Missouri Raid in the American Civil War. It is also known as the Battle of Trading Post. In late 1864, Confederate Major General Sterling Price invaded the state of Missouri with a cavalry force, attempting to draw Union troops away from the primary theaters of fighting further east. After several victories early in the campaign, Price's Confederate troops were defeated at the Battle of Westport on October 23 near Kansas City, Missouri. The Confederates then withdrew into Kansas, camping along the banks of the Marais des Cygnes River on the night of October 24. Union cavalry pursuers under Brigadier General John B. Sanborn skirmished with Price's rearguard that night, but disengaged without participating in heavy combat.

The Battle of Mine Creek, also known as the Battle of the Osage, was fought on October 25, 1864, in Linn County, Kansas as part of Price's Missouri Expedition during the American Civil War. Major General Sterling Price of the Confederate States Army had begun an expedition in September 1864 to restore Confederate control of Missouri. After being defeated at the Battle of Westport near Kansas City, Missouri on October 23, Price's army began to retreat south through Kansas. Early on October 25, Price's army was defeated at the Battle of Marais des Cygnes. After Marais des Cygnes, the Confederates fell back, but were stalled at the crossing of Mine Creek while a wagon train attempted to cross.
The Battle of Glasgow was fought on October 15, 1864, in and near Glasgow, Missouri, as part of Price's Missouri Expedition during the American Civil War. The battle resulted in the capture of needed weapons and improved Confederate morale, which had been dented after a defeat in the Battle of Pilot Knob.
The Second Battle of Lexington was a minor battle fought during Price's Raid as part of the American Civil War. Hoping to draw Union Army forces away from more important theaters of combat and potentially affect the outcome of the 1864 United States presidential election, Sterling Price, a major general in the Confederate States Army, led an offensive into the state of Missouri on September 19, 1864. After a botched attack at the Battle of Pilot Knob, the strength of the Union defenses at Jefferson City led Price to abandon the main goals of his campaign.

The Battle of Little Blue River was fought on October 21, 1864, as part of Price's Raid during the American Civil War. Major General Sterling Price of the Confederate States Army led an army into Missouri in September 1864 with hopes of challenging Union control of the state. During the early stages of the campaign, Price abandoned his plan to capture St. Louis and later his secondary target of Jefferson City. The Confederates then began moving westwards, brushing aside Major General James G. Blunt's Union force in the Second Battle of Lexington on October 19. Two days later, Blunt left part of his command under the authority of Colonel Thomas Moonlight to hold the crossing of the Little Blue River, while the rest of his force fell back to Independence. On the morning of October 21, Confederate troops attacked Moonlight's line, and parts of Brigadier General John B. Clark Jr.'s brigade forced their way across the river. A series of attacks and counterattacks ensued, neither side gaining a significant advantage.
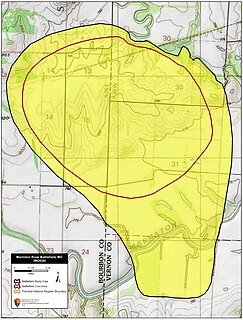
The Battle of Marmiton River, also known as Shiloh Creek or Charlot's Farm, occurred on October 25, 1864, in Vernon County, Missouri during the American Civil War. Major General Sterling Price of the Confederate States Army commenced an expedition into Missouri in September 1864, with hopes of challenging Union control of the state. After a defeat at the Battle of Westport on October 23, Price began to retreat south, and suffered a serious defeat at the Battle of Mine Creek early on October 25. The afternoon of the 25th, Price's wagon train became stalled at the crossing of the Marmaton River in western Missouri. A delaying force led by Brigadier General Joseph O. Shelby attempted to hold off Union cavalry commanded by Brigadier General John McNeil and Lieutenant Colonel Frederick W. Benteen. Shelby was unable to drive off the Union force, although fatigue of the Union cavalry's horses prevented close-quarters action. At nightfall, the Confederates disengaged and destroyed much of their wagon train. Price was again defeated on October 28 at the Second Battle of Newtonia, and the Confederate retreat continued until the survivors reached Texas in early December.

Landis's Missouri Battery, also known as Landis's Company, Missouri Light Artillery, was an artillery battery that served in the Confederate States Army during the early stages of the American Civil War. The battery was formed when Captain John C. Landis recruited men from the Missouri State Guard in late 1861 and early 1862. The battery fielded two 12-pounder Napoleon field guns and two 24-pounder howitzers for much of its existence, and had a highest reported numerical strength of 62 men. After initially serving in the Trans-Mississippi Theater, where it may have fought in the Battle of Pea Ridge, the unit was transferred east of the Mississippi River. The battery saw limited action in 1862 at the Battle of Iuka and at the Second Battle of Corinth.
Wade's Battery was an artillery battery in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The battery was mustered into Confederate service on December 28, 1861; many of the members of the battery had previously served in the Missouri State Guard. Assigned to the First Missouri Brigade, the battery saw action at the Battle of Pea Ridge and the Second Battle of Corinth in 1862. In 1863, the battery fought at the Battle of Grand Gulf, where Captain William Wade, first commander of the battery, was killed. The battery later saw action at the Battle of Champion Hill, Battle of Big Black River Bridge, and the Siege of Vicksburg. When the Confederates surrendered at the end of the Siege of Vicksburg, the men of the battery became prisoners of war. After a prisoner exchange, the men of the battery were combined with Landis's Battery and Guibor's Battery on October 3, 1863, and Wade's Battery ceased to exist as a separate unit.

The 6th Missouri Infantry was an infantry regiment of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The regiment was formed on August 26, 1862, when two existing units were combined. Later that year, the regiment was then lightly engaged at the Battle of Iuka and saw heavy action at the Second Battle of Corinth. In 1863, the regiment was engaged at the Battle of Port Gibson, and was part of a major charge at the Battle of Champion Hill. After a defeat at the Battle of Big Black River Bridge, the regiment took part in the siege of Vicksburg, where it saw heavy fighting. The siege of Vicksburg ended on July 4 with a Confederate surrender; after being exchanged, the regiment combined with the 2nd Missouri Infantry to form the 2nd and 6th Missouri Infantry (Consolidated). The 6th Missouri Infantry ceased to exist as a separate unit.
The 3rd Missouri Light Battery was an artillery battery of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The battery originated as a Missouri State Guard unit active in late 1861, and was officially transferred to the Confederate States Army on January 28, 1862. The battery provided artillery support at the Battle of Pea Ridge in March 1862, and was lightly engaged at the Battle of Iuka in September. In October 1862, the battery was lightly engaged at the Second Battle of Corinth and saw action at the Battle of Davis Bridge, where it lost at least one cannon. The 3rd Light Battery saw action at the Battle of Champion Hill on May 16, 1863, and had its cannons captured at the Battle of Big Black River Bridge the next day. After participating in the Siege of Vicksburg, the battery was captured on July 4, 1863 and was paroled and exchanged. The battery was then consolidated with the Jackson Missouri Battery; the 3rd Light Battery designation was continued. In early 1864, the battery received replacement cannons and was assigned to the defense of Mobile Bay. The 3rd Light Battery saw action at the Battle of Spanish Fort in March and April 1865. When the Confederate Department of Alabama, Mississippi, and East Louisiana surrendered on May 4, 1865, the battery was again captured; the men of the battery were paroled on May 10, ending their military service.
The 9th Missouri Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The unit was formed on November 16, 1862, and was originally commanded by Colonel John Bullock Clark Jr. At the Battle of Prairie Grove on December 7, 1862, the regiment was officially in Brigadier General John S. Roane's brigade, although it served with Brigadier General Mosby M. Parsons' brigade for most of the battle. After spending the summer of 1863 harassing Union Navy shipping on the Mississippi River, the regiment was reorganized, with elements of an Arkansas unit being replaced with the 8th Missouri Infantry Battalion. After the reorganization, the regiment fought in the Battle of Pleasant Hill and the Battle of Jenkins' Ferry in April 1864. On June 7, 1865, the men of the regiment were paroled; they would eventually be sent back to Missouri via steamboat.
The 12th Missouri Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. After mustering into Confederate service on October 22, 1862, as White's Missouri Infantry, the regiment, as Ponder's Missouri Infantry, fought in the Battle of Prairie Grove on December 7, where it charged the Union lines several times. On May 3, 1863, the regiment was named the 9th Missouri Infantry Regiment, and fought under that name until December 15, 1863, when it was renamed the 12th Missouri Infantry Regiment. On July 4, 1863, the regiment, as part of Brigadier General Mosby M. Parsons' brigade, broke through the Union lines at the Battle of Helena. However, Parsons' flanks were exposed, and the Confederates were driven from the field, suffering heavy losses. After Helena, only 168 men remained in the regiment. On November 22, 1863, the survivors of the regiment were combined into two companies, which were then attached to the 10th Missouri Infantry Regiment, although the 12th Missouri Infantry was still treated as a separate unit for reporting purposes. In April 1864, the 12th Missouri Infantry fought at the battles of Pleasant Hill and Jenkins' Ferry. On September 29, 1864, the survivors of the 12th Missouri Infantry were officially merged into the 10th Missouri Infantry, ending the 12th's separate service career.
Slayback's Missouri Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment of the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. Originally formed as Slayback's Missouri Cavalry Battalion, the unit consisted of men recruited in Missouri by Lieutenant Colonel Alonzo W. Slayback during Price's Raid in 1864. The battalion's first action was at the Battle of Pilot Knob on September 27; it later participated in actions at Sedalia, Lexington, and the Little Blue River. In October, the unit was used to find an alternate river crossing during the Battle of the Big Blue River. Later that month, Slayback's unit saw action at the battles of Westport, Marmiton River, and Second Newtonia. The battalion was briefly furloughed in Arkansas before rejoining Major General Sterling Price in Texas in December. Probably around February 1865, the battalion reached official regimental strength after more recruits joined.
Hiram Bledsoe's Missouri Battery was an artillery battery that served in the Missouri State Guard and the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The battery was formed when the Missouri State Guard was formed as a pro-secession state militia unit in response to the Camp Jackson affair. As part of the Missouri State Guard, the unit was engaged in the Engagement near Carthage and the Battle of Wilson's Creek during mid-1861, before fighting at the Battle of Dry Wood Creek and the Siege of Lexington later that year when Major General Sterling Price led the Guard northwards towards the Missouri River. After the Missouri State Guard retreated into Arkansas in early 1862, Bledsoe's Battery served during the Confederate defeat at the Battle of Pea Ridge in March. The battery, as part of the Army of the West, transferred across the Mississippi River into Tennessee in April, where it left the Guard to enter Confederate service on April 21.

The 1st Missouri Field Battery was a field artillery battery that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The battery was formed by Captain Westley F. Roberts in Arkansas in September 1862 as Roberts' Missouri Battery and was originally armed with two 12-pounder James rifles and two 6-pounder smoothbore guns. The unit fought in the Battle of Prairie Grove on December 7, as part of a Confederate offensive. Roberts' Battery withdrew after the battle and transferred to Little Rock, Arkansas, where Roberts resigned and was replaced by Lieutenant Samuel T. Ruffner.

The 8th Missouri Infantry Regiment was an infantry regiment that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. The American Civil War began in April 1861 with the Battle of Fort Sumter, and fighting soon escalated. Beginning in May, events in the state of Missouri led to an expansion of the war into that state. In 1862, Confederate recruiting activities took place in Missouri, and a cavalry regiment was formed in Oregon County. On September 2, the unit entered Confederate service, but was soon reclassified as infantry. After many of the unit's men transferred to other units, the regiment was reclassified as a battalion and named the 7th Missouri Infantry Battalion. Under the name Mitchell's Missouri Infantry, the unit was part of a Confederate offensive at the Battle of Prairie Grove on December 7. During the battle, the unit made several charges against the Union lines, but was repeatedly repulsed by artillery fire. The regiment spent most of early 1863 encamped near Little Rock and Pine Bluff in Arkansas, and may have been part of an expedition to the Mississippi River.
The capture of Sedalia occurred during the American Civil War when a Confederate force captured the Union garrison of Sedalia, Missouri, on October 15, 1864. Confederate Major General Sterling Price, who was a former Governor of Missouri and had commanded the Missouri State Guard in the early days of the war, had launched an invasion into the state of Missouri on August 29. He hoped to distract the Union from more important areas and cause a popular uprising against Union control of the state. Price had to abandon his goal of capturing St. Louis after a bloody repulse at the Battle of Fort Davidson and moved into the pro-Confederate region of Little Dixie in central Missouri.
Nichols's Missouri Cavalry Regiment served in the Confederate States Army during the late stages of the American Civil War. The cavalry regiment began recruiting in early 1864 under Colonel Sidney D. Jackman, who had previously raised a unit that later became the 16th Missouri Infantry Regiment. The regiment officially formed on June 22 and operated against the Memphis and Little Rock Railroad through August. After joining Major General Sterling Price's command, the unit participated in Price's Raid, an attempt to create a popular uprising against Union control of Missouri and draw Union troops away from more important theaters of the war. During the raid, while under the command of Lieutenant Colonel Charles H. Nichols, the regiment was part of an unsuccessful pursuit of Union troops who were retreating after the Battle of Fort Davidson in late September.
The 13th Missouri Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry unit that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. In early April 1863, Captain Robert C. Wood, aide-de-camp to Confederate Major General Sterling Price, was detached to form an artillery unit from some of the men of Price's escort. Wood continued recruiting for the unit, which was armed with four Williams guns, and grew to 275 men by the end of September. The next month, the unit fought in the Battle of Pine Bluff, driving back Union Army troops into a barricaded defensive position, from which the Union soldiers could not be dislodged. By November, the unit, which was known as Wood's Missouri Cavalry Battalion, had grown to 400 men but no longer had the Williams guns. In April 1864, Wood's battalion, which was also known as the 14th Missouri Cavalry Battalion, played a minor role in the defeat of a Union foraging party in the Battle of Poison Spring, before spending the summer of 1864 at Princeton, Arkansas. In September, the unit joined Price's Raid into the state of Missouri, but their assault during the Battle of Pilot Knob failed to capture Fort Davidson.
The 10th Texas Field Battery was an artillery battery that served in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. After being formed in early 1861 by Benjamin H. Pratt, the battery served with a cavalry formation led by Colonel William Henry Parsons for part of 1862. It was called upon to enter Missouri in support of troop movements related to the Battle of Prairie Grove, but this did not occur. It then operated along the Mississippi River in early 1863, harassing enemy shipping. The unit then participated in Marmaduke's Second Expedition into Missouri and the Battle of Pine Bluff in 1863. Late in 1864, the battery, now under the command of H. C. Hynson, served in Price's Raid, participating in several battles and skirmishes, including the disastrous Battle of Mine Creek. One source claims the unit's service ended on May 26, 1865, while a Confederate report dated June 1, 1865, states that it existed but did not have cannons. Confederate forces in the Trans-Mississippi Department surrendered on June 2.








