Related Research Articles

Language is a structured system of communication that consists of grammar and vocabulary. It is the primary means by which humans convey meaning,both in spoken and written forms,and may also be conveyed through sign languages. Human language is characterized by its cultural and historical diversity,with significant variations observed between cultures and across time. Human languages possess the properties of productivity and displacement,which enable the creation of an infinite number of sentences,and the ability to refer to objects,events,and ideas that are not immediately present in the discourse. The use of human language relies on social convention and is acquired through learning.
The following outline is provided as an overview and topical guide to linguistics:
Language acquisition is the process by which humans acquire the capacity to perceive and comprehend language. In other words,it is how human beings gain the ability to be aware of language,to understand it,and to produce and use words and sentences to communicate.
Total physical response (TPR) is a language teaching method developed by James Asher,a professor emeritus of psychology at San JoséState University. It is based on the coordination of language and physical movement. In TPR,instructors give commands to students in the target language with body movements,and students respond with whole-body actions.
Readability is the ease with which a reader can understand a written text. The concept exists in both natural language and programming languages though in different forms. In natural language,the readability of text depends on its content and its presentation. In programming,things such as programmer comments,choice of loop structure,and choice of names can determine the ease with which humans can read computer program code.

Vocabulary development is a process by which people acquire words. Babbling shifts towards meaningful speech as infants grow and produce their first words around the age of one year. In early word learning,infants build their vocabulary slowly. By the age of 18 months,infants can typically produce about 50 words and begin to make word combinations.
Language development in humans is a process which starts early in life. Infants start without knowing a language,yet by 10 months,babies can distinguish speech sounds and engage in babbling. Some research has shown that the earliest learning begins in utero when the fetus starts to recognize the sounds and speech patterns of its mother's voice and differentiate them from other sounds after birth.
Poverty of the stimulus (POS) is the controversial argument from linguistics that children are not exposed to rich enough data within their linguistic environments to acquire every feature of their language. This is considered evidence contrary to the empiricist idea that language is learned solely through experience. The claim is that the sentences children hear while learning a language do not contain the information needed to develop a thorough understanding of the grammar of the language.
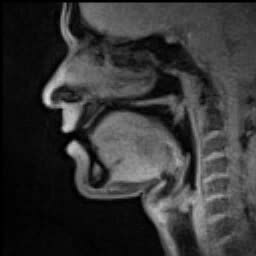
Speech is a human vocal communication using language. Each language uses phonetic combinations of vowel and consonant sounds that form the sound of its words,and using those words in their semantic character as words in the lexicon of a language according to the syntactic constraints that govern lexical words' function in a sentence. In speaking,speakers perform many different intentional speech acts,e.g.,informing,declaring,asking,persuading,directing,and can use enunciation,intonation,degrees of loudness,tempo,and other non-representational or paralinguistic aspects of vocalization to convey meaning. In their speech,speakers also unintentionally communicate many aspects of their social position such as sex,age,place of origin,physical states,psychological states,physico-psychological states,education or experience,and the like.
The audio-lingual method or Army Method is a method used in teaching foreign languages. It is based on behaviorist theory,which postulates that certain traits of living things,and in this case humans,could be trained through a system of reinforcement. The correct use of a trait would receive positive feedback while incorrect use of that trait would receive negative feedback.
Bootstrapping is a term used in language acquisition in the field of linguistics. It refers to the idea that humans are born innately equipped with a mental faculty that forms the basis of language. It is this language faculty that allows children to effortlessly acquire language. As a process,bootstrapping can be divided into different domains,according to whether it involves semantic bootstrapping,syntactic bootstrapping,prosodic bootstrapping,or pragmatic bootstrapping.
Clinical linguistics is a sub-discipline of applied linguistics involved in the description,analysis,and treatment of language disabilities,especially the application of linguistic theory to the field of Speech-Language Pathology. The study of the linguistic aspect of communication disorders is of relevance to a broader understanding of language and linguistic theory.
The comprehension approach to language learning emphasizes understanding of language rather than speaking it. This is in contrast to the better-known communicative approach,under which learning is thought to emerge through language production,i.e. a focus on speech and writing.
Language teaching,like other educational activities,may employ specialized vocabulary and word use. This list is a glossary for English language learning and teaching using the communicative approach.
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. Linguistics is based on a theoretical as well as a descriptive study of language and is also interlinked with the applied fields of language studies and language learning,which entails the study of specific languages. Before the 20th century,linguistics evolved in conjunction with literary study and did not employ scientific methods. Modern-day linguistics is considered a science because it entails a comprehensive,systematic,objective,and precise analysis of all aspects of language –i.e.,the cognitive,the social,the cultural,the psychological,the environmental,the biological,the literary,the grammatical,the paleographical,and the structural.
The natural approach is a method of language teaching developed by Stephen Krashen and Tracy Terrell in the late 1970s and early 1980s. It aims to foster naturalistic language acquisition in a classroom setting,and to this end it emphasizes communication,and places decreased importance on conscious grammar study and explicit correction of student errors. Efforts are also made to make the learning environment as stress-free as possible,by lowering the affective filter. In the natural approach,language output is not forced,but allowed to emerge spontaneously after students have attended to large amounts of comprehensible language input. Comprehensible input is the content that language learners are exposed to in the target language. This is an integral part of the Natural Approach. Krashen suggests that language learners should be able to understand the comprehensible input provided at their current levels of language acquisition,while also making it as interesting and engaging as possible.
Syntactic bootstrapping is a theory in developmental psycholinguistics and language acquisition which proposes that children learn word meanings by recognizing syntactic categories and the structure of their language. It is proposed that children have innate knowledge of the links between syntactic and semantic categories and can use these observations to make inferences about word meaning. Learning words in one's native language can be challenging because the extralinguistic context of use does not give specific enough information about word meanings. Therefore,in addition to extralinguistic cues,conclusions about syntactic categories are made which then lead to inferences about a word's meaning. This theory aims to explain the acquisition of lexical categories such as verbs,nouns,etc. and functional categories such as case markers,determiners,etc.
Statistical learning is the ability for humans and other animals to extract statistical regularities from the world around them to learn about the environment. Although statistical learning is now thought to be a generalized learning mechanism,the phenomenon was first identified in human infant language acquisition.
A late talker is a toddler experiencing late language emergence (LLE),which can also be an early or secondary sign of an autism spectrum disorder,or other developmental disorders,such as fetal alcohol spectrum disorder,attention deficit hyperactivity disorder,intellectual disability,learning disability,social communication disorder,or specific language impairment. Lack of language development,comprehension skills,and challenges with literacy skills are potential risks as late talkers age. Outlook for late talkers with or without intervention is generally favorable. Toddlers have a high probability of catching up to typical toddlers if early language interventions are put in place. Language interventions include general language stimulation,focused language stimulation and milieu teaching.
Developmental Language Disorder (DLD) is identified when a child has problems with language development that continue into school age and beyond. The language problems have a significant impact on everyday social interactions or educational progress,and occur in the absence of autism spectrum disorder,intellectual disability or a known biomedical condition. The most obvious problems are difficulties in using words and sentences to express meanings,but for many children,understanding of language is also a challenge. This may not be evident unless the child is given a formal assessment.
References
- ↑ University roster
- ↑ Rieber, Robert W. (2012), "Winitz, Harris", in Rieber, Robert W. (ed.), Encyclopedia of the History of Psychological Theories, Springer US, pp. 1197–1198, doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-0463-8_276, ISBN 9781441904638
- ↑ Winitz, Harris; Reeds, James (1975). Comprehension and problem solving as strategies for language training. Mouton.
- ↑ Winitz, Harris (1981). "Input Considerations in the Comprehension of First and Second Language*". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 379 (1): 296–308. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1981.tb42017.x. ISSN 1749-6632.
- ↑ Winitz, H. (Ed) Native Language and Foreign Language Acquisition Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences Vol 379