Related Research Articles

Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized silicate grains, cemented together by another mineral. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.

Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the accumulation or deposition of mineral or organic particles at Earth's surface, followed by cementation. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. The geological detritus originated from weathering and erosion of existing rocks, or from the solidification of molten lava blobs erupted by volcanoes. The geological detritus is transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice or mass movement, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lithology may refer to either a detailed description of these characteristics, or a summary of the gross physical character of a rock. Examples of lithologies in the second sense include sandstone, slate, basalt, or limestone.

Conglomerate is a sedimentary rock made up of rounded gravel-sized pieces of rock surrounded by finer-grained sediments. The larger fragments within conglomerate are called clasts, while the finer sediment surrounding the clasts is called the matrix. The clasts and matrix are typically cemented by calcium carbonate, iron oxide, silica, or hardened clay.

Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus, chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks by physical weathering. Geologists use the term clastic to refer to sedimentary rocks and particles in sediment transport, whether in suspension or as bed load, and in sediment deposits.
The Mount Pleasant Caldera is a large eroded Late Devonian volcanic caldera complex, located in the northern Appalachian Mountains of southwestern New Brunswick, Canada. It is one of few noticeable pre-Cenozoic calderas, and its formation is associated to a period of crustal thinning that followed the Acadian orogeny in the northern Appalachian Mountains. It sits relatively near to the coastline.

The Enon Formation is a geological formation found in the Eastern and Western Cape provinces in South Africa. It is the lowermost of the four formations found within the Uitenhage Group of the Algoa Basin, its type locality, where it has been measured at a maximum thickness of 480 metres (1,570 ft). Discontinuous outcrops are also found in the Worcester-Pletmos and Oudshoorn-Gamtoos Basins, including isolated occurrences in the Haasvlakte, Jubilee, and Soutpansvlakte Basins near the small town Bredasdorp.
Igneous rocks are found in Bukit Timah, Woodlands, and Pulau Ubin island. Granite makes up the bulk of the igneous rock. Gabbro is also found in the area and is found in an area called Little Guilin, named for its resemblance to Guilin in South China. This area is in Bukit Gombak. Sedimentary rocks are found on the western part of Singapore, which is mainly made of sandstone and mudstones. It also includes the southwestern area. Metamorphic rocks are found in the northeastern part of Singapore, and also on Pulau Tekong, off the east coast of Singapore. The rocks are mainly made up of quartzite, and also make up the Sajahat Formation.

Roundness is the degree of smoothing due to abrasion of sedimentary particles. It is expressed as the ratio of the average radius of curvature of the edges or corners to the radius of curvature of the maximum inscribed sphere.
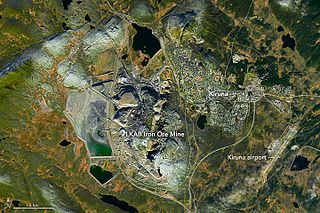
The Kiruna mine is the largest and most modern underground iron ore mine in the world. The mine is located in Kiruna in Norrbotten County, Lapland, Sweden. The mine is owned by Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara AB (LKAB), a large Swedish mining company. In 2018 the mine produced 26.9 million tonnes of iron ore. The Kiruna mine has an ore body which is 4 km (2.5 mi) long, 80 metres (260 ft) to 120 metres (390 ft) thick and reaching a depth of up to 2 km (1.2 mi). Since mining began at the site in 1898, the mine has produced over 950 million tonnes of ore. As of 2020, the main haulage level is 1,365 m below the ore outcrop at Kiirunavaara that existed prior to mining.

The Clarence Moreton Basin is a Mesozoic sedimentary basin on the easternmost part of the Australian continent. It is located in the far north east of the state of New South Wales around Lismore and Grafton and in the south east corner of Queensland. It is the part of the Great Artesian Basin that extends to the east coast in Australia's central eastern lowlands.
The La Toca Formation is a geologic formation in the northern and eastern part of the Dominican Republic. The formation, predominantly an alternating sequence of marls and turbiditic sandstones, breccias and conglomerates, is renowned for the preservation of insects and other arthropods in amber, known as Dominican amber. The formation is dated to the Burdigalian to Langhian stages of the Miocene period.

The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.

The Iron Quadrangle is a mineral-rich region covering about 7,000 square kilometres (2,700 sq mi) in the central-southern part of the Brazilian state Minas Gerais. The area is known for its extensive deposits of gold, diamonds, and iron ore, being the source of approximately 40% of all gold produced in Brazil between the years 1500 and 2000. The deposits themselves pertain to the Minas Supergroup, a sequence of meta-sedimentary rocks initially formed in the Paleoproterozoic, about 2.5 Ga. In the 2010s, there have been two collapses of large tailings dams, which caused extensive damage and loss of life.
Kiruna porphyry is a group of igneous rocks found near Kiruna in northernmost Sweden. The Kiruna Porphyry formed 1,880 to 1,900 million years ago during the Paleoproterozoic Era in connection to the Svecofennian orogeny.

The Big Rock Formation is a formation that crops out in the Tusas Mountains of northern New Mexico. Detrital zircon geochronology gives a maximum age for the formation of 1665 Mya, corresponding to the Statherian period.

The Tuerto Formation is a geologic formation exposed around the Ortiz Mountains of New Mexico. It is estimated to be of Pliocene to Pleistocene age, and forms the gravel cap of the Ortiz surface, one of the first pediment surfaces recognized by geologists.

The Vasquez Formation (Tvz) is a geologic formation cropping out at the eponymous Vasquez Rocks in southern California. The formation dates to the Late Oligocene to Early Miocene.
The Röddinge Formation is a geologic formation in Skåne County, southern Sweden. It is Early Jurassic (Sinemurian-Toarcian) in age. It is a unit with a limited degree of exposure, being identified mostly by its deposits on the Fyledalen Fault Zone, specially on Kurremölla, where is present the main fossil deposit. It is a unit known mostly for large museum collections and estimated to have a thickness of several hundreds of meters. It is also known for its large iron deposits. It is correlated with the mostly marine Rya Formation of western Skåne County, the Volcanic deposits of the Djupadal Formation and specially the Sorthat Formation of Bornholm. Most likely, the coarse-grained nature of the Röddinge Formation is linked to rapid erosion of a tectonically active hinterland.
Kurravaara conglomerate is a rock unit of polymict conglomerate found in northernmost Sweden. It rest confomably on top of greenstones that were originally basaltic lavas and tuff. In one locations both rock units interdigitate. The conglomerate has boulders of porphyritic trachyandesite, iron-apatite oxide and those that are a blend of both rock types. Greenstones are also found as boulders. In some locations the unit is poor in boulders and is made mostly of metatuff. It is overlain by the Hopukka Formation, but no clear contact exists as rock units grade into each other.
References
- 1 2 3 Andersson, J.B., Bauer, T.E., & Martinsson, O. (2021). Structural Evolution of the Central Kiruna Area, Northern Norrbotten, Sweden: Implications on the Geologic Setting Generating Iron Oxide-Apatite and Epigenetic Iron and Copper Sulfides. Economic Geology .
- 1 2 Offerberg, Jan (1967). Beskrivning till berggrundskartbladen Kiruna NV, NO, SV, SO (in Swedish). Stockholm: Sveriges Geologiska Undersökning. pp. 94–95.