Related Research Articles

Kiruna is the northernmost city in Sweden, situated in the province of Lapland. It had 17,002 inhabitants in 2016 and is the seat of Kiruna Municipality in Norrbotten County. The city was originally built in the 1890s to serve the Kiruna Mine.
Bergslagen is a historical, cultural, and linguistic region located north of Lake Mälaren in northern Svealand, Sweden, traditionally known as a mining district. In Bergslagen, the mining and metallurgic industries have been important since the Middle Ages although Malmfälten, the mining district of northernmost Sweden centred at the towns of Kiruna and Malmberget, has been of greater importance during the 20th century.

Skarns or tactites are coarse-grained metamorphic rocks that form by replacement of carbonate-bearing rocks during regional or contact metamorphism and metasomatism. Skarns may form by metamorphic recrystallization of impure carbonate protoliths, bimetasomatic reaction of different lithologies, and infiltration metasomatism by magmatic-hydrothermal fluids. Skarns tend to be rich in calcium-magnesium-iron-manganese-aluminium silicate minerals, which are also referred to as calc-silicate minerals. These minerals form as a result of alteration which occurs when hydrothermal fluids interact with a protolith of either igneous or sedimentary origin. In many cases, skarns are associated with the intrusion of a granitic pluton found in and around faults or shear zones that commonly intrude into a carbonate layer composed of either dolomite or limestone. Skarns can form by regional or contact metamorphism and therefore form in relatively high temperature environments. The hydrothermal fluids associated with the metasomatic processes can originate from a variety of sources; magmatic, metamorphic, meteoric, marine, or even a mix of these. The resulting skarn may consist of a variety of different minerals which are highly dependent on both the original composition of the hydrothermal fluid and the original composition of the protolith.

Gällivare is a locality and the seat of Gällivare Municipality in Norrbotten County, province of Lapland, Sweden with 8,449 inhabitants in 2010. The town was founded in the 17th century. Together with nearby towns Malmberget and Koskullskulle it forms a conurbation with some 15,000 inhabitants. This conurbation is the second northernmost significant urban area of Sweden after Kiruna.
Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara Aktiebolag (LKAB) is a state-owned Swedish mining company. The company mines iron ore at Kiruna and at Malmberget in northern Sweden. The company was established in 1890, and has been 100% state-owned since the 1950s. The iron ore is processed to pellets and sinter fines, which are transported by Iore trains (Malmbanan) to the harbours at Narvik and Luleå and to the steel mill at Luleå (SSAB). Their production is sold throughout much of the world, with the principal markets being European steel mills, as well as North Africa, the Middle East and Southeast Asia. LKAB's mines supply at least 80% of Europe's iron ore.

Various theories of ore genesis explain how the various types of mineral deposits form within Earth's crust. Ore-genesis theories vary depending on the mineral or commodity examined.
Malmfälten is a major mining district in Sweden, centred on the northern towns of Kiruna and Malmberget.

The Iron Ore Line is a 398-kilometre (247 mi) long railway line between Riksgränsen and Boden in Norrbotten County, Sweden, owned by Trafikverket. The line also contains two branches, from Kiruna to Svappavaara and from Gällivare to Koskullskulle. The term is often colloquially used to also include the Ofoten Line, from Riksgränsen to Narvik in Norway, and the northernmost part of the Main Line Through Upper Norrland from Boden to Luleå. The railway from Narvik to Luleå is 473 kilometres (294 mi) long.

Iore, often stylized IORE, is a class of 34 electric locomotives built by Adtranz and its successor Bombardier Transportation for the Swedish mining company LKAB's railway division Malmtrafik. The class is a variation of Adtranz's Octeon modular product platform, thus related to Bombardier's later TRAXX platform. The locomotives are considered to be one of the most powerful locomotives and haul iron ore freight trains on the Iron Ore Line and Ofoten Line in Sweden and Norway, respectively. The 8,600-tonne 68-car trains are hauled by two single-ended Co′Co′ locomotives, each with a power output of 5,400 kW (7,200 hp). Each operates with 600 kilonewtons tractive effort and has a maximum speed of 80 km/h (50 mph). Delivery of the first series of 18 locomotives was made from 2000 to 2004, and they replaced some of the aging Dm3 and El 15 units. In 2007, eight more vehicles were ordered, with production to be completed by 2011, by which time, another four double units were ordered. These units were scheduled to be delivered from 2013 to 2014.

LKAB Malmtrafik, earlier Malmtrafik i Kiruna AB (MTAB), is a Swedish railway company which operates the iron ore freight trains on the Iron Ore Line and the Ofoten Line. MTAB is a wholly owned subsidiary of the mining company Luossavaara–Kiirunavaara (LKAB). In Norway, operations are handled by the subsidiary Malmtrafikk AS (MTAS). Malmtrafik hauls ore from LKAB's mines in Kiruna, Malmberget and Svappavaara to the ports of Luleå and Narvik, the latter located in Norway. The company owns 28 Iore locomotives and 750 hopper cars. Each train is 68 cars long and weighs 8,600 tonnes, allowing the company to transport 33 million tonnes per year.

Svappavaara is a locality situated in Kiruna Municipality, Norrbotten County, Sweden with 417 inhabitants in 2010. It is a mining village. Mining was started around 1650. Large scale iron mining started in 1965. The mine was closed in 1983, but enrichment of iron ore from the mine at Kiruna is still going on. The mine is owned by LKAB, and there is an ongoing project to open it again for production around year 2015.

Kiirunavaara is a mountain situated in Kiruna Municipality in Norrbotten County, Sweden. It contains one of the largest and richest bodies of iron ore in the world.

Johan Olof Hjalmar Lundbohm was a Swedish geologist and chemist and the first managing director of LKAB in Kiruna. He made a strong contribution to the design of the new community of Kiruna in Lapland.
Iron oxide copper gold ore deposits (IOCG) are important and highly valuable concentrations of copper, gold and uranium ores hosted within iron oxide dominant gangue assemblages which share a common genetic origin.
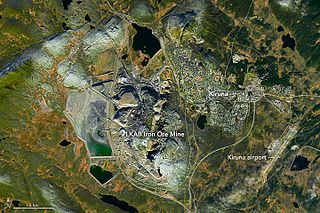
The Kiruna mine is the largest and most modern underground iron ore mine in the world. The mine is located in Kiruna in Norrbotten County, Lapland, Sweden. The mine is owned by Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara AB (LKAB), a large Swedish mining company. In 2018 the mine produced 26.9 million tonnes of iron ore. The Kiruna mine has an ore body which is 4 km (2.5 mi) long, 80 metres (260 ft) to 120 metres (390 ft) thick and reaching a depth of up to 2 km (1.2 mi). Since mining began at the site in 1898, the mine has produced over 950 million tonnes of ore. As of 2020, the main haulage level is 1,365 m below the ore outcrop at Kiirunavaara that existed prior to mining.
The Malmberget mine is one of the largest iron ore mines in the world. The mine is located in Malmberget in Norrbotten County, Lapland, it is owned by Luossavaara-Kiirunavaara AB (LKAB). The mine has an annual production capacity of over 5 million tonnes of iron ore and has reserves amounting to 350 million tonnes of ore grading 43.8% iron, resulting 153.3 million tonnes of iron. In 2009, the mine produced 4.3 million tonnes of iron.

Tosham hill range, located at and in the area around Tosham, with an average elevation of 207 meters, and the rocks exposed in and around Tosham hills are part of subsurface north-western spur of Alwar group of Delhi supergroup of Aravalli Mountain Range, belong to the Precambrian Malani igneous suite of rocks and have been dated at 732 Ma BP. This range in Aravalli Craton is a remnant of the outer ring of a fallen chamber of an extinct volcano. Tosham hill range covers the hills at Tosham, Khanak, and Riwasa as well as the small rocky outcrops at Nigana, Dulehri, Dharan, Dadam, and Kharkari Makhwan. Among these, Khanak hill is the largest in area and tallest in height.

The geology of Sweden is the regional study of rocks, minerals, tectonics, natural resources and groundwater in the country. The oldest rocks in Sweden date to more than 2.5 billion years ago in the Precambrian. Complex orogeny mountain building events and other tectonic occurrences built up extensive metamorphic crystalline basement rock that often contains valuable metal deposits throughout much of the country. Metamorphism continued into the Paleozoic after the Snowball Earth glaciation as the continent Baltica collided with an island arc and then the continent Laurentia. Sedimentary rocks are most common in southern Sweden with thick sequences from the last 250 million years underlying Malmö and older marine sedimentary rocks forming the surface of Gotland.

The geology of North Macedonia includes the study of rocks dating to the Precambrian and a wide array of volcanic, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks formed in the last 539 million years.
Hauki quartzite is a rock unit of quartz arenite found in northernmost Sweden. More arkosic parts are of reddish colour but otherwise made of light grey rocks. Apart from quart arenite the unit hosts some conglomerates with clasts of phyllite and quartz porphyry. The clasts are derived from the nearby units of Hopukka Formation, Loussavaara Formation and Matojärvi Formation.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Lundqvist, Thomas (2009). Porfyr i Sverige: En geologisk översikt (in Swedish). pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-91-7158-960-6.
- 1 2 3 4 "kirunaporfyrer". Nationalencyklopedin (in Swedish). Retrieved 12 December 2019.
- ↑ Brewer, T.S.; Pharao, T.C. (1990). "Early Precambrian basic rocks of the Baltic Shield". In Hall, R.P.; Hughes, D.J. (eds.). Early Precambrian Basic Magmatism. Blackie. p. 291.