Related Research Articles
The Scott Mountains are a large number of isolated peaks lying south of Amundsen Bay in Enderby Land of East Antarctica, Antarctica. Discovered on 13 January 1930 by the British Australian New Zealand Antarctic Research Expedition (BANZARE) under Sir Douglas Mawson. He named the feature Scott Range after Captain Robert Falcon Scott, Royal Navy. The term mountains is considered more appropriate because of the isolation of its individual features.

Arrowsmith Peninsula is a cape about 40 miles (64 km) long on the west coast of Graham Land, west of Forel Glacier, Sharp Glacier and Lallemand Fjord, and northwest of Bourgeois Fjord, with Hanusse Bay lying to the northwest. It was surveyed by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (FIDS) in 1955-58 and named for Edwin Porter Arrowsmith, Governor of the Falkland Islands.
Leon Head is a prominent rocky headland, 880 metres (2,900 ft) high, forming the south side of the mouth of Brøgger Glacier and the southeast side of the entrance to Undine South Harbour, on the south coast of South Georgia. The headland was roughly charted in 1819 by a Russian expedition under Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, following a survey by the South Georgia Survey, 1951–52, for the Spanish vessel Leon, which sighted South Georgia in 1756.

King Edward Cove is a sheltered cove in the west side of Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia. This cove and its surrounding features, frequented by early sealers at South Georgia, was charted by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition, 1901–04, under Otto Nordenskiöld who named it Grytviken. That name, meaning 'Pot Bay,' was subsequently assumed by the whaling station and settlement built in 1904. The cove got its present name in about 1906 for King Edward VII of the United Kingdom.

Barff Peninsula is a peninsula forming the east margin of Cumberland East Bay, South Georgia Island. It is 8 miles (13 km) long and extends northwest from Sörling Valley to Barff Point, its farthest extremity. It was probably first seen by the British expedition under James Cook in 1775. The peninsula as a whole takes its name from Barff Point, which was named for Royal Navy Lieutenant A.D. Barff of HMS Sappho, who, assisted by Captain C.A. Larsen, sketched a map of Cumberland Bay in 1906. Barff Point is considered the eastern headland of East Cumberland Bay.
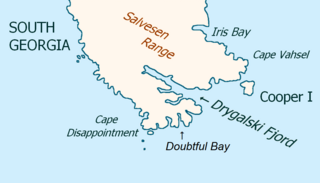
Drygalski Fjord is a bay 1 mile (1.6 km) wide which recedes northwestwards 7 miles (11 km), entered immediately north of Nattriss Head along the southeast coast of South Georgia. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Wilhelm Filchner, and named for Professor Erich von Drygalski, the leader of the First German Antarctica Expedition, 1901–03.

Larsen Harbour is a narrow 2.6 miles (4.2 km) long inlet of indenting volcanic rocks and sheeted dykes known as the Larsen Harbour Formation. It is a branch of Drygalski Fjord, entered 2.5 miles (4 km) west-northwest of Nattriss Head, at the southeast end of South Georgia Island. It was charted by the Second German Antarctic Expedition, 1911–12, under Filchner, who named it for Captain Carl Anton Larsen a Norwegian explorer, who made significant contributions to the exploration of Antarctica. The most significant of these was the first discovery of fossils on the continent, for which he received the Back Grant from the Royal Geographical Society. Larsen is also considered the founder of the Antarctic whaling industry and the settlement and whaling station of Grytviken, South Georgia.

Busen Point or Busen Peninsula is a headland forming the southeast side of the entrance to Stromness Bay, on the north coast of South Georgia island. It lies on the Lewin Peninsula in between Stromness Bay and Cumberland West Bay.
O'Connor Peak is a mountain peak, 675 m, standing west of Long Point on Barff Peninsula, South Georgia. Charted by a Norwegian Antarctic Expedition, 1927–28, and named Mount Bryde. Recharted by DI in 1929 and named after Midshipman W. P. O'Connor, Royal Navy Reserve, who assisted with the survey.
Harmer Glacier is a glacier 3 nautical miles (6 km) long, flowing southwest from Starbuck Peak to the sea close north of Ranvik, on the south coast of South Georgia. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Sir Sidney F. Harmer.
Hodges Glacier is a small glacier 1 nautical mile (2 km) west of Grytviken, South Georgia, flowing from the south side of Petrel Peak to the foot of Mount Hodges. The name was recommended by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee and derives from association with Mount Hodges.
Blechnum Peaks are three peaks, the highest 640 metres (2,100 ft) high, on the north–south ridge between Gulbrandsen Lake and Olsen Valley on the north coast of South Georgia. They were named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee, following British Antarctic Survey biological work in the area, after the rare fern Blechnum penna-marina, whose occurrence in South Georgia is known only from the north and east slopes of these peaks and from the adjacent Olsen Valley.
Calf Head is a rocky headland on the north coast of South Georgia, 3 nautical miles (6 km) northwest of Cape Harcourt. The name "Kalber-Berg" was given by the German group of the International Polar Year Investigations, 1882–83, but was limited to the summit of the headland. The feature was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey, 1951–52, who reported that a name is more essential for its seaward extremity in order to distinguish it from Cape Harcourt, with which it is easily confused when viewed from the north and northwest. The English form of the name, Calf Head, was recommended by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1954. Sacramento Bight lies on the coast between Calf Head and Cape Harcourt.
Johnson Peak is a low mountain, 2,010 metres (6,600 ft) high, which forms the western part of the Hart Hills in Antarctica. It was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names in 1982 after Robert J.R. Johnson, a newspaper correspondent attached to the United States Antarctic Research Program Pagano Nunatak – Hart Hills expedition of 1964–65.
Mount Fagerli is a mountain rising to 1,880 metres (6,170 ft) in the Allardyce Range of South Georgia, standing 1 nautical mile (2 km) southwest of Marikoppa on the north side of Kjerulf Glacier. It was surveyed by the South Georgia Survey in the period 1951–57, and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Soren Fagerli, Manager of the Compañía Argentina de Pesca station in Grytviken from 1938 to 1948.

Ferguslie Peninsula is a peninsula 2.4 km (1.5 mi) long, lying between Browns Bay and Macdougal Bay on the north coast of Laurie Island, in the South Orkney Islands of Antarctica. The peninsula was charted in 1903 by the Scottish National Antarctic Expedition under William Speirs Bruce, who named it for Ferguslie, the residence of James Coats, chief patron of the expedition.
Mills Peak is a peak 1 nautical mile (2 km) southwest of Cape Douglas, rising to 625 metres (2,050 ft) in the northern portion of Barff Peninsula, South Georgia.
Husdal is a short valley running west-southwest from the head of Husvik Harbour, South Georgia. It was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in the Norwegian form "Husdal" in association with the disused Husvik whaling station at the head of Husvik Harbour.
McCance Glacier is the 30-km long and 5 km wide glacier draining the Hutchison Hill area on the west slopes of Avery Plateau on Loubet Coast in Graham Land, Antarctica. It flows north-northwestwards along the west side of Osikovo Ridge, Kladnitsa Peak and Rubner Peak and enters Darbel Bay.
Karrakatta Valley is a short valley trending west-northwest from Husvik Harbor, Stromness Bay, South Georgia. It was named after the hulk Karrakatta on a slipway at the abandoned whaling station at the head of Husvik Harbor. Built in Oslo in 1912, she served as a whale catcher off Western Australia, and was last used at the slipway to provide steam to the adjacent engineering shop, probably until 1959. The valley was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1990.
References
- ↑ "Headland Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior . Retrieved 4 June 2012.
![]() This article incorporates public domain material from "Headland Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.
This article incorporates public domain material from "Headland Peak". Geographic Names Information System . United States Geological Survey.