
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or plane area refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while surface area refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve or the volume of a solid . Two different regions may have the same area ; by synecdoche, "area" sometimes is used to refer to the region, as in a "polygonal area".
The number π is a mathematical constant that is the ratio of a circle's circumference to its diameter, approximately equal to 3.14159. The number π appears in many formulae across mathematics and physics. It is an irrational number, meaning that it cannot be expressed exactly as a ratio of two integers, although fractions such as are commonly used to approximate it. Consequently, its decimal representation never ends, nor enters a permanently repeating pattern. It is a transcendental number, meaning that it cannot be a solution of an equation involving only finite sums, products, powers, and integers. The transcendence of π implies that it is impossible to solve the ancient challenge of squaring the circle with a compass and straightedge. The decimal digits of π appear to be randomly distributed, but no proof of this conjecture has been found.
A multiplication algorithm is an algorithm to multiply two numbers. Depending on the size of the numbers, different algorithms are more efficient than others. Efficient multiplication algorithms have existed since the advent of the decimal numeral system.

In mathematics, a square number or perfect square is an integer that is the square of an integer; in other words, it is the product of some integer with itself. For example, 9 is a square number, since it equals 32 and can be written as 3 × 3.
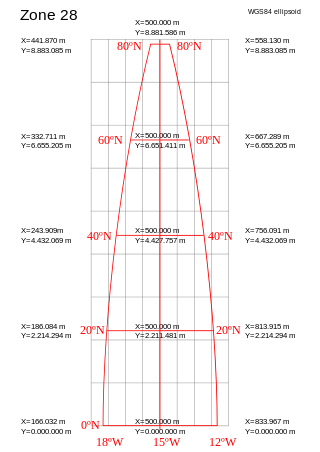
A projected coordinate system – also called a projected coordinate reference system, planar coordinate system, or grid reference system – is a type of spatial reference system that represents locations on Earth using Cartesian coordinates (x, y) on a planar surface created by a particular map projection. Each projected coordinate system, such as "Universal Transverse Mercator WGS 84 Zone 26N," is defined by a choice of map projection (with specific parameters), a choice of geodetic datum to bind the coordinate system to real locations on the earth, an origin point, and a choice of unit of measure. Hundreds of projected coordinate systems have been specified for various purposes in various regions.
In mathematics, taking the nth root is an operation involving two numbers, the radicand and the index or degree. Taking the nth root is written as , where x is the radicand and n is the index. This is pronounced as "the nth root of x". The definition then of an nth root of a number x is a number r which, when raised to the power of the positive integer n, yields x:
Significant figures, also referred to as significant digits or sig figs, are specific digits within a number written in positional notation that carry both reliability and necessity in conveying a particular quantity. When presenting the outcome of a measurement, if the number of digits exceeds what the measurement instrument can resolve, only the number of digits within the resolution's capability are dependable and therefore considered significant.

The Ordnance Survey National Grid reference system (OSGB), also known as British National Grid (BNG), is a system of geographic grid references used in Great Britain, distinct from latitude and longitude.
In numerical analysis, the Kahan summation algorithm, also known as compensated summation, significantly reduces the numerical error in the total obtained by adding a sequence of finite-precision floating-point numbers, compared to the obvious approach. This is done by keeping a separate running compensation, in effect extending the precision of the sum by the precision of the compensation variable.
Trial division is the most laborious but easiest to understand of the integer factorization algorithms. The essential idea behind trial division tests to see if an integer n, the integer to be factored, can be divided by each number in turn that is less than the square root of n. For example, for the integer n = 12, the only numbers that divide it are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12. Selecting only the largest powers of primes in this list gives that 12 = 3 × 4 = 3 × 22.

Mental calculation consists of arithmetical calculations using only the human brain, with no help from any supplies or devices such as a calculator. People may use mental calculation when computing tools are not available, when it is faster than other means of calculation, or even in a competitive context. Mental calculation often involves the use of specific techniques devised for specific types of problems. People with unusually high ability to perform mental calculations are called mental calculators or lightning calculators.
In number theory, the integer square root (isqrt) of a non-negative integer n is the non-negative integer m which is the greatest integer less than or equal to the square root of n,

1,000,000, or one thousand thousand, is the natural number following 999,999 and preceding 1,000,001. The word is derived from the early Italian millione, from mille, "thousand", plus the augmentative suffix -one.

The Military Grid Reference System (MGRS) is the geocoordinate standard used by NATO militaries for locating points on Earth. The MGRS is derived from the Universal Transverse Mercator (UTM) grid system and the Universal Polar Stereographic (UPS) grid system, but uses a different labeling convention. The MGRS is used as geocode for the entire Earth.
A tetrad is an area 2 km x 2 km square. The term refers to any of the 25 such squares which make up a standard hectad.
Methods of computing square roots are algorithms for approximating the non-negative square root of a positive real number . Since all square roots of natural numbers, other than of perfect squares, are irrational, square roots can usually only be computed to some finite precision: these methods typically construct a series of increasingly accurate approximations.
C-squares is a system of spatially unique, location-based identifiers (geocodes) for areas on the surface of the earth, represented as cells from a latitude- and longitude-based Discrete Global Grid at a hierarchical set of resolution steps, obtained by progressively subdividing 10×10 degree World Meteorological Organization squares; the term "c-square" is also available for use to designate any component cell of the grid. Individual cell identifiers incorporate literal values of latitude and longitude in an interleaved notation, together with additional digits that support intermediate grid resolutions of 5, 0.5, 0.05 degrees, etc.
In Britain, a variety of status categorisation schemes exist, for sites, species and habitats. These include, for species and habitats, Red Data Book threat categories, national rarity and scarcity assessments and Biodiversity Action Plan statuses, and for sites, statutory statuses such as the SSSI concept, and non-statutory statuses such as county wildlife sites.
The Open Location Code (OLC) is a geocode based in a system of regular grids for identifying an area anywhere on the Earth. It was developed at Google's Zürich engineering office, and released late October 2014. Location codes created by the OLC system are referred to as "plus codes".
A mathematical constant is a key number whose value is fixed by an unambiguous definition, often referred to by a special symbol, or by mathematicians' names to facilitate using it across multiple mathematical problems. Constants arise in many areas of mathematics, with constants such as e and π occurring in such diverse contexts as geometry, number theory, statistics, and calculus.





