
A jet engine is a type of reaction engine, discharging a fast-moving jet of heated gas that generates thrust by jet propulsion. While this broad definition may include rocket, water jet, and hybrid propulsion, the term jet engine typically refers to an internal combustion air-breathing jet engine such as a turbojet, turbofan, ramjet, pulse jet, or scramjet. In general, jet engines are internal combustion engines.

Air Commodore Sir Frank Whittle, was an English engineer, inventor and Royal Air Force (RAF) air officer. He is credited with having invented the turbojet engine. A patent was submitted by Maxime Guillaume in 1921 for a similar invention which was technically unfeasible at the time. Whittle's jet engines were developed some years earlier than those of Germany's Hans von Ohain, who designed the first-to-fly turbojet engine.

A jet aircraft is an aircraft propelled by jet engines.

The turbojet is an airbreathing jet engine which is typically used in aircraft. It consists of a gas turbine with a propelling nozzle. The gas turbine has an air inlet which includes inlet guide vanes, a compressor, a combustion chamber, and a turbine. The compressed air from the compressor is heated by burning fuel in the combustion chamber and then allowed to expand through the turbine. The turbine exhaust is then expanded in the propelling nozzle where it is accelerated to high speed to provide thrust. Two engineers, Frank Whittle in the United Kingdom and Hans von Ohain in Germany, developed the concept independently into practical engines during the late 1930s.

Hans Joachim Pabst von Ohain was a German physicist, engineer, and the designer of the first turbojet engine to power an aircraft. Together with Frank Whittle he is widely described as the co-inventor of the turbojet engine. Hans von Ohain was still a university student when in January 1930, Whittle filed his first patent for a turbojet engine. Von Ohain stated in his biography, that "My interest in jet propulsion began in the fall of 1933 when I was in my seventh semester at Göttingen University. I didn't know that many people before me had the same thought.". He quickly caught up with Whittle due to the support by Heinkel and his design, "an axial-flow engine as opposed to Sir Frank's centrifugal flow engine, that was eventually adopted by most manufacturers by the 1950's."

The Heinkel He 178 was an experimental aircraft designed and produced by the German aircraft manufacturer Heinkel. It was the world's first aircraft to fly using the thrust from a turbojet engine.

The Junkers Jumo 004 was the world's first production turbojet engine in operational use, and the first successful axial compressor turbojet engine. Some 8,000 units were manufactured by Junkers in Germany late in World War II, powering the Messerschmitt Me 262 fighter and the Arado Ar 234 reconnaissance/bomber, along with prototypes, including the Horten Ho 229. Variants and copies of the engine were produced in Eastern Europe and the USSR for several years following the end of WWII.

The BMW 003 is an early axial turbojet engine produced by BMW AG in Germany during World War II. The 003 and the Junkers Jumo 004 were the only German turbojet engines to reach production during World War II.

Erich Karl Warsitz was a German test pilot of the 1930s. He held the rank of Flight-Captain in the Luftwaffe and was selected by the Reich Air Ministry as chief test pilot at Peenemünde West. He is remembered as the first person to fly an aircraft under liquid-fueled rocket power, the Heinkel He 176, on June 20, 1939 and also the first to fly an aircraft under turbojet power, the Heinkel He 178, on August 27 the same year.
This article outlines the important developments in the history of the development of the air-breathing (duct) jet engine. Although the most common type, the gas turbine powered jet engine, was certainly a 20th-century invention, many of the needed advances in theory and technology leading to this invention were made well before this time.

The Heinkel HeS 011 or Heinkel-Hirth 109-011(HeS - Heinkel Strahltriebwerke) was an advanced World War II jet engine built by Heinkel-Hirth. It featured a unique compressor arrangement, starting with a low-compression impeller in the intake, followed by a "diagonal" stage similar to a centrifugal compressor, and then a three-stage axial compressor. Many of the German jet-powered aircraft designs at the end of the war were designed to use the HeS 011, but the HeS 011 engine was not ready for production before the war ended in Europe and only small numbers of prototypes were produced.
The HeS 30(HeS - Heinkel Strahltriebwerke) was an early jet engine, originally designed by Adolf Müller at Junkers, but eventually built and tested at Heinkel. It was possibly the best of the "Class I" engines, a class that included the more famous BMW 003 and Junkers Jumo 004. As it started somewhat later than these two designs, and was thus expected to enter service later, the Reichluftfahrtministerium (RLM) ordered Heinkel to stop work on the design and put their efforts into more advanced designs.

The Heinkel HeS 3 was the world's first operational jet engine to power an aircraft. Designed by Hans von Ohain while working at Heinkel, the engine first flew as the primary power of the Heinkel He 178, piloted by Erich Warsitz on 27 August 1939. Although successful, the engine had too little thrust to be really useful, and work started on the more powerful Heinkel HeS 8 as their first production design.
The Heinkel HeS 40(HeS - Heinkel Strahltriebwerke) was an experimental constant-volume jet engine designed by Adoph Müller's team at Heinkel starting some time in 1940 or 41. It was based on the mechanical layout of the HeS 30, but replaced the conventional flame cans with oversized ones including large poppet valves that sealed off the chambers during firing. Constant-volume combustion, similar to the Otto cycle used in most piston engines, is considerably more fuel efficient than the constant-pressure combustion used in a typical jet engine.
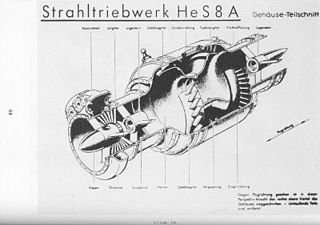
The Heinkel HeS 8 was an early jet engine designed by Hans von Ohain while working at Heinkel. It was the first jet engine to be financially supported by the RLM, bearing the official name 109-001. Had development continued it would have been known as the Heinkel 001, but it does not appear this was used in practice.
The Porsche 005 was a small, single-use turbojet design intended to power a long-range version of the V-1 flying bomb. At the end of World War II, the design of the Porsche 005 turbojet had not been finalised and no parts had been constructed.
Internal combustion engines date back to between the 10th and 13th centuries, when the first rocket engines were invented in China. Following the first commercial steam engine in 1698, various efforts were made during the 18th century to develop equivalent internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794, Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794, Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the river in France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen and oxygen-powered internal-combustion engine. Fitted to a crude four-wheeled wagon, François Isaac de Rivaz first drove it 100 metres in 1813, thus making history as the first car-like vehicle known to have been powered by an internal-combustion engine.

The Power Jets W.1 was a British turbojet engine designed by Frank Whittle and Power Jets. The W.1 was built under contract by British Thomson-Houston (BTH) in the early 1940s. It is notable for being the first British jet engine to fly, as the "Whittle Supercharger Type W1", powering the Gloster E.28/39 on its maiden flight at RAF Cranwell on 15 May 1941. The W.1 was superseded by the Power Jets W.2.
The Junkers Jumo 109-012, known colloquially post-war as Jumo 012, was a turbojet engine under development in Germany during the Second World War. In essence, it was a scaled up version of the Jumo 004. It was intended to power the EF 132 and variants of the Ju 287.













