
Gallic acid (also known as 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoic acid) is a trihydroxybenzoic acid with the formula C6H2(OH)3CO2H. It is classified as a phenolic acid. It is found in gallnuts, sumac, witch hazel, tea leaves, oak bark, and other plants. It is a white solid, although samples are typically brown owing to partial oxidation. Salts and esters of gallic acid are termed "gallates".

Nyctanthes arbor-tristis, also known as the Night-flowering jasmine and Parijat(Parvati chi phula) is a species of Nyctanthes native to South Asia and Southeast Asia.

Bauhinia purpurea is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae, native to the Indian subcontinent and Myanmar, and widely introduced elsewhere in tropical and subtropical areas of the world. Common names include orchid tree, purple bauhinia, camel's foot, butterfly tree, and Hawaiian orchid tree.

Cistus salviifolius, common names sage-leaved rock-rose, salvia cistus or Gallipoli rose, is a shrub of the family Cistaceae.
Prodelphinidin is a name for the polymeric tannins composed of gallocatechin. It yields delphinidin during depolymerisation under oxidative conditions.

Procyanidin C2 is a B type proanthocyanidin trimer, a type of condensed tannin.

Procyanidin B5 is a B type proanthocyanidin.

Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata. It exists as at least 2 major epimers.

Selliguea feei is a fern belonging to the genus Selliguea in the family Polypodiaceae. This fern can be collected in Indonesia. The species name feei commemorates the botanist Antoine Laurent Apollinaire Fée.
Prorobinetidins are a type of condensed tannins formed from robinetinidol. They form robinetinidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Stryphnodendron adstringens is a species of legume in the genus Stryphnodendron found in Brazil.
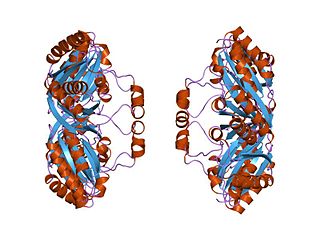
In molecular biology the Bacterial Microcompartment (BMC) domain is a protein domain found in a variety of shell proteins, including CsoS1A, CsoS1B and CsoS1C of Thiobacillus neapolitanus and their orthologs from other bacteria. These shell proteins form the polyhedral structure of the carboxysome and related structures that plays a metabolic role in bacteria. The BMC domain consists of about 90 amino acid residues, characterized by β-α-β motif connected by a β-hairpin.

The pomegranate ellagitannins, which include punicalagin isomers, are ellagitannins found in the sarcotestas, rind (peel), bark or heartwood of pomegranates.
Propelargonidins are a type of condensed tannins formed from epiafzelechin. They yield pelargonidin when depolymerized under oxidative conditions.

Geranin A is an A type proanthocyanidin of the propelargonidin sub type. Its structure is epi-afzelechin-(4β→8, 2β→O→7)-afzelechin.

Paullinia pinnata is a flowering plant species in the genus of Paullinia found in South America and Africa.

4-Methylphenethylamine (4MPEA), also known as para-methylphenethylamine, is an organic compound with the chemical formula of C9H13N. 4MPEA is a human trace amine associated receptor 1 (TAAR1) agonist, a property which it shares with its monomethylated phenethylamine isomers, such as amphetamine (α-methylphenethylamine), β-methylphenethylamine, and N-methylphenethylamine (a trace amine). 4MPEA also appears to inhibit the human cytochrome P450 enzymes CYP1A2 and CYP2A6, based upon the published literature.

11β-Methyl-19-nortestosterone (11β-MNT) is a synthetic and orally active anabolic–androgenic steroid (AAS) and a derivative of nandrolone (19-nortestosterone) which was developed by the Contraceptive Development Branch (CDB) of the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD) and has not been marketed at this time.














